What is break/fix?
The break/fix model is a traditional method of providing IT support in which services are rendered only when needed, typically after something breaks.
Companies or individuals contact an IT service provider when they encounter an issue, and pay based on the time and materials required to resolve it. Fees may be billed hourly or at a flat rate for specific services such as virus removal or data recovery.
This reactive approach contrasts with modern proactive service models, and while it is still relevant in some scenarios, its popularity has declined in favor of more comprehensive IT support strategies.
Break/fix vs. managed services
The rise of managed IT services has reshaped how businesses handle their technology needs. Unlike break/fix providers who step in only when issues occur, managed service providers (MSPs) offer continuous IT monitoring, maintenance and support under a service-level agreement.
Managed services typically operate on a monthly subscription basis, helping clients budget more effectively while minimizing downtime through proactive problem prevention. MSPs use tools such as remote monitoring and management software and professional services automation (PSA) platforms to maintain systems efficiently and predictably.
In contrast, break/fix services offer no such ongoing engagement or preventive care, leaving clients vulnerable to unexpected disruptions and costs.
Decline in the popularity of break/fix
While the break/fix model was once the standard, it has declined sharply due to its inherent limitations:
- Reactive nature. It addresses issues only after they've occurred, often leading to prolonged downtime.
- Unpredictable costs. Clients may face unexpectedly high bills during critical failures.
- Lack of accountability. Since break/fix providers profit from problems, there's little incentive to prevent them.
Businesses today prioritize continuity and security, especially as cyberthreats and remote work demands increase. As a result, the managed services model has become the preferred approach for long-term IT stability and growth.
When break/fix still makes sense
Despite its drawbacks, break/fix services remain useful in certain cases:
- Small businesses with minimal IT infrastructure and low budgets.
- Short-term projects or one-off IT repairs and upgrades.
- Startups or solopreneurs needing occasional help without long-term contracts.
For these situations, break/fix can be a cost-effective way to access technical expertise without committing to monthly fees.
Transitioning from break/fix to managed services
For IT companies operating under a break/fix model, transitioning to managed services offers the potential for stable revenue and long-term client relationships. However, the shift requires operational and cultural changes:
- Switch to recurring revenue. Establish monthly pricing packages that deliver consistent value to clients.
- Emphasize preventive care. Use monitoring tools to identify and resolve problems before they affect the business.
- Train sales and support staff. Equip teams with knowledge about consultative selling and long-term client success.
- Invest in PSA tools. Streamline back-end operations to improve efficiency and scale client services.
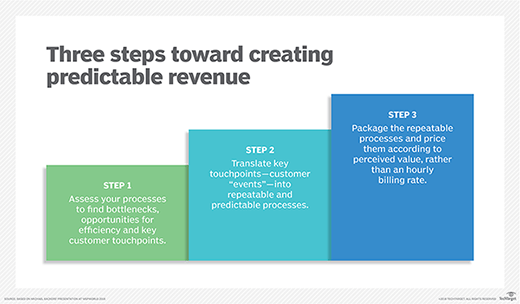
Over time, this shift boosts profitability and builds trust with clients seeking more predictable, responsive and secure IT support.
Learn about the managed service business model and explore key insights for starting and managing a service provider business.






