What is a channel strategy?
A channel strategy is a vendor's plan for delivering a product or service to end customers through direct or indirect sales channels. It defines the structure, partners, and tactics used to distribute offerings, support customers, and maximize market reach.
Channel strategy is an essential component of a company's broader go-to-market (GTM) approach, ensuring products reach their intended audience efficiently and competitively.
The purpose of a channel strategy
In B2B and business-to-consumer contexts alike, a channel strategy helps companies:
- Identify the most effective sales and distribution channels.
- Engage partners appropriate for specific product and service needs.
- Expand into new geographic or vertical markets.
- Optimize resource allocation for marketing and sales.
For example, a company selling low-complexity software may rely on self-service digital sales, while one selling enterprise infrastructure may need help from systems integrators or value-added resellers (VARs) to implement and support customer deployments.
Types of channel strategies
Organizations can pursue a variety of channel strategies depending on product type, target market, and their growth objectives:
Direct sales
A direct channel strategy involves the vendor selling products or services directly to customers. Common direct sales methods include:
- In-house sales teams engaging with enterprise buyers
- E-commerce websites supporting online self-service purchases
- Catalog or phone-based sales for niche or legacy markets.
Direct sales provide vendors with complete control over pricing, messaging, and customer relationships.
Indirect sales
An indirect strategy uses intermediaries such as channel partners to sell and support products. Common partner types include:
- Retailers and e-tailers
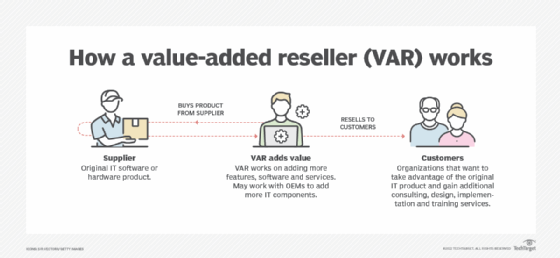
- VARs that bundle solutions and offer services
- Distributors that supply products to a network of resellers
- Managed Service Providers (MSPs)
- Consultants
- Original Equipment Manufacturers
- Independent software vendors
In a one-tier distribution model, vendors sell directly to VARs. In a two-tier model, vendors sell to distributors, who then sell to VARs or retailers.
Channel partner programs often support these relationships with training, marketing support, deal registration, and partner portals.
Consumer channels
In consumer markets, companies may deploy:
- Multichannel strategies, combining direct methods (e.g., catalogs, email) and indirect ones (e.g., social media, retail).
- Omnichannel strategies, delivering seamless customer experiences across all digital and physical touchpoints.
These models are used in B2B contexts increasingly as well, especially for SaaS and digital-first offerings.
How to create a channel strategy
Developing a channel strategy requires a structured approach:
- Define the GTM objectives. Align the strategy with broader company goals such as market expansion, revenue growth, or customer retention.
- Segment the market. Identify key customer types and their buying preferences.
- Assess product complexity. Simpler products may suit digital channels; complex solutions often need expert partners.
- Evaluate potential channel types. Consider direct vs. indirect and the specific partner roles required.
- Design incentives and support. Create a partner program with onboarding, enablement, and performance incentives.
- Establish rules of engagement. Avoid channel conflict by clarifying roles and lead ownership.
For example, a vendor may use direct sales for large enterprise clients while assigning SMB accounts to channel partners.
Channel conflict and segmentation
When vendors use both direct and indirect channels, conflicts can arise if boundaries are not clear. Common causes of channel conflict include:
- Direct sales teams targeting accounts already served by partners
- Unclear or overlapping sales territories
- Competition over pricing or discounts.
To mitigate these issues, companies may:
- Segment accounts by size, industry, or geography
- Define lead ownership and sales stages in partner agreements
- Use deal registration tools to protect partner opportunities
- Publish rules of engagement to guide internal and partner behavior.
Successful segmentation ensures partners feel supported rather than undercut. This careful approach encourages long-term loyalty and performance.
Channel strategy in digital transformation
As organizations shift toward subscription-based and digital-first business models, channel strategies must align accordingly:
- SaaS distribution. Cloud marketplaces (e.g., AWS Marketplace, Microsoft Azure Marketplace) enable partners to resell SaaS offerings.
- Self-service onboarding. Partners increasingly help customers onboard and adopt products using digital tools.
- Recurring revenue models. Channel programs must support monthly recurring revenue tracking, upselling and renewals.
- Data-driven partner management. As part of partner relationship management, vendors can use analytics to assess partner performance, optimize incentives, and forecast channel ROI.
A modern channel strategy emphasizes agility, automation and customer lifetime value over one-time product sales.
Metrics to measure channel strategy effectiveness
Vendors use a variety of metrics to evaluate and refine their channel strategies:
- Channel revenue contribution. The percentage of overall revenue that channel partners generate
- Partner performance. Sales volume, deal size, win rate, and customer satisfaction by partner
- Onboarding success rate. Speed and effectiveness of partner enablement
- Channel conflict resolution time. Average time to resolve disputes between direct and indirect teams
- Market coverage. Breadth of customer segments, industries, or geographies that partners serve.
These key performance indicators help vendors gauge the success of their partner mix, investment priorities, and support programs and can guide them in making necessary adjustments.
Learn how customer communications management, facilitated by generative AI and other technologies, is key to improving customer experience success for B2B and B2C businesses alike.





