What is a channel partner?
A channel partner is a person or organization that partners with a manufacturer or producer to market, sell, and deliver their products or services to the end customer. They form part of a company's distribution channel, which is the path a product takes from producer to consumer.
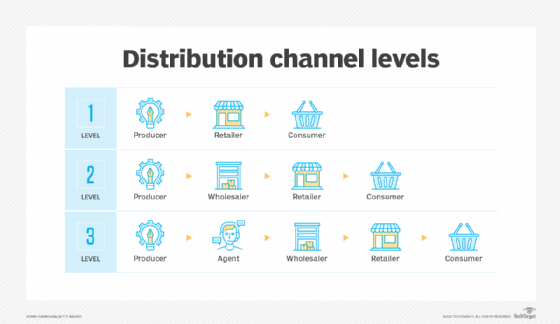
While channel partner is a term perhaps most familiar in the tech industry, the idea of using intermediaries to reach customers is ubiquitous and seen in many industries such as food and beverage, apparel, and automobiles.
Bridging gaps between vendors and end customers, channel partners help extend market reach, provide localized support, and deliver specialized services. Channel partners often receive incentives, training, and technical resources from the manufacturer or producer (commonly called the vendor) to support their efforts.
Channel partners can be a wide variety of entities, including:
- Retailers. An example is a large supermarket chain selling a food producer's products.
- Distributors. These companies buy products in bulk from manufacturers/vendors and sell them to retailers or other businesses.
- Value-added resellers (VARs). These partners sell a product but also add their own services to it, like a company that sells software and also offers implementation and training.
- Affiliates. Individuals or businesses that earn a commission for referring customers to a company's products.
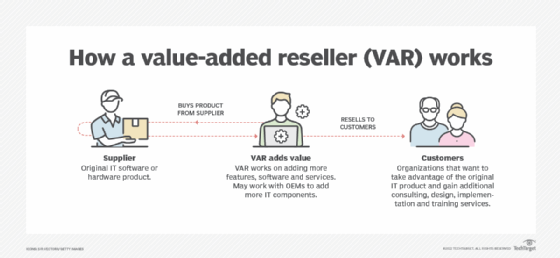
Channel partners in technology
In technology, channel partner models have evolved. Each plays a distinct role:
- VARs. These partners resell hardware, software, or services with additional value, such as custom configuration, installation, training, or support. Initially prominent in the minicomputer era of the 1970s, VARs remain influential in networking and cloud services today.
- Systems integrators (SIs). These partners specialize in connecting and customizing IT systems from different vendors to meet complex business needs. SIs became especially prominent during the 1980s as enterprise IT environments grew more complex.
- Consultants. IT consultants provide expert advice and planning services without necessarily reselling products. Some focus on strategic digital transformation, cloud adoption, cybersecurity, or compliance.
- Managed service providers (MSPs). MSPs remotely manage a customer's IT infrastructure and end-user systems. Many VARs have transitioned into or added MSP services as recurring revenue models have gained popularity.
- Distributors. Distributors act as intermediaries between vendors and resellers, supplying a wide range of products. They often provide logistics, credit services, and partner enablement.
- Original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and independent software vendors (ISVs). OEMs build hardware that includes a vendor's product, while ISVs develop software that can be bundled with or enhance the vendor's offering.
Many channel partners today combine multiple roles, providing consulting, integration, resale, and managed services.
Partnering among channel partners
Channel partners frequently form alliances with one another to:
- Expand into new vertical markets or regions.
- Fill gaps in service offerings or expertise.
- Leverage joint solutions to address larger or more complex client needs.
For example, a VAR might partner with a specialized security consultant to deliver a bundled offering. Likewise, multiple MSPs may join forces to provide 24/7 support across different time zones.
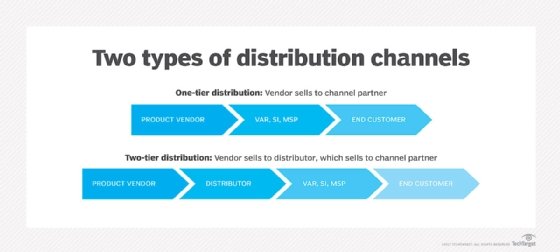
VAR-to-VAR partnerships also occur when firms collaborate to bid on large projects, exchange services, or take advantage of one another's certifications or compliance capabilities. Successful partnerships typically depend on mutual benefit and trust.
Optimizing channel partner relationships
Vendor-partner relationships are often formalized through a channel partner program. Leading IT vendors such as AWS, Microsoft, Cisco, Dell Technologies, Oracle, HPE and IBM all operate formal channel partner programs to engage with and support their partners. These programs offer a variety of resources to attract, enable, and retain partners, such as:
- Training and certification programs;
- Product and marketing support;
- Deal registration and lead sharing tools;
- Incentives, rebates, and co-selling opportunities;
- Access to beta programs or early product releases; and
- Co-branding and joint marketing campaigns.
Vendor channel managers (also called channel account managers) help onboard new partners and maintain active relationships. Many vendors also deploy partner portals and use partner relationship management (PRM) platforms to centralize tools, metrics, and communication.
Clear expectations, transparency in sales engagement, and accessible technical support are key to strong vendor-partner collaboration. Getting all that right requires developing and applying a sensible strategy.
Channel partner certifications
Certification programs validate that a channel partner has met specific technical and business requirements to represent a vendor's products or services. These certifications benefit both the vendor and partner:
- Vendors gain assurance that certified partners can deliver high-quality deployments.
- Partners can differentiate themselves in the market and qualify for exclusive program tiers.
For example:
- Cisco offers tiered certifications (Select, Premier, Gold, etc.) with increasing levels of training, rebates and support.
- AWS grants benefits such as market development funds to consulting partners who meet specific technical and staffing benchmarks.
Certification levels often influence deal access, service margins, and partner directory visibility.
Channel partners vs. direct sales
Technology vendors often balance both direct sales and channel sales strategies. Here's how the two approaches differ:
- Direct sales. Internal sales representatives engage directly with end customers, often focusing on large or strategic accounts.
- Channel sales. Third-party partners manage the sales and delivery process, often for SMBs or regional markets.
To prevent channel conflict (where both sales teams compete for the same account), vendors typically publish rules of engagement that outline:
- Which team owns specific types of leads
- How deal registration protects a partner's opportunity
- Incentive structures for each channel
Some vendors prioritize a channel-first model, relying almost entirely on partners to generate and close sales, while others maintain a hybrid approach.
Benefits of using channel partners
Engaging with channel partners offers several strategic benefits to vendors:
- Scalability. Partners extend sales and service capabilities without requiring internal hiring or infrastructure, such as an extensive sales force, retail locations or a distribution network.
- Market penetration. Local partners bring market knowledge and access to niche industries or underserved regions.
- Faster time to market. Established channel networks accelerate product adoption and deployment. This can be especially important for a tech startup.
- Customer trust. Many end users prefer working with local or specialized firms they already know.
- Cost efficiency. Channel sales often reduce the vendor's cost of customer acquisition.
For partners, benefits include revenue diversification, recurring revenue opportunities, access to new technologies, and additional marketing support (by leveraging the vendor's brand and resources).
Trends shaping the future of channel partnerships
The channel landscape is evolving rapidly as IT consumption patterns shift. Emerging trends include:
- XaaS (Everything as a Service). As businesses adopt subscription-based models, partners are adapting to sell and manage SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS services.
- Ecosystem orchestration. Vendors are encouraging partners to collaborate and co-innovate, rather than compete.
- AI and automation. Partners are building service offerings around AI-powered solutions and automating service delivery.
- Partner marketplaces. Vendors now offer digital marketplaces where partners can publish, sell, or bundle their solutions.
- Security and compliance focus. With increasing cyber threats, partners with strong security and regulatory expertise are in high demand.
Vendors must continue to invest in tools that enable channel partners and flexible program models to meet partners where they are in their journey.
Having a working go-to-market strategy with trustworthy distribution partners is important in supply chain management. Learn about therisks that come with the supply chain, and what companies can do to avoid falling behind.






