host virtual machine (host VM)
What is host virtual machine (host VM)?
A host virtual machine is the server component of a virtual machine the underlying hardware that provides computing resources to support a particular guest VM. Together, the host virtual machine and guest virtual machine make up a virtual machine server.
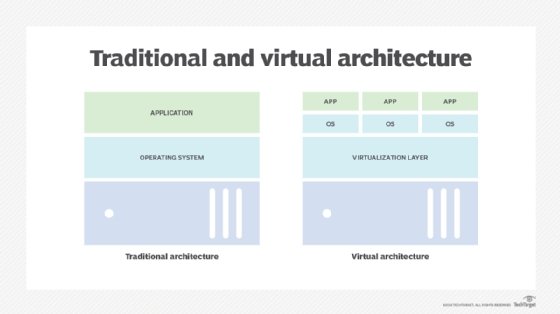
Virtualization technologies such as XenServer by Citrix Systems, Microsoft Hyper-V and VMware vSphere install a layer of abstraction between the host and guest virtual machines.
The host virtual machine explained
A host VM is an important virtualization technique. It lets users create a guest VM with a user operating system (OS), applications and compute resources. Simply put, the host machine is the machine creating the guest VM.
The host VM requests its compute power from the host server. Its data is stored in a virtualization environment that is integrated with the virtualization manager application.
Every host machine is assigned infrastructure resources that are statically or dynamically scalable. It is also assigned security and statistical information about their performance and throughput. The virtualization server does these assignments to manage the operation of all host machines.
Multiple host VMs can be hosted on a single physical server. Moreover, each host VM on this single server can execute and operate without affecting the operations of the other host VMs on that server. Furthermore, because the environment is isolated from the rest of the system, anything running inside the VM doesn't interfere with anything else running on the host hardware.
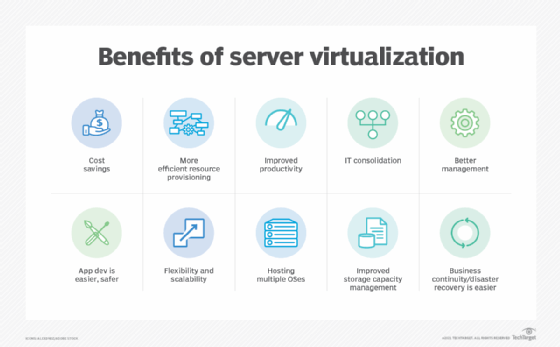
Benefits of a host virtual machine
Using virtual servers on a host VM instead of physical hardware provides many benefits including the following:
- Resource sharing. A VM host enables multiple guest virtual machines to operate on a single physical machine, sharing its computational resources, such as CPU, memory and disk space.
- Cost savings. The efficient resource usage and consolidation of servers can result in cost savings. Reducing the number of physical servers decreases initial hardware expenses as well as ongoing maintenance and energy consumption. It also minimizes the need for physical space within data centers, which further lowers operating costs.
- High availability. Host VMs offer features such as live migration and fault tolerance to enhance the availability of guest VMs. Live migration enables the seamless transfer of running guest VMs between hosts without interruption, ensuring continuous operation. Meanwhile, fault tolerance mechanisms provide redundancy and automatic failover in case of host failures.
- Easy provisioning and management. Host VMs enable the quick creation, deployment and cloning of guest VMs, making it easier to scale up or down as needed. Additionally, host VMs often offer tools and utilities for managing and monitoring the virtualization environment.
- Isolation and security. Each guest VM operates autonomously within its isolated virtual environment, ensuring heightened security. Therefore, any type of malware attacks targeting one guest VM are confined and unable to spread to others. Additionally, host VMs generally incorporate security features such as virtual firewalls and intrusion detection systems for added protection.
- Quick disaster recovery (DR). A host VM provides quick DR through features including VM snapshots, automated orchestration of site failover and failback, frequent non-disruptive testing of recovery plans, cloning and policy-based application-agnostic protection. These features simplify replication, safeguard virtual machines and shorten recovery periods.
- Testing and development. Host VMs are occasionally used for testing new software, performing updates and developing applications in a safe and isolated environment.
Host virtual machine vs. guest virtual machine
The host VM and guest VM are the two components of a VM. Here are the main differences between the two:
- The host VM is hosted and operated from a remote cloud server. Its functionalities are similar to those of a guest VM. However, the host VM is accessed differently from a guest VM.
- The guest VM is an independent instance of an OS and associated software and information. It is also known as a guest computer, guest OS or guest.
- The host VM is the physical machine that provides the guest VM with computing hardware resources, such as processing power, memory, disk, network input/output (I/O).
- A guest VM can exist on a single physical machine but is usually distributed across multiple hosts for load balancing. Thus, one or more virtual guest machines can run on a physical host computer. It can also be moved between host servers to accommodate demand fluctuations or use resources more efficiently.
- Similarly, a host VM may exist as part of the resources of a single physical machine or as smaller parts of the resources of multiple physical machines.
- A virtual machine monitor, or hypervisor, intermediates between the host and guest VM. Moreover, it isolates individual guest VMs from one another and makes it possible for a host to support multiple guests running different guest operating systems such as Windows or Linux.
Architecture of the host VM
The architecture of a host VM includes the following components:
- Hardware layer. The hardware layer or the host VM layer contains the physical network interface cards (NICs), memory, CPU and Ethernet management port. The aim of NICs is to support hardware virtualization based on single root I/O virtualization, an approach in which virtual functions are managed by the guest OS and the host VM manages physical NICs.
- OS and hypervisor. The OS and hypervisor layer acts as an intermediary and contains the OS and the hypervisor. The hypervisor mediates between the host and guest VMs, creating a barrier and ensuring isolation between them. This isolation enables the host to support multiple guests running different operating systems simultaneously.
- Guest VM and host utilities. This layer contains the guest virtual machines along with host utilities.
Setting up a virtual machine server or the host VM
Similar to physical machines, each VM will need RAM and CPU. In addition, the host server also requires sufficient storage. Setting up a virtual machine server requires the following steps:
- Ensure sufficient RAM -- as much fast RAM as one can get -- and CPUs with as many cores as possible. Sufficient disk space of at least 8 GB to 20 GB should also be available as VMs require a great amount of computer resources.
- Consider Serial Advanced Technology Attachment or Serial Attached Small Computer System Interface drives to store virtual server images.
- Use virtualization software, or hypervisors, such as Hyper-V, VMware or Citrix XenServer to set up the VM server.
- Choose the right network connection that needs to be set up for the VM, the guest OS to run and the location where the VM's files will be stored.
Virtualization functions by separating physical hardware and devices from the applications operating on that hardware. Learn the difference between Type 1 vs. Type 2 hypervisor and their specific use cases. Explore the key differences between containers vs. VMs and see what to know for your virtualized storage selection process. Become familiar with storage virtualization software options and check out virtual server management best practices.







