storage (computer storage)
Data storage is the collective methods and technologies that capture and retain digital information on electromagnetic, optical or silicon-based storage media. Storage is used in offices, data centers, edge environments, remote locations and people's homes. Storage is also an important component in mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Consumers and businesses rely on storage to preserve information ranging from personal photos to business-critical data.
Storage is frequently used to describe devices that connect to a computer -- either directly or over a network -- and that support the transfer of data through input/output (I/O) operations. Storage devices can include hard disk drives (HDDs), flash-based solid-state drives (SSDs), optical disc drives, tape systems and other media types.
Why data storage is important
With the advent of big data, advanced analytics and the profusion of internet of things (IoT) devices, storage is more important than ever to handle the growing amounts of data. Modern storage systems must also support the use of artificial intelligence (AI), machine leaning and other AI technologies to analyze all this data and derive its maximum value.
Today's sophisticated applications, real-time database analytics and high-performance computing also require highly dense and scalable storage systems, whether they take the form of storage area networks (SANs), scale-out and scale-up network-attached storage (NAS), object storage platforms, or converged, hyper-converged or composable infrastructure.
By 2025, it is expected that 163 zettabytes (ZB) of new data will be generated, according to a report by IT analyst firm IDC. The estimate represents a potential tenfold increase from the 16 ZB produced through 2016. IDC also reports that in 2020 alone 64.2 ZB of data was created or replicated.
How data storage works
The term storage can refer to both the stored data and to the integrated hardware and software systems used to capture, manage, secure and prioritize that data. The data might come from applications, databases, data warehouses, archives, backups, mobile devices or other sources, and it might be stored on premises, in edge computing environments, at colocation facilities, on cloud platforms or any combination of these.
Storage capacity requirements define how much storage is needed to support this data. For instance, simple documents might require only kilobytes of capacity, while graphic-intensive files, such as digital photographs, can take up megabytes, and a video file can require gigabytes of storage.
Computer applications commonly list the minimum and recommended capacity requirements needed to run them, but these tell only part of the story. Storage administrators must also take into account how long the data must be retained, applicable compliance regulations, whether data reduction techniques are being used, disaster recovery (DR) requirements and any other issues that can impact capacity.
This video from CHM Nano Education explains the role of magnetism in data storage.
A hard disk is a circular platter coated with a thin layer of magnetic material. The disk is inserted on a spindle and spins at speeds of up to 15,000 revolutions per minute (rpm). As it rotates, data is written on the disk surface using magnetic recording heads. A high-speed actuator arm positions the recording head to the first available space on the disk, allowing data to be written in a circular fashion.
On an electromechanical disk such as an HDD, blocks of data are stored within sectors. Historically, HDDs have used 512-byte sectors, but this has started to change with the introduction of the Advanced Format, which can support 4,096-byte sectors. The Advanced Format increases bit density on each track, optimizes how data is stored and improves format efficiency, resulting in greater capacities and reliability.
On most SSDs, data is written to pooled NAND flash chips that use either floating gate cells or charge trap cells to retain their electrical charges. These charges determine the binary bit state (1 or 0). An SSD is not technically a drive but more like an integrated circuit made up of millimeter-sized silicon chips that can contain thousands or even millions of nanotransistors.
Many organizations use a hierarchical storage management system to back up their data to disk appliances. Backing up data is considered a best practice whenever data needs to be protected, such as when organizations are subject to legal regulations. In some cases, an organization will write its backup data to magnetic tape, using it as a tertiary storage tier. However, this approach is practiced less commonly than in years past.
An organization might also use a virtual tape library (VTL), which uses no tape at all. Instead, data is written sequentially to disks but retains the characteristics and properties of tape. The value of a VTL is its quick recovery and scalability.
Measuring storage amounts
Digital information is written to target storage media through the use of software commands. The smallest unit of measure in a computer memory is a bit, which has a binary value of 0 or 1. The bit's value is determined by the level of electrical voltage contained in a single capacitor. Eight bits make up one byte.
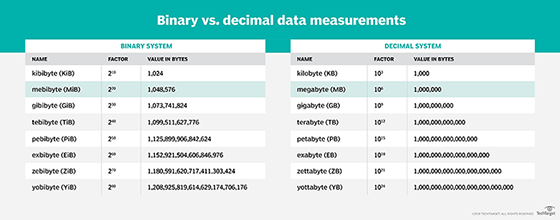
Computer, storage and network systems use two standards when measuring storage amounts: a base-10 decimal system and a base-2 binary system. For small storage amounts, discrepancies between the two standards usually make little difference. However, those discrepancies become much more pronounced as storage capacities grow.
The differences between the two standards can be seen when measuring both bits and bytes. For example, the following measurements show the differences in bit values for several common decimal (base-10) and binary (base-2) measurements:
- 1 kilobit (Kb) equals 1,000 bits; 1 kibibit (Kib) equals 1,024 bits
- 1 megabit (Mb) equals 1,000 Kb; 1 mebibit (Mib) equals 1,024 Kib
- 1 gigabit (Gb) equals 1,000 Mb; 1 gibibit (Gib) equals 1,024 Mib
- 1 terabit (Tb) equals 1,000 Gb; 1 tebibit (Tib) equals 1,024 Gib
- 1 petabit (Pb) equals 1,000 Tb; 1 pebibit (Pib) equals 1,024 Tib
- 1 exabit (Eb) equals 1,000 Pb; 1 exbibit (Eib) equals 1,024 Pib
The differences between the decimal and binary standards can also be seen for several common byte measurements:
- 1 kilobyte (KB) equals 1,000 bytes; 1 kibibyte (KiB) equals 1,024 bytes
- 1 megabyte (MB) equals 1,000 KB; 1 mebibyte (MiB) equals 1,024 KiB
- 1 gigabyte (GB) equals 1,000 MB; 1 gibibyte (GiB) equals 1,024 MiB
- 1 terabyte (TB) equals 1,000 GB; 1 tebibyte (TiB) equals 1,024 GiB
- 1 petabyte (PB) equals 1,000 TB; 1 pebibyte (PiB) equals 1,024 TiB
- 1 exabyte (EB) equals 1,000 PB; 1 exbibyte (EiB) equals 1,024 PiB
Storage measurements can refer to a device's capacity or the amount of data stored in the device. The amounts are often expressed using the decimal naming conventions -- such as kilobyte, megabyte or terabyte -- whether the amounts are based on the decimal or binary standards.
Fortunately, many systems now distinguish between the two standards. For example, a manufacturer might list the available capacity on a storage device as 750 GB, which is based on the decimal standard, while the operating system lists the available capacity as 698 GiB. In this case, the OS is using the binary standard, clearly showing the discrepancy between the two measurements.
Some systems might provide measurements based on both values. An example of this is IBM Spectrum Archive Enterprise Edition, which uses both decimal and binary units to represent data storage. For instance, the system will display a value of 512 terabytes as 512 TB (465.6 TiB).
Few organizations require a single storage system or connected system that can reach an exabyte of data, but there are storage systems that scale to multiple petabytes. Given the rate at which data volumes are growing, exabyte storage might eventually become a common occurrence.
What is the difference between RAM and storage?
Random access memory (RAM) is computer hardware that temporarily stores data that can be quickly accessed by the computer's processor. The data might include OS and application files, as well as other data critical to the computer's ongoing operations. RAM is a computer's main memory and is much faster than common storage devices such as HDDs, SSDs or optical disks.
A computer's RAM ensures that the data is immediately available to the processor as soon as it's needed.
The biggest challenge with RAM is that it's volatile. If the computer loses power, all data stored in RAM is lost. If a computer is turned off or rebooted, the data must be reloaded. This is much different than the type of persistent storage offered by SSDs, HDDs or other non-volatile devices. If they lose power, the data is still preserved.
Although most storage devices are much slower than RAM, their non-volatility make them essential to carrying out everyday operations.
Storage devices are also cheaper to manufacture and can hold much more data than RAM. For example, most laptops include 8 GB or 16 GB of RAM, but they might also come with hundreds of gigabytes of storage or even terabytes of storage.
RAM is all about providing instantaneous access to data. Although storage is also concerned with performance, it's ultimate goal is to ensure that data is safely stored and accessible when needed.
Evaluating the storage hierarchy
Organizations increasingly use tiered storage to automate data placement on different storage media. Data is placed in a specific tier based on capacity, performance and compliance. Data tiering, at its simplest, starts by classifying the data as either primary or secondary and then storing it on the media best suited for that tier, taking into account how the data is used and the type of media it requires.
The meanings of primary and secondary storage have evolved over the years. Originally, primary storage referred to RAM and other built-in devices, such as the processor's L1 cache, and secondary storage referred to SSDs, HDDs, tape or other non-volatile devices that supported access to data through I/O operations.
Primary storage generally provided faster access than secondary storage due to the proximity of storage to the computer processor. On the other hand, secondary storage could hold much more data, and it could replicate data to backup storage devices, while ensuring that active data remained highly available. It was also cheaper.
Although these usages still persist, the terms primary and secondary storage have taken on slightly different meanings. These days, primary storage -- sometimes referred to as main storage -- generally refers to any type of storage that can effectively support day-to-day applications and business workflows. Primary storage ensures the continued operation of application workloads central to a company's day-to-day production and main lines of business. Primary storage media can include SSDs, HDDs, storage-class memory (SCM) or any devices that deliver the performance and capacity necessary to maintain everyday operations.
In contrast, secondary storage can include just about any type of storage that's not considered primary. Secondary storage might be used for backups, snapshots, reference data, archived data, older operational data or any other type of data that isn't critical to primary business operations. Secondary storage typically supports backup and DR and often includes cloud storage, which is sometimes part of a hybrid cloud configuration.
Digital transformation of business has also prompted more and more companies to use multiple cloud storage services, adding a remote tier that extends secondary storage.
Types of data storage devices/mediums
In its broadest sense, data storage media can refer to a wide range of devices that provide varying levels of capacity and speed. For example, it might include cache memory, dynamic RAM (DRAM) or main memory; magnetic tape and magnetic disk; optical discs such as CDs, DVDs and Blu-rays; flash-based SSDs, SCM devices and various iterations of in-memory storage. However, when using the term data storage, most people are referring to HDDs, SSDs, SCM devices, optical storage or tape systems, distinguishing them from a computer's volatile memory.
Spinning HDDs use platters stacked on top of each other coated in magnetic media with disk heads that read and write data to the media. HDDs have been widely used in personal computers, servers and enterprise storage systems, but they're quickly becoming supplanted by SSDs, which offer superior performance, provide greater durability, consume less power and come in a smaller footprint. They're also starting to reach price parity with HDDs, although they're not there yet.

Most SSDs store data on non-volatile flash memory chips. Unlike spinning disk drives, SSDs have no moving parts and are increasingly found in all types of computers, despite being more expensive than HDDs. Some manufacturers also ship storage devices that use flash storage on the back end and high-speed cache such as DRAM on the front end.
Unlike HDDs, flash storage does not rely on moving mechanical parts to store data, resulting in faster data access and lower latency than HDDs. Flash storage is non-volatile like HDDs, allowing data to persist in memory even if the storage system loses power, but flash has not yet achieved the same level of endurance as the hard disk, leading to hybrid arrays that integrate both types of media. (Cost is another factor in the development of hybrid storage.) However, when it comes to SSD endurance, the types of workloads and NAND devices can also play an important role in a device's endurance, and in this regard, SSDs can vary significantly from one device to the next.
Since 2011, an increasing number of enterprises have implemented all-flash arrays based on NAND flash technology, either as an adjunct or replacement to hard disk arrays. Organizations are also starting to turn to SCM devices such as Intel Optane SSDs, which offer faster speeds and lower latency than flash-based storage.

At one time, internal and external optical storage drives were commonly used in consumer and business systems. The optical discs might store software, computer games, audio content or movies. They could also be used as secondary storage for any type of data. However, advancements in HDD and SSD technologies -- along with the rise of internet streaming and Universal Serial Bus (USB) flash drives -- have diminished the reliance on optical storage. That said, optical discs are much more durable than other storage media and they're inexpensive to produce, which is why they're still used for audio recordings and movies, as well as for long-term archiving and data backup.

Flash memory cards are integrated in digital cameras and mobile devices, such as smartphones, tablets, audio recorders and media players. Flash memory is also found on Secure Digital cards, CompactFlash cards, MultiMediaCard (MMC) cards and USB memory sticks.
Physical magnetic floppy disks are rarely used these days, if at all. Unlike older computers, newer systems are not equipped with floppy disk drives. Use of floppy disks started in the 1970s, but the disks were phased out in the late 1990s. Virtual floppy disks are sometimes used in place of the 3.5-inch physical diskette, allowing users to mount an image file like they would the A: drive on a computer.
Enterprise storage vendors provide integrated NAS systems to help organizations collect and manage large volumes of data. The hardware includes storage arrays or storage servers equipped with hard drives, flash drives or a hybrid combination. A NAS system also comes with storage OS software to deliver array-based data services.

Many enterprise storage arrays come with data storage management software that provides data protection tools for archiving, cloning, or managing backups, replication or snapshots. The software might also provide policy-based management to govern data placement for tiering to secondary data storage or to support a DR plan or long-term retention. In addition, many storage systems now include data reduction features such as compression, data deduplication and thin provisioning.
Common storage configurations
Three basic designs are used for many of today's business storage systems: direct-attached storage (DAS), NAS and storage area network (SAN).

The simplest configuration is DAS, which might be an internal hard drive in an individual computer, multiple drives in a server or a group of external drives that attach directly to the server though an interface such as the Small Computer System Interface (SCSI), Serial Attached SCSI (SAS), Fibre Channel (FC) or internet SCSI (iSCSI).
NAS is a file-based architecture in which multiple file nodes are shared by users, typically across an Ethernet-based local area network (LAN). A NAS system has several advantages. It doesn't require a full-featured enterprise storage operating system, NAS devices can be managed with a browser-based utility and each network node is assigned a unique IP address, helping to simplify management.
Closely related to scale-out NAS is object storage, which eliminates the necessity of a file system. Each object is represented by a unique identifier, and all the objects are presented in a single flat namespace. Object storage also supports the extensive use of metadata.
A SAN can be designed to span multiple data center locations that need high-performance block storage. In a SAN environment, block devices appear to the host as locally attached storage. Each server on the network can access shared storage as though it were a direct-attached drive.
Modern storage technologies
Advances in NAND flash, coupled with falling prices in recent years, have paved the way for software-defined storage. Using this configuration, an enterprise installs commodity-priced SSDs on X86-based servers and then uses third-party storage software or custom open source code to apply storage management.
Non-volatile memory express (NVMe) is an industry-standard protocol developed specifically for flash-based SSDs. NVMe is quickly emerging as the de facto protocol for flash storage. NVMe flash enables applications to communicate directly with a central processing unit (CPU) via Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) links, bypassing the need to transmit SCSI command sets through a network host bus adapter.
NVMe can take advantage of SSD technology in a way not possible with SATA and SAS interfaces, which were designed for slower HDDs. Because of this, NVMe over Fabrics (NVMe-oF) was developed to optimize communications between SSDs and other systems over a network fabric such as Ethernet, FC and InfiniBand.
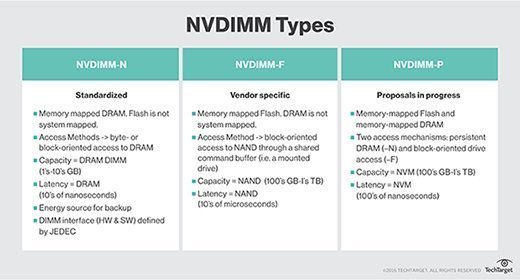
A non-volatile dual in-line memory module (NVDIMM) is a hybrid NAND and DRAM device with integrated backup power that plugs into a standard DIMM slot on a memory bus. NVDIMM devices process normal calculations in the DRAM but use flash for other operations. However, the host computer requires the necessary basic input-output system (BIOS) drivers to recognize the device.
NVDIMMs are used primarily to extend system memory or improve storage performance, rather than to add capacity. Current NVDIMMs on the market top out at 32 GB, but the form factor has seen density increases from 8 GB to 32 GB in just a few years.
Major data storage vendors
Consolidation in the enterprise market has winnowed the field of primary storage vendors in recent years. Those that penetrated the market with disk products now derive most of their sales from all-flash or hybrid storage systems that incorporate both SSDs and HDDs.
Market-leading vendors include:
- Dell EMC, the storage division of Dell Technologies
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE)
- Hitachi Vantara
- IBM Storage
- Infinidat
- NetApp
- Pure Storage
- Quantum Corporation
- Qumulo
- Tintri
- Western Digital
Smaller vendors such as Drobo, iXsystems, QNAP and Synology also sell various types of storage products. In addition, a number of vendors now offer hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) solutions, including Cisco, DataCore, Dell EMC, HPE, NetApp, Nutanix, Pivot3, Scale Computing, StarWind and VMware. Many enterprise storage vendors also offer branded converged and composable infrastructure products.
Learn about data storage management advantages and challenges and ways to manage your data storage strategy.







