customer data management (CDM)
What is customer data management (CDM)?
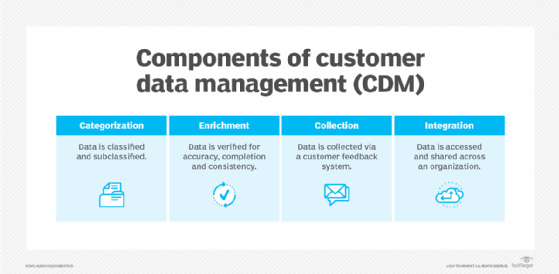
Customer data management (CDM) is a set of administrative processes that allow data about customers and customer interactions from different source systems to be aggregated and normalized. The primary goal of CDM is to provide all individuals in an organization with a holistic, unified view of individual customers and customer segments. CDM is a subset of master data management (MDM).
CDM as a discipline includes the people, processes and technologies an organization has in place to collect, access and organize customer data. Effective CDM can provide organizations with multiple benefits, such as greater visibility of customers and communication channels, higher customer satisfaction and retention rates, increased data quality and higher revenue. Popular CDM vendors include Oracle, Hadoop, SAP and IBM.
How does CDM work?
Organizations can implement CDM with in-house software tools or cloud computing services that collect, analyze and organize customer information in a single, consistent platform. Once in place, the data can be accessed in real time by all relevant departments across the entire organization, including sales, marketing and customer support.
CX teams can use CDM software to do the following:
- Initiate an instant response to customer feedback or issues.
- Identify and contact a target audience segment.
- Identify and contact specific marketing-qualified leads (MQLs) and sales-qualified leads (SQLs).
Best practices for customer data management
Customer data can become extensive and hard to manage, so best practices should be put into place to optimize results. CDM best practices include the following:
Data consolidation. It is important to keep all customer data in the same central location. If data is kept and updated in multiple places, customer information can become inconsistent. Each customer should only have one record that serves as the single source of truth (SSOT) for all information across departments and platforms.
Data governance. Once data has been collected, organizations should document standards for how data will be stored, retrieved and used. Elements of data governance include monitoring data access permissions and outlining file naming conventions.
Data relevance. It's important to only keep customer data that is relevant to business goals. Collecting irrelevant data decreases operational efficiency when putting the data to use and lowers customer experience scores.
Data quality. Data should be managed frequently to optimize resources. To ensure data quality, organizations must verify that all data is valid, has been scrubbed and is up to date.
Data security. Once in place, CDM services should be secure. Customer privacy needs to be protected and security best practices, such as data encryption, routine audits and external backups, should be implemented.
Editor's note: This article was written in 2019. TechTarget editors revised it to improve the reader experience.





