database marketing
What is database marketing?
Database marketing is a systematic approach to the gathering, consolidation and processing of consumer data. Database marketing is also a form of direct marketing and may be called customer relationship management.
Data of both customers and potential customers are collected and are maintained in a company's database. The process of collecting this data allows an organization to better know and market to its customers, leading to more potential sales.
Who benefits from database marketing?
Organizations such as retailers, technology vendors, insurance companies and other service providers may make use of database marketing as a marketing strategy. This approach to marketing is most useful for organizations that have large customer bases, since they will generate more transaction data, meaning more aspects to find new prospects.
Although databases have been used to hold consumer data in traditional marketing for a long time, the database marketing approach is differentiated by containing much more consumer data. The data is also processed and used in different ways in database marketing.
In database marketing, marketers will use the collected data for the following purposes:
- learn more about customers;
- select target markets for specific marketing campaigns (through customer segmentation);
- compare customers' value to the company; and
- provide more specialized offerings for customers.
Types of collected data may include the following:
- customers' names;
- addresses;
- emails;
- phone numbers;
- purchase history;
- job titles;
- website cookies; and
- customer support tickets.
After data collection and storage, the data can then be analyzed and used by marketing teams to make a more personalized interaction for each customer and to attract new potential customers.
How does database marketing work?
Database marketing starts by collecting data from various sources. Names, addresses, emails, phone numbers, purchase history and other data can be tracked.
The data can be collected through various means, including the following:
- tracking user cookies;
- purchase history;
- newsletter subscriptions;
- anything that requires the signing of forms, such as contest entry forms, offering free sample products, product warranty cards, etc.;
- leads from marketing and sales teams; and
- purchased from third parties -- although different countries may have different laws regarding what types of data can be bought and sold.
This information, once gathered, is then stored in a database. Larger organizations might house that database in a data warehouse. A data warehouse will receive different data sets from separate departments that have any relevant information regarding customers or potential customers. Having a data warehouse will also allow an organization to process large amounts of data.
The data can be filtered through database analysis using marketing software. The data can be separated by factors like demographic or potential prospect behaviors. The database should be kept as up-to-date as possible.
It should be assumed that a customer or potential customer's data will change over time. To keep from collecting outdated information, an organization should place more focus on information that is less likely to change, such as names, phone numbers and emails.
Database marketing benefits
Database marketing can provide benefits to marketers, advertisers and consumers in the following ways:
- Finds the best channel to contact customers.
- Identifies customer groups, such as loyal, first-time or potential customers.
- Organizes prospects on existing and potential demographics, such as potential interests.
- Prioritizes valuable accounts.
- Personalizes marketing messages toward individual prospects.
- Potential to increase customer retention.
- Data collected can be used for future promotional campaigns.
- Saves expenses on sending campaigns to unlikely customers.
Database marketing challenges
Despite the benefits an organization can see from database marketing, there can also be a few challenges as well. Those include the following:
- The collected data can become outdated. If someone changes jobs, for example, their job title and business email may change. Their address may even change if they had to move for the new position. Data should be kept up to date as much as possible.
- The data originally collected will also be incorrect if the individual inputs incorrect information. Using drop-down menus and checkboxes on forms can help acquire more accurate information. However, with limited options, this too may limit accuracy.
- The cost of managing a database server could be high if there's no way to get value from the information being collected.
- Accidently marketing to the wrong contacts, or grouping contacts together incorrectly, will drive customers away.
Types of database marketing
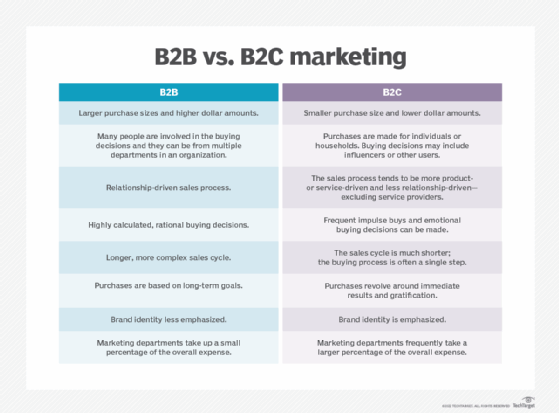
Database marketing can take place in two forms, consumer database marketing and business database marketing. The difference between the two is the target audience.
Consumer database marketing. Businesses that sell directly to a consumer, or B2C organizations, use this approach. Data collected in consumer database marketing includes the following:
- names;
- email addresses;
- phone numbers;
- addresses;
- genders; and
- locations.
To gain this information, an organization may implement giveaways, contests, account registrations or offers for free shipping. Once that information is stored, it can be used by sending personalized mail or emails to consumers.
Business database marketing. Organizations that sell directly to other businesses, or B2B organizations, use this approach. The data collected in business database marketing includes the following:
- company revenue;
- names;
- emails;
- phone numbers;
- job titles;
- website cookies; and
- purchase history.
B2B organizations would want to collect such data through LinkedIn, event registrations, whitepaper downloads, industry reports, demos, free trial offers or webinars. Once this data is collected and stored, an organization can start marketing through benefit-focused emails or targeted social media ads. Account-based marketing will help in maintaining a small, detailed business database.
A database used for business database marketing may be smaller than a B2C database. Organizations that employ business database marketing may only focus on large target accounts, so there's no need for a large database to store large amounts of customer information.
Database marketing tips and strategies
There are numerous tips and strategies regarding database marketing. Some basic tips include the following:
- Know the audience being marketed to. If an organization lacks detailed customer profiles, they may not have as much informed insight into who their prospect customers are.
- Know the data that will be the most useful to collect. It may be information like demographics, activity or transaction history.
- Respect a customer's privacy. Personal information found on social media may be easy to find and having an abundance of identifying information could be useful, but potential customers will not like having so much personal data about them being kept -- especially without their knowledge.
- Work with other internal teams. Sales, support and marketing teams will all have information about customers to collect because they often work directly with customers.
- Use marketing software. Software tools should help make it possible to see different data points at once, view customer type or organize data by service and product categories.
- Keep data as up-to-date as possible. Information can deteriorate pretty quickly as people move, change jobs and email addresses, or make other life changes. It is important to value information that is likely not to change often over information that will.
- Implement strategies such as multichannel marketing or predictive analytics.
Real-world examples of database marketing
A couple examples of database marketing could be an e-commerce app that uses data about transaction history to better and quickly assess a customer service call or a food delivery app using transaction data to find which times a customer is most likely to order from them.
However, some real-life examples of database marketing can be found in Facebook, Amazon and Netflix.
- Facebook will segment user data by name, email, phone number, gender, date of birth, location, and interests. This allows Facebook to create personalized experiences for their users and information for marketers.
- Amazon will collect data such as what users have viewed, purchased or put in a wish list. Amazon will then cross-reference this with what other users have bought and use the resulting data to try and sell new items to the potential buyer. This process creates a recommendations engine, which is based on consumer behavior.
- Netflix will track data about what shows and movies a user views, then cross-references that data with what similar users have viewed to provide recommendations.
Editor's note: This article was written by Alexander S. Gillis in 2020. TechTarget editors revised it in 2022 to improve the reader experience.







