
Getty Images
Sales vs. account management: What's the difference?
Sales and account management teams work together to increase revenue. However, these roles have different goals, responsibilities, skills and relationship timeframes.
Customer acquisition offers little value to businesses if those customers quickly churn.
B2B customer accounts can generate a significant amount of revenue over time, so organizations often assign each customer their own account manager to answer questions, solve problems and maintain customer satisfaction. While sales representatives initially find those leads and close deals, account managers focus on customer retention and upselling. Sales and account management teams have similarities, but they each interact with customers at different phases of the customer journey.
Organizations should know the difference between these teams so they can create an effective strategy for sales and customer retention.
What is sales?
Sales describes all the activities organizations use to turn leads into customers. B2C organizations, like retail stores, often have a simple sales process. For example, a sales associate might encourage a man browsing the footwear section to buy a pair of sneakers.
B2B organizations, on the other hand, have more complex sales processes. For instance, a SaaS company's sales rep might use a CRM system to find leads that visited the company's website and send them personalized email content about how the SaaS product could improve their businesses. If the lead shows interest, the rep could eventually close the sale.
Sales reps serve as a customer's main point of contact with an organization from initial outreach to a deal's closing. They typically earn a base salary in addition to a commission for every deal they close.
What is account management?
Account management is a strategy B2B organizations use to retain and grow their existing customer accounts. Organizations can assign each customer an account manager to serve as the customer's point of contact in the post-sale phase.
Account managers frequently check in with their assigned customers and answer questions about their accounts or products. They also focus on upselling and cross-selling to grow accounts and increase revenue. In some cases, account managers take on a customer success role and help customers create strategies to meet long-term business goals.
What's the difference between sales and account management?
CX leaders should understand the four key differences between sales and account management so they can effectively acquire and retain customers.
1. Goals
Sales and account management teams each help organizations increase profits, but they do so in different ways.
The goal of sales teams is to find new leads and convert them into customers. They work with marketing teams to identify sales-qualified leads -- individuals interested in the company's products -- and personally reach out to them. Sales reps build rapport with these leads and send them educational material to encourage them to buy a product or service.
The goal of account managers, on the other hand, is to retain and grow existing accounts. While sales teams only interact with customers during the initial sales process, account managers work with them indefinitely. They build long-term relationships to foster trust and customer loyalty, and encourage customers to consider subscription upgrades and complementary products.
2. Responsibilities
A sales rep's responsibilities center around presale interactions, whereas account managers offer post-sale services.
Common responsibilities of a sales rep include the following:
- Make cold calls.
- Use sales software to find new leads.
- Build rapport with leads.
- Create sales presentations.
- Schedule meetings with leads.
- Give product demos.
- Create sales forecasts.
Account management responsibilities include the following:
- Build long-term relationships with existing customers.
- Answer product and account questions.
- Offer technical assistance.
- Monitor customer satisfaction.
- Understand customer needs and pain points.
- Tell customers about new product offerings and features.
- Upsell and cross-sell relevant products.
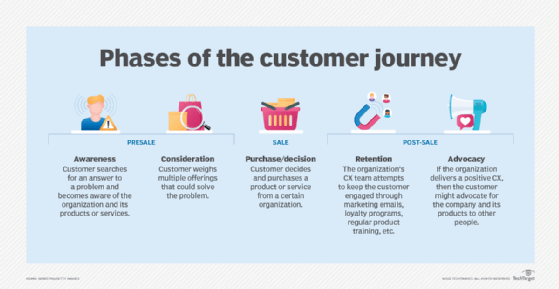
3. Skills
Sales reps and account managers are both customer-facing roles, so they each require people skills and the ability to negotiate. However, account managers need more customer service and strategic planning skills than sales reps.
Sales reps should possess the following skills and characteristics:
- Friendliness. Sales reps need a level of friendliness to help them quickly build rapport with leads.
- Persuasion and negotiation. A sales rep's main goal is to close a deal, which requires them to persuade undecided customers and negotiate prices.
- Storytelling. Stories can enhance sales presentations because people tend to remember stories over statistics.
- Active listening. Sales reps can make more personal connections with leads if they use active listening to remain present in conversations.
- Confidence. A confident sales rep can make potential buyers feel confident about a product or service.
The following skills and characteristics help account managers retain customers:
- Friendliness. Friendly account managers make customers feel welcomed and heard, and help build customer trust and loyalty.
- Communication. Account managers frequently reach out to their customers to learn about problems or questions they might have. They also keep customers up to date on new products or services.
- Empathy. Frustrated customers contact account managers when they have trouble with a product or service. Empathy can help them understand the customer's perspective and offer quality assistance.
- Strategic thinking. To make upsells and cross-sales, account managers must think strategically about how different products, features and offers could address customers' pain points.
- Negotiation and persuasion. Account managers need negotiation and persuasion skills to help grow accounts through upselling and cross-selling.
4. Relationship timeframe
The relationship between sales reps and leads typically ends when the lead makes a purchase. In B2B, the timeframe from initial outreach to conversion can range from a few weeks to several months. After leads become customers, the sales rep passes them on to their assigned account managers.
The relationship between account managers and customers, on the other hand, lasts until the customer churns, which might be several years. Account managers attempt to build close relationships with customers over long periods to increase customer retention.
How sales and account management teams work together
Sales and account management teams regularly communicate with each other to ensure customers have a smooth transition from the presale to post-sale phases.
Before sales reps hand off customers to an account manager, they should brief the account manager on important details collected throughout the sales process, such as business goals and pain points. This information can help account managers understand the customer's perspective and anticipate their needs.
As account managers build long-term relationships with customers, they can reach out to the sales team with opportunities, such as referrals and cross-sell opportunities. Some account managers might be responsible for closing these deals themselves, but others might transfer customers to the sales team to finalize purchases.
Overall, all B2B organizations need a sales team to bring in new customers, but not every company needs a dedicated account management team. For example, an SMB might assign account management tasks to their sales reps. However, large enterprises with many customers and complex products typically create specialized sales and account management departments.








