
How to use generative AI for sales
Sales teams can use generative AI to create personalized content, coach sales reps and improve forecasting. However, challenges include scaling and data readiness.
Generative AI won't replace sales representatives, but it can change how they work.
Since ChatGPT's public launch in late 2022, CRM vendors, such as Microsoft, Salesforce and HubSpot, have released generative AI (GenAI) capabilities for their sales offerings. Use cases for sales fall into three broad categories: content generation, data analysis and task automation. These categories include a wide range of capabilities, from crafting personalized emails and designing sales proposals to analyzing customer data for lead scoring and forecasting. Although each use case has its place, experts expect data analysis to offer the most ROI.
 Liz Miller
Liz Miller
"What sellers are really looking for is: 'What tells me about the next deal? What tells me about how I could be proactive about this outreach?' … AI allows us to be far more proactive," said Liz Miller, vice president and principal analyst at Constellation Research.
However, AI implementation comes with challenges, such as scaling its use across processes, achieving data readiness and measuring ROI. Sales teams must address these hurdles to unlock GenAI's full potential.
How can sales teams use GenAI?
GenAI's sales use cases fall within three overarching categories: content generation, data analysis and task automation.
1. Content generation
Write personalized emails. Sales reps can use GenAI tools to quickly draft personalized emails for inbound and outbound leads. These tools can draw on CRM data, such as customers' names, their past interactions and product demos they've watched, to craft an email that addresses their needs and catches their eye.
These tools can also pull data from sources like LinkedIn or company websites to find items like contacts or previous employers that sales reps have in common with outbound leads. AI tools can then use that information to generate emails so reps can build an initial rapport with cold leads.
Sales reps typically interact with these tools from a chat window in their email systems' interface. The tools can suggest responses to each email and let users input custom prompts, such as "write a cold sales email to John Smith about our new product." The tool then generates a draft which users can edit.
Design sales proposal slides. Sales teams can use GenAI tools to create visual artifacts, such as presentation slides, in addition to text. A well-designed presentation can win over customers and prospects, but not all sales reps have an eye for design.
GenAI presentation tools let sales reps use natural language to design slide decks and other forms of AI art. For example, a sales rep could prompt the tool and write: "Create a sales proposal for a B2B tech company." The tool could then generate a deck of slides that includes key sales proposal elements, such as an "about us" slide, pie charts and user quotes. The sales rep could then fill in the slide deck with their unique company information.
Improve sales chatbots. GenAI's advanced natural language processing capabilities can enhance customer-facing chatbots. For years, organizations have deployed sales chatbots across their company websites to engage customers, answer product questions and collect information. However, these tools can feel overly scripted and robotic.
GenAI's ability to understand complex queries and generate humanlike responses can make these chatbots more helpful and engaging than past generations of chatbots.
2. Data analysis
Coach sales reps in real time. GenAI tools can analyze sales interactions, such as email, live chat and video conferencing conversations, in real time and coach sales reps along the way. To enable sales coaching, organizations must customize their AI tools. They can collect and feed large amounts of past sales interaction data into the tool to help it recognize company terminology and elements of successful and unsuccessful sales interactions.
A customer might ask a sales rep, "What makes your product different from competitors?" The tool can then quickly generate a cue card to replicate how sales reps successfully answered this question in the past. The sales rep could then choose to use the suggestion or not.
GenAI can also help sales reps identify unsuccessful behaviors that cost them valuable leads. For example, a tool could analyze a sales rep's interaction history to learn their deals often fall through when they try to set up a meeting too early in the relationship. The sales rep could then work on building a rapport before trying to sell.
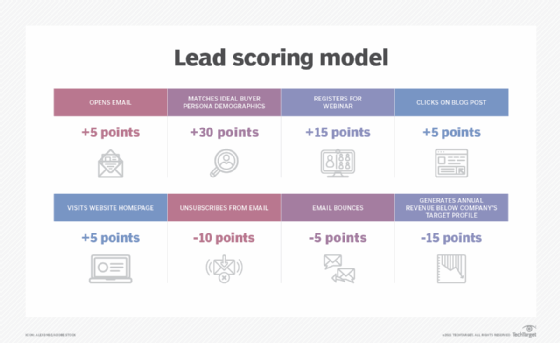
Lead scoring. Sales teams can have hundreds or thousands of leads, depending on their organization's size. GenAI tools can quickly analyze massive amounts of customer data to enhance lead scoring efforts and help sales reps know which prospects to prioritize.
To accurately score leads, these tools can analyze the following types of customer data:
- Website behavior.
- Demographics, such as age and gender.
- Firmographics, such as employer size and industry.
- Job title.
- Purchase history.
- Social media engagement.
GenAI tools can synthesize all this data to attribute a score to each lead. They can also process information in real time, so scores change regularly as new data comes in.
Improve forecasting. All departments within an organization rely on sales forecasts -- whether monthly, quarterly or annually -- for resource allocation. GenAI's ability to analyze large amounts of unstructured data, such as sales interactions, can improve the accuracy of these forecasts.
If a sales forecast predicts an organization will bring in $50 million more in revenue than the previous year, it might decide to increase technology and hiring budgets for production and marketing teams. Yet, if the forecast is wrong, organizations might need to lay off employees, cut budgets and halt production. GenAI tools can analyze information in CRM systems, along with data about the economy and competitors' pricing, to predict future revenue more quickly and accurately than a team of humans.
3. Task automation
Add contacts to a CRM system. Sales reps spend a lot of time adding contact information to CRM systems -- especially those in large enterprises with complex sales processes. GenAI can speed up this process, as it lets sales reps use natural language prompts to input data, as opposed to manually filling out fields. For example, a sales rep could type, "add [email protected] and follow up next week." The tool could then automatically input the contact email and action item into the CRM contact list.
Research leads. GenAI tools can help sales reps research leads directly from their CRM systems. For example, a sales rep at a Houston-based healthcare SaaS company could ask the tool for a list of all large hospitals and healthcare providers in the Houston area. The tool could then offer up a list that includes company descriptions, addresses, key contacts and an option to automatically add the information to the CRM system.
Summarize recorded interactions. GenAI can summarize interactions from calls, emails and video chats so sales reps can look back on important details. These tools can automatically add interaction highlights as notes in the CRM system to save sales reps' time.
Enhance CPQ processes. Sales teams rely on configure price quote (CPQ) software to calculate pricing for complex products, configurations and bundles. Traditionally, these tools turn customer inputs, such as required features and the number of users, into customized quotes.
However, GenAI can turn price quoting into a more immersive and personalized experience, Miller said. For instance, AI-powered CPQ tools can offer a conversational interface that can make real-time pricing adjustments based on customer feedback.
Additionally, GenAI can analyze customer inputs alongside broad datasets, such as purchase history, industry trends and competitor offerings, to recommend complementary products and upgrades that align with the customers' goals. This approach enhances quote accuracy while uncovering cross-selling and upselling opportunities.
6 challenges of GenAI for sales
Despite the various use cases of GenAI, sales teams can struggle to scale AI deployment beyond initial experiments, track ROI and effectively manage customer data.
1. Scaling
Sales teams often experiment with GenAI for singular use cases, such as drafting email outreach and automating request for proposal responses. While this approach offers an entry point for AI implementation, teams often fail to expand it beyond those isolated use cases.
"The experiment runs, we see that there's a boost to efficiency … and then the experiment kind of stalls there. It doesn't then scale to the next process, or to the next selling procedure, or to the next point of operations," Miller said.
To overcome this challenge, sales and IT leaders can adopt a more strategic and holistic approach to AI implementation. For instance, they should create a long-term vision for the AI tool and find ways to integrate it across the entire sales lifecycle, rather than just singular use cases.
2. Measuring ROI
Initial excitement about GenAI often causes sales teams to explore its capabilities before they develop measurable objectives for the tool. This lack of clarity results in vague outcomes and difficulty measuring ROI.
"We're implementing AI with a bit of blinders on and without saying, 'Okay, [here is] what I am going for,'" Miller said.
Without a clear end goal -- for example, increasing sales by 10% in the second half of the year -- sales teams might struggle to justify the value of their AI investments. To avoid this issue, sales teams can define specific outcomes from the outset and work backward to identify AI use cases most likely to help them achieve those goals.
3. Data readiness
Effective GenAI relies on quality data. However, sales and marketing teams have historically struggled to manage large volumes of customer data, which limits their ability to use AI effectively. During AI implementation projects, teams commonly react to disorganized and missing data in one of two extreme ways: give up on the project altogether or invest a significant amount of time, money and effort to improve their data management processes.
"When we realized we didn't have the right data … what we've always gone out and done is thrown money at the problem to try to get to perfect rather than standing back for just a second and asking where we start," Miller said.
Brands can take a more practical approach that begins with existing data assets and improves incrementally. Sales leaders should talk with their CIOs about which data to start with and how to enrich it over time, Miller said.
GenAI itself can play a key role in data enrichment because it can operate with incomplete data and fill gaps to make existing data more useful. For example, if a sales team has incomplete customer profiles, such as missing job titles or industry information, GenAI can analyze past interactions and infer missing details based on patterns. Brands can then feed the enriched data back into GenAI tools to achieve deeper sales insights and increased personalization.
4. Data protection
To use GenAI most effectively, sales teams need to train a tool on their company data, which includes personally identifiable information, such as customer names, email addresses and credit card information. Organizations must implement security measures, such as encryption and access controls, to protect this information and achieve compliance with data privacy regulations.
5. Lack of empathy
Although GenAI can write personalized emails at scale, these messages might lack the personal touch and empathy of an actual person. Sales reps should use the tool to create first drafts and then edit them manually.
6. False information
If GenAI tools don't have enough information to answer a question, they sometimes generate false answers, which can negatively affect CX. For example, a chatbot could give customers incorrect pricing information for a product. To increase accuracy, organizations should extensively train these tools on their knowledge bases -- which they should keep up-to-date -- then regularly test and monitor output quality.
Organizations that want to adopt GenAI have different implementation options. If they need a lot of flexibility and have an internal team of AI developers and experts, they can build their own tool. However, this option can take considerable time and effort.
Alternatively, sales leaders can purchase a GenAI tool and train it on their company data. Standalone tools can integrate with an organization's existing CRM or email system, whereas other GenAI tools come as features within larger CRM platforms.
Editor's note: This article was updated to reflect changes in generative AI technology.
Tim Murphy is associate site editor for Informa TechTarget's SearchCustomerExperience and SearchContentManagement sites.









