What is HR automation? Examples, benefits and challenges
Human resources automation, or HR automation, is a method of using software to automate and streamline repetitive and laborious HR tasks.
HR personnel can use automated tools to save time and improve how they manage personnel. As a result of these efficiency gains, HR teams can increase their productivity and produce better quality, error-free output. They can also augment their skills and competencies by dedicating their efforts to more complex tasks, such as planning, strategizing, employee engagement and retention, and decision-making, thus increasing the value of the HR function to the organization.
Can HR be automated?
HR departments and personnel are crucial to the ongoing operations of organizations in every country and industry. However, many everyday HR tasks and activities -- such as timekeeping or employee onboarding -- involve a lot of manual and repetitive processing, paperwork and administration.
These manual tasks take up a lot of time and effort, preventing HR personnel from making more meaningful contributions to the organization using their specialized skills and expertise. Automating these time-intensive, lower-skill activities can help them use their time more productively.
Common examples of automated HR processes
HR automation is about digitizing repetitive and time-consuming HR tasks to eliminate or minimize the need for manual work and human input. The HR management tasks that can be automated to some or to a maximum extent include the following activities:
- Day-to-day HR administration, such as paperwork and standardized forms.
- Payroll, including paycheck disbursals, salary changes and tasks related to employee payouts.
- Benefits administration and management, including benefits that employees can access with self-service tools.
- Email reminders, including notifications and memos sent to employees for signing up for training programs, completing surveys, completing self-performance reviews, etc.
- Talent acquisition and new employee recruitment, which involves activities like sourcing and attracting candidates, filtering resumes and application tracking.
- Internal candidate recruitment, including referral programs and promotions.
- New employee onboarding, including setting up access to IT resources and conducting orientation training.
- Employee offboarding, including removing access to IT resources and scheduling exit interviews.
- Training and development, such as tracking employee training and skill set management.
- Timekeeping, including hours worked, sick days, vacation and personal time off.
- Preparing and processing tax forms, contracts, confidentiality agreements and nondisclosure agreements.
- Creating and maintaining employee records.
- Ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, such as annual safety training, and sharing compliance guidelines with employees.
- Job title classification and organizational structuring.
- Employee performance tracking, including bonuses, disciplinary actions and terminations.
- HR support or service desk requests, such as responding to employee FAQs, sending training reminders, suggesting learning resources, sending job satisfaction surveys and soliciting feedback regarding training programs, benefits, company culture, etc.
Benefits of HR automation
Automating HR tasks can help HR professionals save time by freeing HR personnel to take on more valuable or complex organizational tasks. This can also improve HR efficiency, reduce the possibilities of human error and help strengthen the organization's regulatory compliance posture.
Automating simple but tedious processes gives HR departments the bandwidth to work closely with top leaders to create employee engagement strategies or design new training and development programs.
Other examples of more valuable or complex HR tasks that require unique human capabilities and cannot be automated include strategic planning, employee relationship management, coaching and mentoring, and even some aspects of recruitment and performance management.
HR automation delivers many benefits:
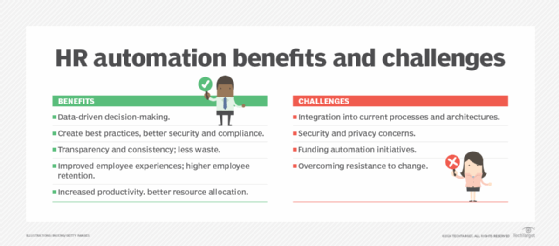
- Less waste. Switching to automation enables HR departments to decrease paperwork, reducing materials costs and manual workflows.
- Data-driven decision-making. Automation software can collect and track HR-relevant data across the organization, enabling decision-makers to analyze existing processes, assess their effectiveness and determine what changes are required to optimize the processes and benefit the organization.
- Creation of best practices. Leadership can use the collected data from automation software to run reports, measure actionable items, analyze employee experience and find patterns within the data that might indicate opportunities or risks. This information can be used to create comprehensive HR policies and best practices that benefit the organization and its workforce.
- Transparency and consistency. Automating HR workflows can improve transparency and accountability in the HR department. For multilocation businesses, automation can create consistent HR practices and ensure that those practices are implemented equitably throughout the organization.
- Improved employee experience. Automation makes self-service possible. Employees can log into a self-service portal to easily update their data (e.g., contact details), make changes to their benefits, submit expense reports, apply for leave or sign up for new training courses. By allowing employees to self-manage these aspects of their employment, instead of making them rely on HR personnel or use complex HR workflows (send an email, fill out a form, etc.), HR automation can improve the employee experience.
- Increased employee productivity. Since automation and self-service enable employees to spend less time on HR processes and manual HR workflows, employees can focus more on their core tasks and responsibilities.
- Higher employee retention and lower churn. Enhanced employee experiences directly correlate to workplace satisfaction and foster a culture where employees feel empowered to do their best at work. Employees who feel supported and valued are less likely to leave the organization. This can reduce attrition and increase employee retention.
What are the challenges of HR automation?
Although HR task automation provides many benefits for organizations, it also has challenges and limits. Notably, many HR tasks involve sensitive matters and require emotional intelligence and soft skills. These types of complex human interactions cannot be automated in a satisfactory way.
For example, an employee who is requesting bereavement leave after the death of a spouse or child might interpret an automated response as cold and uncaring. Such an interpretation can negatively affect their view of the organization.
On a more organizational level, activities that require more creativity and personalization -- culture setting, performance review discussions, exit interviews and change management, for example -- require human intervention and are not amenable to automation.
There are other, more technical challenges of adopting HR automation:
- Integration into current processes and architectures. Some HR automation software is specialized, with features focused on specific processes. As a result, it can be difficult to integrate the products into the organization's IT infrastructure. That said, many products are also available that can be easily integrated with the organization's tech stack and work seamlessly with other standalone enterprise tools, including identity and access management, learning management systems, payroll and more.
- Security and privacy concerns. HR software collects a significant amount of sensitive data. Organizations might not have clarity on how the data is stored, resulting in inadequate or missing security controls, leaving them vulnerable to data breaches and regulatory fines. To mitigate these concerns, companies should select HR automation software incorporating robust data security and privacy features, such as access controls, encryption and data backup.
- Funding automation initiatives. Any new IT initiative comes with a price tag, and HR automation is no exception. Implementing these tools requires the buy-in of senior leadership, particularly from a budget perspective. HR leaders must be able to demonstrate the benefits and savings to executives to obtain funding to buy and implement the right software.
- Overcoming resistance to change. As with most digital transformation projects, HR automation can garner significant resistance from HR and other teams. Before making costly software investments, decision-makers must clearly communicate the benefits of HR automation and garner buy-in from all relevant stakeholders.
HR automation and compliance
In addition to the efficiency and productivity gains of HR automation, it helps companies comply with many employment laws and industry-specific regulations. These might include the following:
- Labor laws and regulations. These tools can automatically distribute required annual notices, process government-protected leave requests, send reminders about expiring credentials and securely maintain employee information.
- Workplace safety. From automating background checks to environmental safety training, HR automation systems can help firms to comply with employee safety, privacy and health regulations that apply to their specific industry or country.
- U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity laws and similar antidiscrimination laws worldwide. Automation software can mitigate human bias in candidate evaluation and hiring decisions.
- Wages and benefits. Technology can help automate benefits enrollment and management and ensure compliance with regulations surrounding minimum wages and overtime pay.
- Immigration. HR automation systems include capabilities to manage and track international employees' immigration status and ensure that work authorization documentation remains up-to-date and compliant with immigration laws and regulations.
HR automation technologies have evolved rapidly over the past few years. Tools are available that streamline HR workflows, such as performance management, tax filing and benefits/compensation management, and automate compliance. These tools can keep track of regulations and incorporate any changes into HR workflows to prevent compliance breaks and associated fines/penalties.
Furthermore, HR personnel can use various tools to manage benefits, compensation, taxation and other crucial aspects to ensure that the company remains compliant with all relevant tax, labor and other laws and regulations.
Some automated systems also ensure secure data storage using role-based access controls, encryption and other measures to protect sensitive employee data and ensure data privacy and compliance. HR automation software can also simplify compliance audits. The tools might provide audit trails that enable organizations to demonstrate compliance with regulatory authorities.
Some HR automation software can also enhance physical security. For example, it can automatically deactivate badge access for a departing employee during offboarding. It can also automatically send reminder emails to staff whose credentials must be renewed soon. These capabilities can also improve data security and support the organization's compliance objectives.
Important automation features in HR software
When investing in HR technology, specifically HR automation software, organizations should look out for these key features:
- Recruitment and hiring tools. The tool must automatically collect and analyze employee data, including new recruits or applicants. It should include features to determine salary structures, organize the details of job applicants and automatically accept or reject applicants based on certain criteria. The best software also simplifies talent acquisition and recruitment, including applicant tracking systems.
- Employee self-service tools. Accessible and user-friendly self-service portals enable staff to access important information and features. Through the portal, they can request time off, submit expense reports, enroll in new training courses, update their personal information and more. The software should also give staff and managers real-time access to important employee records and forms.
- Payroll and benefits tools. The software should include pay and benefits calculators; features to enable and adjust direct deposit, download pay stubs and access tax forms so HR staff don't have to manage or track these tasks manually; and ways to automate benefits eligibility, selection and updates.
- Efficient workflow tools. Workflow tools include updates that can be pushed automatically to organized recipient lists. They can also collect feedback and manage process steps, again helping HR personnel save time and minimize administrative hassles.
- Time and leave tracking tools. Tools for automated shift scheduling and management, time allocation, leave entitlement and balance, and overtime calculations improve transparency throughout the organization, minimize conflicts (e.g., between staff and HR) and enable HR staff to focus on other more important tasks.
- Performance evaluation tools. Performance evaluation tools include feedback tracking, performance review organization and data collection. The software might also include features to catch turnover trends and low performance issues.
- Employee training tools. Built-in training tools let HR teams easily manage employees' training and development plans, track employee competencies, monitor each employee's learning progress and identify gaps that need to be addressed.
- Talent management and retention tools. Talent management tools can gather feedback about employee experiences and workplace satisfaction and predict improvement areas. Retention features can also spot common behaviors that might lead to resignations, such as an employee leaving early or taking too many unplanned leaves, enabling leadership to address those issues and boost that person's engagement.
- Data analytics tools. With HR analytics features, the tool can analyze data and find patterns or trends to aid decision-making. The best tools also provide detailed reports, visualizations, insights and alerts to help management identify problems and implement fixes to improve workforce engagement, performance and retention.
- Integrations. The tool must integrate and synchronize data with all other enterprise systems to enable more informed data-driven decision-making.
It's also a good idea to look for tools that use advanced technologies, such as intelligent automation, AI, machine learning and natural language processing (NLP). AI-powered systems can simplify many HR processes, including human capital management and employee self-service.
AI and machine learning capabilities also create opportunities for personalization. For example, chatbots and virtual assistants with generative AI (GenAI) and NLP capabilities can provide tailored responses to employee questions in natural, humanlike language. In this way, these tools can provide around-the-clock HR support and enhance employee experience and workplace satisfaction.
NLP- and GenAI-enabled tools can also help speed up recruitment and vendor management processes. For example, an applicant tracking system can organize information about job seekers, track candidates through the hiring process, schedule interviews and send automated emails to candidates and recruiters. Similarly, HR staff can use GenAI to compile candidate requirements and open a request within the firm's vendor management system to identify and source new vendors.
Manual intervention is not, or is rarely, required; this frees HR staff to focus on other, more strategic aspects of recruitment and talent management.
Well-known providers of HR automation software
As more organizations understand the value of HR automation, many software vendors have started offering HR automation products. These products cover a wide range of HR processes, including payroll, onboarding, time and attendance, HR data management, performance management, learning management and human capital management.
The following are some well-known HR automation vendors:
- ADP.
- APS Payroll Systems.
- BambooHR.
- Cezanne HR.
- Checkbox.
- ClearCompany.
- Deputy.
- Gusto.
- IBM.
- Oracle.
- People HR.
- Namely.
- SAP SuccessFactors.
- Workday.
- Workable.
- Zoho.
HR can use robotic process automation (RPA) to automate manual processes, standardize common tasks, quickly complete existing tasks and free workers to spend more time on complex projects. Explore what RPA means for HR operations.







