What is multi-access edge computing? Benefits and use cases
Multi-access edge computing (MEC) is a network architecture concept that brings cloud computing capabilities and IT services closer to the edge of the network, where data is generated and consumed.
As a form of edge computing, MEC enables local data processing, typically at mobile and cellular base stations or other edge nodes, reducing reliance on centralized cloud servers. This localized approach reduces latency and enhances responsiveness for applications that require real-time or near-real-time performance.
MEC differs from the more general concept of edge computing, which focuses on processing data close to its source. The multi-access aspect of MEC applies not only to mobile networks but also to fixed broadband, Wi-Fi and other types of access networks, enabling faster, low-latency and context-aware data processing.
How does multi-access edge computing work?
MEC creates a distributed computing architecture that reduces the time it takes for data to travel to its destination. The following steps explain how data flows in MEC:
- Deployment at the edge. MEC servers are installed at the edge of the network, such as cellular base stations, Wi-Fi access points and local data centers. These servers host applications and services that traditionally run in centralized clouds.
- Data generation. When end users generate data from their devices, such as smartphones, sensors and vehicles, it's directed to the nearest edge server or access point instead of a remote cloud.
- Traffic interception. The MEC system intercepts relevant data traffic before it reaches the core network and directs it to edge servers for faster local processing.
- Local processing. Edge servers then process the data locally, performing the required computations and delivering immediate insights or actions to the end users.
- Cloud offload. Only essential data is sent to centralized cloud systems for long-term storage, deeper analytics and broader coordination.
These steps ensure that results are delivered to end users with minimal latency, enabling faster and more responsive applications. In essence, MEC acts as a local mini-cloud, offloading traffic from the core network and providing cloud services with real-time, context-aware capabilities.
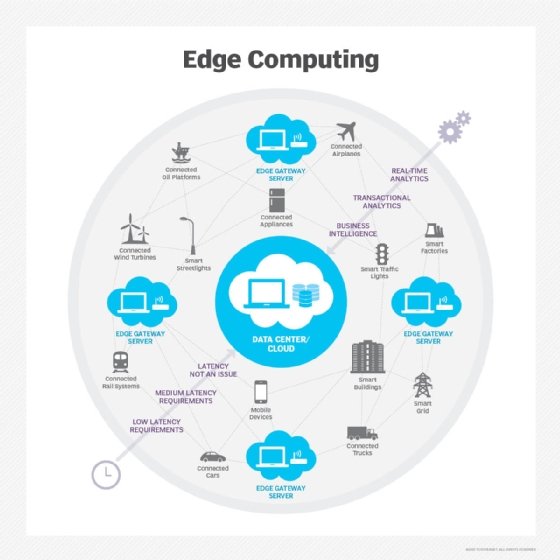
Benefits of multi-access edge computing
Multi-access edge computing offers a range of strategic and operational benefits, especially for industries and applications that require speed, efficiency and localized control. Below are some of the key benefits MEC provides:
- Ultra-low latency. By processing data at the network edge rather than sending it back to distant cloud servers, MEC ensures near-real-time responses, often in the single-digit millisecond (ms) range. This is especially critical for applications such as autonomous vehicles, remote surgical procedures, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR) and cloud gaming, where even millisecond delays can have serious consequences.
- Bandwidth optimization. MEC contributes to more efficient bandwidth use by enabling local data processing. Rather than transmitting all raw data to centralized cloud servers, edge nodes perform computations and filter out nonessential information at the source. This approach reduces network traffic, alleviates pressure on core infrastructure and supports more consistent performance across enterprise and consumer applications.
- Context-aware services. Because edge servers can access real-time data about user location, device status and network conditions, applications can be tailored to the specific needs of the moment. For example, MEC can deliver location-specific advertising, adjust video streaming quality based on bandwidth or support smart city infrastructure with adaptive traffic control.
- Improved reliability and resilience. By enabling localized data processing, MEC improves service reliability and operational resilience. For instance, in the event of disruptions to central cloud connectivity, edge servers can continue to function independently, ensuring uninterrupted support for critical applications.
- Enhanced security and privacy. By processing sensitive data at the edge, organizations can keep it within a local and controlled environment. This reduces the risk of data breaches that can occur when transmitting information to a centralized cloud over long distances.
- Improved quality of service (QoS). The proximity of MEC servers to end users and devices enhances QoS by ensuring a more reliable and consistent user experience. This is beneficial for applications that are sensitive to network fluctuations, such as live video streaming and cloud gaming.
- Cost efficiency. By offloading processing tasks from centralized cloud infrastructure to the network edge, MEC reduces the need for expensive backhaul capacity. This can significantly reduce costs for telecom providers and enterprises, while ensuring high-quality service delivery to end users.
- Scalability and flexibility. With MEC, organizations can deploy services dynamically at the edge and scale up or down based on user demand. This enables faster rollouts of new applications and services without the need for a full network overhaul.
- Support for emerging applications. MEC supports a range of emerging, data-intensive and latency-sensitive applications. In industrial IoT, MEC supports real-time automation and predictive maintenance. In healthcare, it enables remote diagnostics and telesurgery. For smart cities, MEC powers services, such as intelligent traffic monitoring and public safety systems. In entertainment, it enhances immersive AR/VR experiences and cloud gaming.
Challenges of multi-access edge computing
While MEC offers significant benefits, its distributed nature and complexity also present several challenges for deployment, management and security. The following are the key challenges of MEC:
- Infrastructure costs. Unlike centralized cloud systems that concentrate resources in a few large facilities, MEC distributes resources across multiple edge locations. This distributed model increases upfront capital expenses and ongoing operational costs, making large-scale adoption more challenging.
- Complex deployment and management. Managing a distributed MEC environment presents greater operational complexity compared with centralized cloud systems. This is because each site demands careful installation, configuration, ongoing monitoring and routine maintenance. Maintaining consistent performance across geographically dispersed nodes, while coordinating updates and integrating with multiple access networks such as 5G, Wi-Fi and fixed broadband, adds significant logistical and technical challenges for organizations.
- Scalability limitations. While MEC enhances scalability for applications, it also comes with limitations. For example, edge resources, such as storage and compute power, are inherently more constrained than centralized cloud resources, which can restrict the types of workloads that can run efficiently. In addition, scaling applications across multiple edge nodes requires sophisticated orchestration.
- Lack of standardization. The MEC ecosystem is evolving, and a lack of standardized protocols and application programming interfaces increases the risk of vendor lock-in. Proprietary offerings from different vendors often fail to interoperate, making it challenging to build a unified, multivendor edge infrastructure. This fragmentation complicates management and reduces organizational flexibility.
- Security risks. Although MEC can enhance data privacy by processing information locally, it also increases the attack surface. With more distributed sites, each edge server becomes a potential target for cyberattacks, making it challenging to provide consistent security policies, timely patches and physical protection across numerous sites.
- Network dependence. Although MEC reduces reliance on the central cloud, it still depends on high-performance local networks. Therefore, in areas with weak connectivity, MEC performance can be limited. For example, with latency-sensitive use cases such as autonomous vehicles or telesurgery, even small connectivity disruptions can have critical consequences.
- ROI uncertainty. For telecom providers and enterprises, the financial value of MEC can be uncertain. While it promises benefits, such as lower latency and new service opportunities, monetizing these benefits isn't always straightforward. Without clear business models and customer demand, organizations might hesitate to commit to large-scale MEC rollouts.
How 5G affects multi-access edge computing
5G and MEC are interdependent technologies, each amplifying the capabilities of the other. The following is a breakdown of how 5G affects MEC and how this convergence is reshaping digital infrastructure:
- Ultra-low latency and high bandwidth. 5G's ability to deliver latency below 10 ms enhances MEC's effectiveness in supporting real-time applications. Without 5G's fast connection speeds, the round-trip time for data moving between a device and the edge server would be too slow for real-time applications, such as autonomous vehicles, remote surgery and real-time analytics. 5G's architecture provides a fast data pipeline that feeds the local processing power of MEC nodes. In turn, edge computing reduces the physical distance data must travel and accelerates processing, enabling faster and more reliable application performance, especially for bandwidth-intensive applications.
- Network slicing. As a core feature of 5G, network slicing enables operators to partition a single physical network into multiple virtual networks, each optimized for a specific service. Operators dedicate a slice to an MEC application, ensuring guaranteed levels of performance, latency and bandwidth. For example, a slice that supports autonomous vehicles can be optimized for ultra-low latency, while one that serves media streaming can be configured for high bandwidth.
- Massive device connectivity. 5G's support for high device density enables MEC to manage data from thousands of connected endpoints in environments, such as smart factories and urban IoT deployments. By offloading processing to edge nodes, MEC reduces cloud dependency and improves scalability.
- Improved mobile device hand-off. As mobile users or connected devices move from one geographic area to another, 5G's efficient handoff capabilities ensure a smooth transition between different MEC nodes without interrupting service. This is critical for applications where a sudden increase in latency due to a handoff could be disruptive or dangerous.
- Enhanced security framework. 5G introduces enhanced encryption and authentication protocols, which align with MEC's ability to process sensitive information close to its source. Together, they enable organizations to implement end-to-end security strategies that safeguard data throughout its lifecycle. By maintaining sensitive workloads within secure edge environments and transmitting them over protected 5G links, organizations can minimize exposure to external threats while supporting high-performance, security-critical applications.
- Distributed architecture and real-time context awareness. MEC is often deployed alongside 5G radio access network components, providing immediate access to RAN information that's critical for context-aware applications. This proximity lets edge systems respond quickly to changing network conditions and user needs, and provides greater adaptability of services.
Key use cases of multi-access edge computing
MEC is transforming numerous industries by bringing computational power closer to data sources and end users. The following are key use cases of MEC across different industries.
Autonomous vehicles
In the context of self-driving cars, MEC facilitates real-time interaction between vehicles, infrastructure and pedestrians to support safer navigation. By processing sensor data at the edge, MEC enables rapid hazard detection and response, which is critical for collision avoidance systems.
Additionally, it supports dynamic fleet coordination, enabling traffic-aware routing and logistics optimization that improves safety and operational efficiency.
Industrial IoT and smart manufacturing
Manufacturing facilities increasingly rely on connected sensors and automated systems that generate continuous streams of operational data. MEC supports these industrial IoT deployments by enabling real-time monitoring and control of production processes, predictive maintenance of equipment and quality assurance checks. The ability to process this information at the factory edge rather than in remote data centers ensures that manufacturing systems can respond immediately to changing conditions, reducing downtime and improving productivity.
MEC also enhances worker safety, enabling rapid detection of hazardous situations and facilitating immediate corrective actions.
Healthcare and remote medical services
Healthcare applications use MEC to support remote monitoring, telemedicine and emergency response systems. Edge computing enables the processing of patient data from wearable devices and medical sensors in near real time. This facilitates immediate detection of health indicators. In hospital environments, MEC supports the rapid analysis of medical imaging and diagnostic information, accelerating treatment decisions.
The combination of 5G connectivity and edge computing also enhances the capabilities of remote surgery systems. They minimize latency in control mechanisms and video feeds, which improves precision and safety.
Retail
In retail environments, MEC enables real-time, data-driven operations that enhance efficiency and customer experience. For example, autonomous robots equipped with edge processing capabilities can monitor shelf inventory and trigger alerts instantly, improving stock accuracy and replenishment. Low-latency edge computing also powers immersive AR/VR applications, such as virtual try-ons and interactive shopping experiences.
Localized data analysis also supports personalized services, such as targeted promotions and in-store navigation. This lets retailers deliver more responsive and context-aware engagement.
Smart cities
In smart city environments, MEC provides responsive, data-driven services that improve urban efficiency and safety. Real-time traffic management is supported through dynamic signal coordination, congestion alerts and vehicle prioritization. Public safety systems benefit from low-latency edge processing for surveillance, emergency response and crowd monitoring.
Additionally, infrastructure monitoring is enhanced by edge-based sensors that detect faults in utilities, bridges and transit systems. This enables proactive maintenance and reduces service disruptions.
Cloud gaming and interactive entertainment
The gaming industry uses MEC to deliver cloud-based gaming experiences with minimal latency. By processing game logic and rendering at edge locations close to players, gaming platforms can provide responsive gameplay even for titles that require split-second reactions. This approach also reduces the delay between player actions and game responses, providing more sophisticated multiplayer experiences.
MEC supports the delivery of complex gaming experiences to devices with limited processing power, expanding the potential audience for high-end interactive entertainment while maintaining the performance levels that gamers expect.
How to adopt multi-access edge computing technology
A joint AT&T, Google Cloud and IDG survey found that 95% of senior IT decision-makers believe MEC will have a significant or transformational effect on their business, with 51% expecting it to be transformational. These figures underscore MEC's strategic role in enabling next-generation applications across various industries, including manufacturing, retail and healthcare.
The following are steps that organizational decision-makers can take to implement multi-access edge computing successfully:
- Align MEC with business objectives. Organizations should identify use cases where MEC can deliver a measurable difference, such as minimizing latency in production environments, enabling real-time diagnostics and improving customer engagement. Prioritize applications that depend on rapid data processing, localized control or enhanced operational resilience.
- Identify high-impact use cases. Decision-makers should focus on applications that benefit most from edge computing, such as autonomous vehicles, smart manufacturing and AR/VR. They should pilot these use cases to demonstrate MEC's effectiveness in addressing specific business challenges.
- Collaborate with telecom and cloud providers. Organizations must partner with telecommunications companies and cloud service providers to use their existing infrastructure and expertise. Such collaborations can accelerate MEC deployment and reduce associated costs.
- Secure executive buy-in. Organizations should ensure leadership alignment by connecting MEC initiatives to broader strategic outcomes, such as improving operational efficiency, enhancing customer experience and advancing digital transformation. Securing executive sponsorship is important to obtain funding, facilitate cross-functional collaboration and sustain long-term success.
- Integrate MEC into the existing IT infrastructure. Organizations should ensure that MEC options are compatible with their existing IT systems. This integration facilitates seamless data flow and maintains operational continuity.
- Address security and compliance. Organizations should implement strong security measures to protect data processed at the edge and ensure compliance with relevant regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act for healthcare applications.
- Invest in orchestration and monitoring. Organizations should deploy centralized platforms to manage edge nodes, monitor system performance and automate software updates. AI-driven orchestration tools can support the scalable implementation of MEC across multiple locations while ensuring operational consistency and reliability.
- Plan for scalability. Organizations should design MEC deployments with scalability in mind to accommodate future growth and the increasing number of connected devices.
- Invest in training and talent. Organizations should develop internal capabilities by training staff on MEC technologies and processes and consider hiring or partnering with experts to build a skilled workforce.
Organizations are increasingly using edge computing, which is often deployed via purpose-built devices, including edge gateways, to drive business outcomes. Explore key edge computing trends to watch.






