What is malware? Prevention, detection and how attacks work
What is malware?
Malware, or malicious software, is any program or file that's intentionally harmful to a computer, network or server.
Types of malware include computer viruses, worms, Trojan horses, ransomware and spyware. These malicious programs steal, encrypt and delete sensitive data; alter or hijack core computing functions; and monitor end users' computer activity.
What does malware do?
Malware can infect networks and devices and is designed to harm those devices, networks and their users in some way. Depending on the type of malware and its goal, this harm might present itself differently to the user or endpoint. In some cases, the effect of malware is relatively mild and benign, and in others, it can be disastrous.
Malware can typically perform the following harmful actions:
- Data exfiltration. Data exfiltration is a common objective of malware. During data exfiltration, once a system is infected with malware, threat actors can steal sensitive information stored on the system, such as emails, passwords, intellectual property, financial information and login credentials. Data exfiltration can result in monetary or reputational damage to individuals and organizations.
- Service disruption. Malware can disrupt services in several ways. For example, it can lock up computers and make them unusable or hold them hostage for financial gain by performing a ransomware attack. Malware can also target critical infrastructure, such as power grids, healthcare facilities or transportation systems to cause service disruptions.
- Data espionage. A type of malware known as spyware performs data espionage by spying on users. Typically, hackers use keyloggers to record keystrokes, access web cameras and microphones and capture screenshots.
- Identity theft. Malware can be used to steal personal data which can be used to impersonate victims, commit fraud or gain access to additional resources. According to the IBM X-Force Threat Intelligence Index 2024, there was a 71% rise in cyberattacks using stolen identities in 2023 compared to the previous year.
- Stealing resources. Malware can use stolen system resources to send spam emails, operate botnets and run cryptomining software, also known as cryptojacking.
- System damage. Certain types of malware, such as computer worms, can damage devices by corrupting the system files, deleting data or changing system settings. This damage can lead to an unstable or unusable system.
No matter the method, all types of malware are designed to exploit devices at the user's expense and to benefit the hacker -- the person who has designed or deployed the malware.
How do malware infections happen?
Malware authors use a variety of physical and virtual means to spread malware that infects devices and networks, including the following:
- Removable drives. Malicious programs can be delivered to a system with a USB drive or external hard drive. For example, malware can be automatically installed when an infected removable drive connects to a PC.
- Infected websites. Malware can find its way into a device through popular collaboration tools and drive-by downloads, which automatically download programs from malicious websites to systems without the user's approval or knowledge.
- Phishing attacks. Phishing attacks use phishing emails disguised as legitimate messages containing malicious links or attachments to deliver the malware executable file to unsuspecting users. Sophisticated malware attacks often use a command-and-control server that lets threat actors communicate with the infected systems, exfiltrate sensitive data and even remotely control the compromised device or server.
- Obfuscation techniques. Emerging strains of malware include new evasion and obfuscation techniques designed to fool users, security administrators and antimalware products. Some of these evasion techniques rely on simple tactics, such as using web proxies to hide malicious traffic or source Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. More sophisticated cyberthreats include polymorphic malware that can repeatedly change its underlying code to avoid detection from signature-based detection tools; anti-sandbox techniques that enable malware to detect when it's being analyzed and to delay execution until after it leaves the sandbox; and fileless malware that resides only in the system's RAM to avoid being discovered.
- Software from third-party websites. There are instances where malware can be downloaded and installed on a system concurrently with other programs or apps. Typically, software from third-party websites or files shared over peer-to-peer networks falls under this category. For example, a computer running a Microsoft operating system (OS) might end up unknowingly installing software that Microsoft would deem as a potentially unwanted program (PUP). However, by checking a box during the installation, users can avoid installing unwanted software.
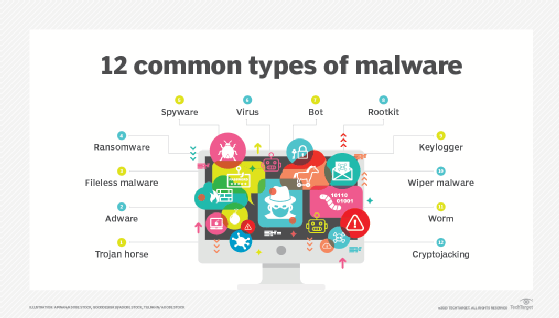
Types of malware
Different types of malware have the following unique traits and characteristics:
- Virus. A virus is the most common type of malware that can execute itself and spread by infecting other programs or files.
- Worm. A worm can self-replicate without a host program and typically spreads without any interaction from the malware authors.
- Trojan horse. A Trojan horse is designed to appear as a legitimate software program to gain access to a system. Once activated following installation, Trojans can execute their malicious functions.
- Spyware. Spyware collects information and data on the device and user, as well as observes the user's activity without their knowledge.
- Ransomware. Ransomware infects a user's system and encrypts its data. Cybercriminals then demand a ransom payment from the victim in exchange for decrypting the system's data.
- Rootkit. A rootkit obtains administrator-level access to the victim's system. Once installed, the program gives threat actors root or privileged access to the system.
- Backdoor virus. A backdoor virus or remote access Trojan (RAT) secretly creates a backdoor into an infected computer system that lets threat actors remotely access it without alerting the user or the system's security programs.
- Adware. Adware tracks a user's browser and download history with the intent to display pop-up or banner advertisements that lure the user into making a purchase. For example, an advertiser might use cookies to track the webpages a user visits to better target advertising.
- Keyloggers. Keyloggers, also called system monitors, track nearly everything a user does on their computer. This includes writing emails, opening webpages, accessing computer programs and typing keystrokes.
- Logic bombs. This type of malicious malware is designed to cause harm and typically gets inserted into a system once specific conditions are met. Logic bombs stay dormant and are triggered when a certain event or condition is met, such as when a user takes a specific action on a certain date or time.
- Exploits. Computer exploits take advantage of existing vulnerabilities, flaws or weaknesses in a system's hardware or software. Instead of depending on social engineering tactics to execute, they exploit technical vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access and perform other malicious activities such as executing arbitrary code inside a system.
How to detect malware
Users might be able to detect malware if they observe unusual activity. Common malware symptoms include the following:
- A sudden loss of disk space.
- Unusually slow computer or device speeds.
- A blue screen of death.
- Repeated system crashes or freezes.
- Changed browser settings and redirects.
- Increase in unwanted internet activity.
- Disabled security features in firewalls and antivirus software.
- Changes in file names and sizes.
- Pop-up advertisements.
- Programs opening and closing by themselves.
Antivirus and antimalware software can be installed on a device to detect and remove malware. These tools can provide real-time protection through constant scanning or detect and remove malware by executing routine system scans.
This article is part of
What is data security? The ultimate guide
Windows Defender, for example, is Microsoft's antimalware software included in various Windows OSes under the Windows Defender Security Center. Windows Defender protects against threats such as spyware, adware and viruses. Users can set automatic Quick and Full scans, as well as set low, medium, high and severe priority alerts.
How to remove malware and which tools to use
Many security software products are designed to detect and prevent malware, as well as remove it from infected systems. Running antimalware tools is the best option to remove malware.
According to networking expert Andrew Froehlich, Westgate Networks, the following is a sampling of enterprise-grade antimalware tools that include ransomware protection. These tools, which are listed in alphabetical order, are designed for organizations of all sizes:
- Bitdefender GravityZone. This tool offers an intuitive risk analysis engine that protects against malware attacks and also ensures adherence to corporate protocols, including patch management, disk encryption and device control.
- Cisco Secure Endpoint. Formerly known as Cisco AMP for Endpoints, it uses advanced threat detection techniques, including machine learning and behavioral analysis, to identify and block malware, ransomware and other malicious activities in real time.
- ESET Protect. ESET Protect provides endpoint protection against various threats, such as malware, ransomware and viruses.
- F-Secure Total. F-Secure Total is a comprehensive internet security suite that provides internet security, virtual private network (VPN) and password management in one subscription.
- Kaspersky Premium. This tool provides endpoint protection, automated threat removal and VPN services.
- Sophos Intercept X. Sophos X uses a combination of signature-based detection, machine learning and behavioral analysis to proactively identify and block malware, ransomware and other cyber threats before they can cause harm to endpoints.
- Symantec Enterprise Cloud. This tool provides data-centric hybrid security for large and complex organizations.
- ThreatDown Endpoint Protection. Formerly Malwarebytes Endpoint Protection, this tool offers a layered protection approach with simplified security management and scalability options for IT organizations.
- Trend Micro Cloud One. Trend Micro Cloud One is designed to offer protection for various workloads, including physical servers, virtual, cloud and containers.
- Webroot Managed Detection and Response. Webroot MDR is designed to provide proactive defense against evolving threats. It achieves this through continuous monitoring and by using expert analysis and actionable workflows.
There could be instances when an antimalware tool might not completely remove the malware infection. It's best to manually inspect the system files, folders, registry entries and startup items in those cases. However, manually removing infected files should be cautiously attempted to avoid accidental deletion of critical files. For severely infected devices, users can also consider restoring the system through data recovery software to retrieve lost or corrupted files from a backup copy created before the infection occurred.
How to prevent malware infections
There are several ways users can prevent malware, including the following:
Use antimalware software
As previously mentioned, installing antimalware software is crucial when protecting PCs and network devices from malware infections.
Exercise caution with email
Users can prevent malware by practicing safe behavior on their computers or other personal devices. This includes not opening email attachments from strange addresses that might contain malware disguised as a legitimate attachment -- such emails might even claim to be from legitimate companies but have unofficial email domains.
Use a firewall
Users should enable or configure a firewall on their network router to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic. Firewalls can help block unauthorized access and protect against the spread of malware.
Update antimalware regularly
Users should update their antimalware software regularly, as hackers continually adapt and develop new techniques to breach security software. Security software vendors respond by releasing updates that patch those vulnerabilities. If users neglect to update their software, they might miss a patch that leaves them vulnerable to a preventable exploit.
Avoid pop-ups
Users should always avoid clicking on pop-ups even if they look legitimate. Clicking on a pop-up advertisement can lead to unintentional downloads of malware or redirect users to malicious websites where malware could be automatically downloaded or installed without their consent. Additionally, web browser settings should be set to block both pop-ups and adware.
Use strong passwords
Strong and unique passwords that aren't easily guessable should be created for all accounts and devices. Additionally, multifactor authentication should be enabled wherever possible, as it requires multiple levels of authentication from a user before they can log in or access a system.
Avoid dubious websites
Users should be selective when browsing online and avoid websites that seem risky, such as those that offer screensavers for download.
Perform regular backups
Users should do regular offsite or offline backups to ensure the most recent version of data can't be breached but is available to be recovered after a malware attack.

How to prevent malware in the enterprise
In enterprise settings, networks are larger than home networks, and more is at stake financially. There are proactive steps companies should take to enforce malware protection and provide endpoint security.
Outward-facing precautions for enterprises include the following:
- Setting up dual approval for business-to-business transactions.
- Setting up second-channel verification for business-to-consumer transactions.
Business-facing, internal precautions for enterprises include the following:
- Using offline malware and threat detection to catch malicious software before it spreads.
- Configuring allowlist security policies whenever possible.
- Setting up strong web browser-level security.
Additionally, companies should provide security awareness training to all employees. Malware infections are often triggered by users unknowingly downloading counterfeit software or falling prey to phishing scams. Security awareness training equips users to recognize social engineering tactics, identify malicious websites and avoid downloading fake apps.
How does malware affect Macs?
Malware can affect Macs as well as Windows devices. Historically, Windows devices are considered to be a larger target for malware than Macs, in part because users can download applications for macOS through the App Store.
In its "Malwarebytes Lab 2020 State of Malware Report," Malwarebytes reported that for the first time ever, malware on Macs outpaced malware on PCs. This is due in part to the popularity of Apple devices, drawing more attention from hackers.
Mac malware can take various forms, including viruses, trojans, adware, spyware and ransomware. A few real-world examples of Mac malware include the following:
- XLoader, 2024. XLoader is a malware-as-a-service available on the darknet for around $49, capable of harvesting logins from browsers, collecting screenshots, logging keystrokes and downloading and executing malicious files.
- Exploit HVNC, August 2023. Hackers can use this malware to remotely gain control of an insecure Mac. This malware is being sold on a Russian cybercrime forum on the dark web known as Exploit.
- Alchimist and Insekt malware, 2022. Alchimist was discovered alongside Mac dropper malware designed to exploit a 2021 vulnerability. Additionally, there was an increase in the number of users reporting fake alert browser pop-ups in October 2022.
- Mac Auto Fixer, August 2018. This PUP was created to infiltrate systems through bundled software packages.
- KeRanger, March 2016. KeRanger was the first ransomware attack to target Mac users, encrypting users' confidential information and demanding payment for recovery.
How does malware affect mobile devices?
Malware can be found on mobile phones and can provide access to a device's components, such as the camera, microphone, GPS or accelerometer. With the rise of mobile device usage and companies letting employees access corporate networks via personal devices, mobile malware is spreading rapidly. For example, malware can be contracted on a mobile device if a user downloads an unofficial application or clicks on a malicious link from an email or text message. A mobile device can also be infected through a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi connection.
Mobile malware is more commonly found on devices that run the Android OS rather than iOS. Malware on Android devices is usually downloaded through applications. Signs that an Android device is infected with malware include unusual increases in data usage, a quickly dissipating battery charge or calls, texts and emails being sent to the device contacts without the user's initial knowledge. Similarly, if a user receives a message from a recognized contact that seems suspicious, it might be from a type of mobile malware that spreads between devices.
Apple iOS devices are rarely infected with malware because Apple vets the applications sold in the App Store. However, it's still possible for an iOS device to be infected with malicious code by opening an unknown link found in an email or text message. iOS devices are also more vulnerable if jailbroken.
History of malware
The term malware was first used by computer scientist and security researcher Yisrael Radai in 1990. However, malware existed long before this.
One of the first known examples of malware was the Creeper virus in 1971, which was created as an experiment by Raytheon BBN (formerly BBN Technologies) engineer Robert Thomas. Creeper was designed to infect mainframes on ARPANET. While the program didn't alter functions or steal or delete data, it moved from one mainframe to another without permission while displaying a teletype message that read, "I'm the creeper: Catch me if you can." Creeper was later altered by computer scientist Ray Tomlinson, who added the ability to self-replicate to the virus and created the first known computer worm.
The concept of malware took root in the technology industry, and examples of viruses and worms began to appear on Apple and IBM PCs in the early 1980s before becoming popularized following the introduction of the World Wide Web and the commercial internet in the 1990s. Since then, malware -- and the security strategies to prevent it -- have only grown more complex.
Similar programs to malware
There are other types of programs that share common traits with malware but are distinctly different.
Common examples of viruses that are similar to malware but aren't technically classified as malware, include the following:
Grayware
Grayware is a category of PUP applications that trick users into installing them on their systems -- such as browser toolbars -- but don't execute any malicious functions once they've been installed. However, there are cases where a PUP might contain spyware-like functionality or other hidden malicious features, in which case it would be classified as malware.
Browser hijackers
Browser hijackers are programs that can perform various actions without user consent. For example, they can change web browser settings, redirect users to unwanted websites and display intrusive ads. While they aren't classified as malware, they can certainly invade a user's privacy and disrupt their browsing experience.
Tracking cookies
Websites often track a user's browsing habits and preferences by placing little text files known as tracking cookies on their devices. They can cause privacy issues and be exploited for data collection and targeted advertising. Google will start decommissioning tracking cookies for its Chrome browser by the end of 2024, with a planned completion date of 2025.
RATs
RATs are legitimate tools that are often used for remote administration and troubleshooting purposes. However, sometimes threat actors can abuse them to gain unauthorized system access and cause privacy issues for users.
Despite belonging to the broader category of malware, ransomware comes with unique traits. Learn to identify the distinct characteristics of ransomware by examining the key differences between malware and ransomware.






