How to collect customer feedback
Businesses that collect customer feedback are more likely to create positive experiences and address issues. Analyzing feedback can show deeper insights into customer sentiment.
For exceptional customer experiences, organizations must understand what customers want and need.
Equally important, organizations should ensure customers feel like they listen to them and aim to make them feel special with personalized service. Collecting customer feedback can help brands improve their customer experience strategies and lead to better personalization.
What is customer feedback?
Customer feedback comprises the ideas, opinions and suggestions that customers have about an organization and its products or services. Feedback can be reactive -- meaning it follows a service or support interaction -- or proactive, meaning it was not driven around an interaction. It can also be positive, negative or neutral, depending on a customer's experience with the brand.
Why is customer feedback important?
Customer feedback is invaluable, as it provides insights that organizations can use to improve their business, including in customer-facing interactions, the agent experience, product development and so on. It also helps brands better understand customers, so they can more easily create personalized experiences.
Types of customer feedback
Customer feedback can be qualitative or quantitative. Those break down as follows:
- Qualitative feedback comes from customers' open-ended comments. Organizations can collect it in focus groups, surveys, online reviews and social media posts.
- Quantitative feedback comes through numerical ratings, such as one to five stars.
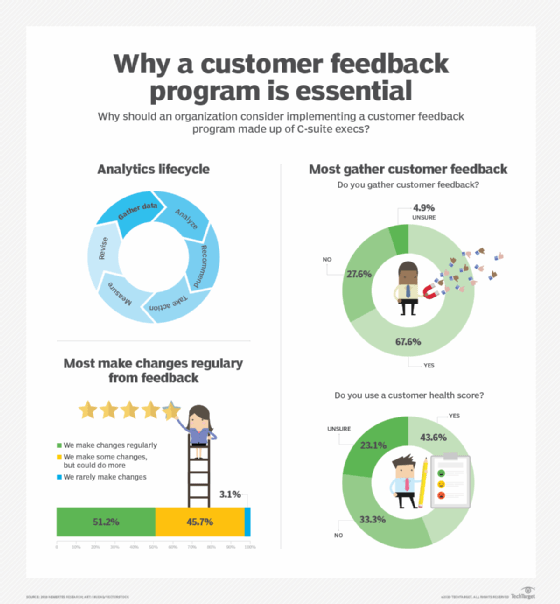
In Metrigy's global "Customer Insights and Analytics: 2023-24" study, 24.5% of 579 companies surveyed gather quantitative ratings from customers, 28.2% gather qualitative comments and 43.2% do both.
What is a customer feedback loop?
A customer feedback loop comprises the request for information, data analysis, actions taken based on the analysis and letting customers who shared feedback know what changes resulted from their input. This final part shows customers that organizations appreciate their feedback and that it can make a difference.
Feedback loops are continuous. Organizations should always assess customer feedback and, based on insights gathered from that information, adapt as necessary.
5 methods to collect customer feedback
Collecting customer feedback can happen at any touchpoint and is often simple and straightforward. However, some methods may need to incentivize customers to get results.
1. Use qualitative and quantitative feedback. Organizations can gather feedback from interactive, responsive and implicit mechanisms. Those break down as follows:
- Interactive feedback comes from one-to-one interviews either in person or over video, focus groups and live chats. This option lets customers share their opinions and ideas about set topics, such as new products or services, changes in pricing or new interaction channels.
- Responsive feedback means customers share how they feel about customer service interactions through a survey, SMS polls, online reviews, social media comments or ratings.
- Implicit feedback requires organizations to analyze statistics, such as website visits and call data, and apply advanced technologies like natural language processing and sentiment analysis to gain insights from recordings. This analysis can uncover trends and get ahead of issues before they escalate.
2. Request feedback immediately following an interaction. If organizations deliver a survey or feedback request form in the moment, customers can more accurately convey their sentiment. They can better understand and relay their feelings at the time of the interaction rather than if the brand requests feedback later. Additionally, gathering feedback right after an interaction correlates to increased business success, according to Metrigy.
3. Add surveys at various touchpoints. This strategy can maximize the potential for gathering feedback, as customers can contact a business in any way they choose. Survey requests can be at the bottom of a receipt, through an SMS poll or at the end of a call.
4. Offer a reward for completing surveys. Even a small incentive can trigger responses from customers. Rewards can include a discount, a free gift or an exclusive promotion.
5. Request feedback from everyone -- not a select few. Organizations shouldn't let agents select who receives a post-interaction survey, but should send them to everyone or to a random selection of customers. If agents self-select customers, they may choose people who had positive experiences. This can lead to an inaccurate reflection of an agent's performance and overall customer satisfaction.
How to use collected data
Using data from customer feedback requires organizations to analyze it and identify what actions to take based on the intelligence gained. Some examples include the following:
- Share feedback with service and support agents so they understand what they do well, or not so well, during customer interactions.
- Recognize, reward or promote agents, or identify new coaching opportunities.
- Determine which interaction channels are most successful and which customer-facing technologies to use.
- Adjust sales and marketing strategies based on trends discovered.
- When a customer leaves a positive rating, such as a five out of five stars, ask them to share an online review.
- If a customer expresses dissatisfaction or other negative sentiment during an interaction, use AI assistance to offer a discount or credit in real time, or follow up later over email, text or a phone call.
- Integrate customer feedback into marketing automation tools.







