What is 3PL (third-party logistics)?
A 3PL (third-party logistics) provider offers outsourced logistics services, which encompass anything that involves management of one or more facets of procurement and fulfillment activities. In business, 3PL has a broad meaning that applies to any service contract that involves storing or shipping items.
A 3PL service might be a single provider, such as transportation management or warehouse space, or it can be a systemwide bundle of services capable of handling supply chain management.
How third-party logistics work
Here is an example of how 3PL arrangements operate in e-commerce: A book publisher hires writers, editors and graphic designers to produce publications, but it might not want to handle the consumer ordering fulfillment process or transportation of book shipments.
Instead, the book publisher uses a fulfillment center to process its online customer orders and hires a trucking carrier to haul its freight. The fulfillment center and carrier both act as 3PL providers. It's possible for a single 3PL provider to fulfill and ship book orders, too.
By contracting with a 3PL company, the book company uses supply and distribution services only when needed, thus controlling shipping costs more effectively while focusing on its core competency of producing books.
The growth of 3PLs
Aspects of 3PLs probably date back hundreds, if not thousands, of years. The Council of Supply Chain Management Professionals traces the actual 3PL abbreviation to five decades ago. "The term 3PL was first used in the early 1970s to identify intermodal marketing companies ... in transportation contracts," the council wrote in a glossary. "Up to that point, contracts for transportation had featured only two parties, the shipper and the carrier."
The Motor Carrier Act of 1980 deregulated the trucking industry, which reduced trucking rates and increased the amount of competition, all of which fed into 3PL concepts. The term 3PL gained traction among consultants and during conferences in the 1990s, likely tied to evolving technology, including the rise of the internet. Later, the Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act of 2008 legally defined 3PL: "The term third-party logistics provider means a person who solely receives, holds or otherwise transports a consumer product in the ordinary course of business but who does not take title to the product."
The growth in online sales and increasing consumer demand for faster delivery and lower prices have spiked demand for 3PL services. 3PLs have also bloomed thanks to tracking technology, such as radio frequency identification (RFID) and global positioning system (GPS), both of which offer extended supply chain visibility. Meanwhile, internet of things (IoT) technology has improved tracking metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) for trucking and other carriers.
According to a frequently cited 2017 report from Armstrong & Associates, a supply chain consultancy, 90% of domestic Fortune 500 companies rely on 3PL providers to handle logistics, compared to the 46% Armstrong reported in 2001.
Does your organization need a 3PL provider?
There are many scenarios in which an organization would express interest in a partnership with a 3PL provider, including the following:
- Costs increase over time. Inefficient management of warehouses or technology can drive up costs, hurting an organization's bottom line. In this scenario, 3PL service providers that specialize in those tasks will handle them better.
- Customer service complaints increase. In certain circumstances, such as spikes in demand for certain goods, an organization's staff might become overwhelmed, leading to more customer complaints. Service providers with track records of ensuring good customer satisfaction are a good alternative.
- New opportunities for expansion. When an organization identifies opportunities to expand its reach into new markets, 3PL providers will help expand its logistics operations, especially if it is geographically dispersed.
- Inventory management hinders productivity. This is especially true of smaller businesses that don't have the budgets for advanced software systems, such as warehouse management software. In any case, however, managing inventory levels requires time and effort by an organization's staff. The 3PL providers that specialize in this will not only manage inventory, but also send the organization real-time updates on inventory levels.
- Migrating to new facilities or regions. A small e-commerce fulfillment center, for example, might start off on a local level, but once it expands and order volumes become too large for a small warehouse, 3PL providers will help migrate to bigger facilities.
- Budgets allow for new 3PL partnerships. Even when there isn't an inherent need for a 3PL provider, paying for a partnership will nonetheless improve logistics operations if an organization can fit one within its budget.
How to select a 3PL provider
There are multiple criteria for assessing the best fit for a 3PL partner. Business leaders should ask the following questions when looking to partner with a service provider:
- Is the provider relevant to a specific industry?
- Does the provider value security and compliance?
- Is there a proven customer service track record?
- Is the pricing structure affordable?
- Will the provider's technology integrate easily?
An organization seeking a long-term partnership with a provider will examine more than just affordable pricing schemes. A good fit will prioritize customer experience, abide by laws and regulations in the jurisdictions where it operates and offer services compatible with the organization's existing technology. Additionally, providers could have certifications and credentials to prove they meet these criteria.
3PL providers
Major 3PL providers are spread across the globe. A list of key providers in the global 3PL service market includes the following companies: Ceva Logistics, C.H. Robinson, DB Schenker, DHL Group, FedEx Corporation, JB Hunt, Kuehne + Nagel, Nippon Express, Panalpina and UPS.
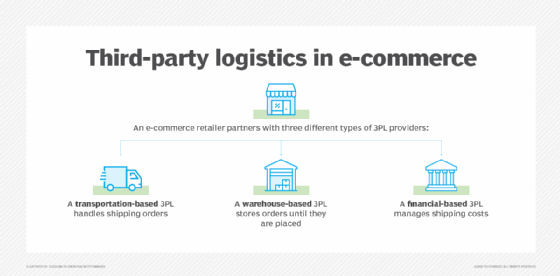
3PL service providers are categorized according to their specific functions and the areas of logistics they specialize in. There are three types of 3PL providers:
- Transportation-based. These transportation services specialize in moving goods between locations. These 3PL providers include parcel carriers, such as FedEx and UPS, as well as other transportation modes including air freight, rail and ocean.
- Warehouse-based. These providers typically process, fulfill and ship orders. Before an order is placed, a 3PL warehouse receives inventory, such as pallets, from the company's supplier or manufacturer and stores it. DHL Supply Chain is an example of a warehouse-based 3PL provider.
- Financial and information-based. As opposed to dealing with physical aspects of logistics, these providers specialize in areas such as freight payment and inventory management using advanced management software. C.H. Robinson is an example of a financial-based 3PL.
The benefits of 3PL
Deciding to partner with a 3PL service provider brings various benefits to an organization, including the following:
- Cost savings. It is cost-effective to entrust a 3PL service to handle logistics operations, such as packaging, warehousing, order fulfillment and distribution. For example, an organization won't have to manage its own warehouse or purchase warehouse management systems to streamline and monitor supply chain operations.
- Scalability of operations. A business using 3PL services can scale its operations more easily. For example, if the publishing company in the previous example suddenly needs to ship more copies of a popular title, a fulfillment center will have an easier time meeting that demand than if the publisher itself had to ship additional copies of the book.
- Improved performance. A 3PL provider's sole focus is to assist with tasks such as managing and transporting orders so a company will more easily meet customers' needs without disruptions.
- Risk reduction. In the event of risks to supply chains, such as disruptions or bottlenecks, the 3PL provider is responsible for mitigating them or finding alternative ways to complete tasks.
- Access to expertise. A 3PL provider should be able to provide expertise to a company in addition to assisting with logistics operations.
- Reverse logistics. In reverse logistics, a company receives goods returned from consumers to be sent back to manufacturers for servicing, refurbishing or recycling. A 3PL provider might have relationships with supply chain partners and expertise in product returns, among other ways to assist in this process.
Challenges of 3PL
Despite compelling benefits, there are also challenges associated with 3PL, including the following:
- Limited visibility. Supply chain visibility becomes an issue when a 3PL provider oversees many of an organization's operations and that organization might not understand how all aspects of those operations are conducted.
- Supply chain disruptions. While 3PL providers are responsible for supply chain risk management, other disruptions such as drops in customer interest in certain products, are out of their control. On the other hand, if demand for product spikes and a 3PL isn't prepared to meet this increase in demand, disruptions occur as well.
- Changing compliance. Since a 3PL provider might do business in various locations, it must be mindful of the laws and regulations in those areas, as well as any updates to them since regulations constantly evolve.
3PL vs. 4PL
The term 4PL (fourth-party logistics) often pops up in discussions about 3PL, but they have key differences. In brief, when 3PL providers outsource any of their own contracted services, they become a 4PL provider. In the example of a book publisher, if the fulfillment center subcontracts out its shrink-wrapping and freight weighing to other companies, then the center acts as a 4PL provider.
Some observers view 3PL providers as managers of a particular outsourced service, while 4PL providers oversee services across an entire supply chain.
Another way to look at a 4PL service is as a provider that acts as a client company's single point of contact in the supply chain; the 4PL provider selects and manages various 3PL activities. 4PL providers are also known as lead logistics providers.
3PL vs. freight forwarding
Freight forwarding and 3PL might sound similar, but there are noticeable differences.
Freight forwarders do not actually ship materials, and instead function as a liaison between a client company and shipping firms. The freight forwarder negotiates prices, determines the best modes of transportation, establishes economical shipping routes and works on other logistics concerns. As noted earlier, 3PL providers handle a broader range of services compared to forwarders.
Also, a 3PL provider takes responsibility for the goods or services being shipped, while a freight forwarder likely will not, given it is just an intermediary.
Once a company establishes one or more 3PL partnerships, that company has the power to determine the success and business value of those partnerships. Learn about multiple KPIs that measure 3PL partnership success.





