What is a reseller?
In the information technology (IT) ecosystem, a reseller is a company that purchases products or services from manufacturers, vendors or distributors and then sells them to customers. These transactions can be business-to-business (B2B) or business-to-consumer (B2C). Resellers play a key role in the indirect sales channel, helping to streamline procurement, offer better pricing and deliver added services for customers.
Purpose of resellers in the IT channel
Resellers serve as intermediaries in the technology supply chain, helping bridge the gap between product creators and end users. Their main objectives include the following:
- Simplifying procurement. Businesses can source multiple IT solutions -- hardware, software, cloud services, etc. -- from a single reseller instead of managing multiple vendor relationships.
- Fulfilling orders efficiently. Resellers typically handle product sourcing, order processing, billing and delivery, which removes logistical burdens from the buyer.
- Offering competitive pricing. Through vendor partnerships and bulk purchasing, resellers can offer bundled deals or better prices than those available when buying directly from original equipment manufacturers, or OEMs.
Many companies, especially small to midsize businesses (SMBs), prefer resellers for convenience, consultative selling and local presence.
How resellers operate
Resellers usually work within partner programs offered by vendors or distributors. These programs provide the following:
- Discounted pricing. Vendors offer tiered discounts (10% to 50% or more) depending on the reseller's purchase volume, specialization or partnership level.
- Deal registration and incentives. Resellers can protect sales opportunities via deal registration and earn rebates or performance-based incentives.
- Marketing and technical support. Vendors may supply resellers with co-branded marketing materials, training and sales support.
Resellers make a profit by buying at a discount and selling at a markup, while managing fulfillment and customer support responsibilities.
Common types of resellers
1. Value-added reseller (VAR)
A VAR is a reseller that adds services such as installation, configuration, training, support or consulting to the core product. For example:
- An IT VAR might bundle networking equipment with on-site setup and integration.
- A software VAR might include licensing, implementation and asset management services.
VARs are common in industries where custom solutions are needed, such as enterprise IT, cybersecurity and healthcare tech.
2. Direct market reseller (DMR)
DMRs sell IT products directly to customers online or via telephone without operating brick-and-mortar stores. This model is popular for high-volume, low-margin consumer and business tech. Examples include: CDW and Newegg.
DMRs often compete on price, product range and fast delivery.
3. Web hosting and infrastructure resellers
In the hosting sector, resellers purchase server space or services from providers and resell them to smaller clients. A web hosting reseller may rebrand services from a larger hosting firm or data center operator.
4. Virtual internet service providers (VISPs)
These are resellers that offer internet services under their own brand while using the infrastructure of a larger ISP. VISPs are particularly common in underserved or niche markets.
Common industries that rely on resellers
Resellers are integral to numerous segments of the IT industry:
- Enterprise software. Large software vendors like Microsoft, Adobe and IBM rely heavily on reseller networks to reach businesses of all sizes.
- Cybersecurity. Companies like Fortinet, Sophos and Palo Alto Networks use VARs to implement and support complex cybersecurity solutions.
- Cloud services. Resellers often partner with cloud providers (e.g., AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure) to help clients onboard and manage services.
- IT hardware. Servers, laptops, printers, networking gear and storage devices are commonly sold through resellers.
- Telecommunications and ISPs. Many small ISPs rely on resellers to reach end users, particularly in regional or rural markets.
Reseller vs. distributor vs. dealer
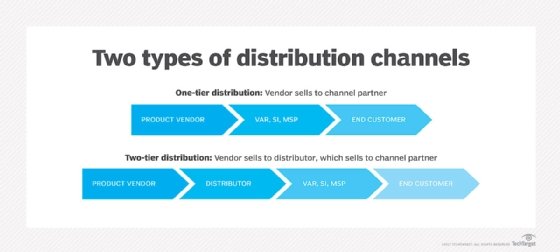
Understanding the distinctions between different channel partner types is critical. A reseller buys from vendors or distributors and sells to end customers, and might add services. A distributor buys in large quantities from manufacturers and sells to resellers or dealers. A dealer, often a small retail-oriented entity, sells directly to consumers. Resellers often work with distributors to gain access to a broader inventory and better pricing.
Trends and challenges in the reseller model
The reseller model is evolving rapidly in response to market demands:
Trends
- Shift to recurring revenue models. Resellers are increasingly selling subscriptions (SaaS, IaaS) instead of one-time purchases.
- Vertical specialization. Many are focusing on specific industries (e.g., healthcare, education) to provide tailored solutions.
- Partner ecosystems. Resellers are forming alliances with other service providers to create bundled offerings.
Challenges
- Margin pressure. Cloud and direct-to-consumer sales channels have eroded traditional hardware resale margins.
- Vendor competition. Some vendors now sell directly to customers, bypassing resellers and increasing channel conflict.
- Technical complexity. Clients expect strategic guidance, forcing resellers to invest in certifications, engineering talent and managed services.
To remain competitive, many resellers are transforming into managed service providers (MSPs) or consultative solution providers.
As businesses demand end-to-end solutions and expert guidance, modern resellers are evolving into value-driven advisors and service providers. Whether through traditional product resale, added services or recurring cloud models, resellers continue to be a crucial part of the IT channel -- connecting vendors with customers and ensuring technology is delivered effectively, securely and strategically.




