file system
What is a file system?
In computing, a file system -- sometimes written filesystem -- is a logical and physical system for organizing, managing and accessing the files and directories on a device's solid-state drive (SSD), hard-disk drive (HDD) or other media. Without a file system, the operating system (OS) would see only large chunks of data without any way to distinguish one file from the next. As data capacities increase, the efficient organization and accessibility of individual files becomes even more important in data storage.
Digital file systems are named for and modeled after the paper-based filing systems used to store and retrieve documents. Despite their shared roots, however, file systems can differ significantly between operating systems such as Microsoft Windows, macOS or Linux. On the other hand, an OS can support multiple file systems despite their differences. In some cases, a file system can also be used across multiple platforms. Some file systems are designed for specific applications, including distributed file systems, disk-based file systems and special-purpose file systems.
How file systems work
A file system stores and organizes data. It can be thought of as a type of index for all the data contained in a storage device. In addition to SSDs and HDDs, file systems are used for optical disks, flash drives and magnetic tape.
File systems specify conventions for naming files, including the maximum number of characters in a name, which characters can be used and -- in some systems -- how long the file name extension can be. In many file systems, file names are not case sensitive.
Along with a file's content data, a file system maintains metadata about the files along with other information. The metadata might include details such as the file size, creation date or location in the directory.
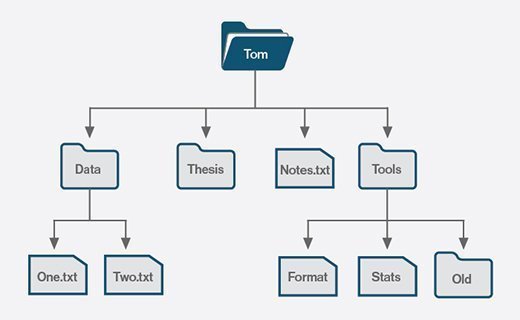
Most file systems organize files in a directory hierarchy, with a file's location described by its path within the directory structure. The directories -- folders in Windows -- are organized into an inverted hierarchical tree structure, with the root directory at the top. Each file is placed in a directory or subdirectory at the desired location within the tree structure.
Before files and directories can be defined on a storage medium, one or more partitions must first be created. A partition is a region of storage that the OS manages separately from other partitions, much like managing individual drives. Each partition can be formatted with a different file system to provide greater flexibility.
Separate partitions help to isolate files and operations from each other, which can benefit performance, security and maintenance. For example, a computer's SSD might contain three partitions: one for the OS files, one for the user files and one for the system's recovery files. If the file system on one partition gets corrupted, the data on a different partition should be safe.
File system architecture
File systems handle both the physical and logical operations associated with managing files. Although they take different approaches to storing file data, they commonly separate metadata from the file's content data. They also store a small amount of other data types, which are used for maintaining the file system and facilitating file access.
A file system divides a partition into blocks, and their size depends on the file system. Most of the blocks are used for the files' content data. The remaining blocks are divided between the files' metadata and the file system's management data. Figure 2 provides a conceptual overview how a file system in a Unix-like environment might organize the data across the individual blocks. In this case, the metadata is stored in index nodes (inodes). An inode is an indexable data structure that maintains details about a file or directory.
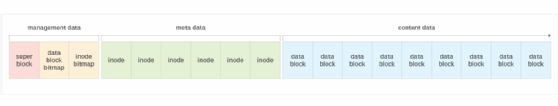
The management data occupies the first few blocks, followed by the inode metadata and then the content data blocks, which consume most of the storage. Here's a breakdown of the different block types:
- Super block. The block contains information about the file system itself, acting as its own metadata repository. For example, the super block might include details about the file system type, total number of blocks, number of inodes or other components.
- Data block bitmap. The block contains a simple bitmap that indicates which data blocks are used or unused. A value of 1 indicates the block is used, and a value of 0 indicates it is unused.
- Inode bitmap. The block contains a simple bitmap that indicates which inodes are used or unused. A value of 1 indicates the inode is used, and a value of 0 indicates it is unused.
- Inodes. The file system maintains an inode for each file and directory. The inode is identified by a unique number and includes the metadata for the associated file or directory. It also includes the address of the data blocks that contain the file's content. In this way, the inode can be used to quickly locate the file.
- Content data blocks. All file content is stored in the data blocks. These blocks represent most of the occupied blocks of the file. The figure shows only a portion of the content data blocks.
File systems use metadata to store and retrieve files and to provide users with information about their files. File systems do not necessarily track the same types of metadata, but they usually maintain the following information:
- Date and time created.
- Date and time modified.
- Data and time last accessed.
- File owner.
- Access permissions.
- File size, including size on disk.
- Attributes such as read-only or hidden.
- Location in the directory hierarchy.
Users can typically access a file's metadata through their systems' interface. In Windows, for example, they can right-click a file and click Properties in the context menu. The same is true in macOS, except users click Get Info instead.
File system access
File systems can restrict read and write access to a particular user or group of users. Along with controlling who can modify or read files, restricting access controls and limits data modification.
File and directory permissions can be used to control who has access to specific resources and what level of access they have. This approach is useful in preventing access by internal users but is not as effective against outside intruders.
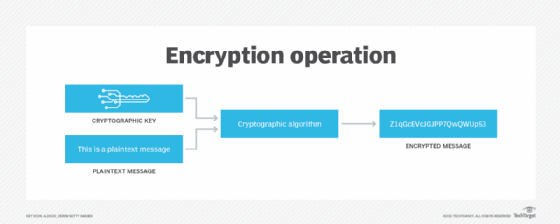
Encrypting files can also prevent user access, but it is focused more on protecting systems from outside attacks. An encryption key is applied to unencrypted text to encrypt it. The key can also be used to decrypt the encrypted text. Only users who have the key can decrypt the file. With encryption, the file system does not need to know the encryption key to manage the data effectively.
Types of file systems
Most operating systems support multiple types of file systems, all with varying physical and logical structures, as well as capabilities. Some file systems can be used across multiple platforms. The three most common PC operating systems are Microsoft Windows, Apple macOS and Linux. The most popular mobile OSes include Apple iOS and Google Android. The primary file systems used on these platforms include the following.
File allocation table (FAT)
FAT is a simple and reliable file system that at one time was used extensively by earlier versions of Windows operating systems. Designed in 1977 for floppy disks, the file system was later adapted for hard disks. Originally, FAT was an 8-bit system, but it was later updated to FAT12 (12-bit), then FAT16 (16-bit) and finally FAT32 (32-bit), which is the primary version still in use. While efficient and compatible with most current OSes, FAT cannot match the performance and scalability of more modern file systems.
Extended File Allocation Table (exFAT)
The exFAT file system is a successor to FAT32. It retains much of the simplicity of FAT as well as its ease of implementation. However, exFAT is a 64-bit file system, so it can support larger capacity storage devices as well as applications that rely on large files. The file system also incorporates extensibility into its design, making it easier to adapt to changes in storage and its usage.
New Technology File System (NTFS)
Also known as NT file system, NTFS has been the default Windows file system since Windows NT 3.1. NTFS offers several improvements over FAT file systems, including better performance, metadata support and resource utilization. NTFS is also supported in the Linux OS through a free, open-source NTFS driver. In addition, macOS includes read-only support for NTFS.
Resilient File System (ReFS)
ReFS is a relatively new Microsoft file system that has been available on Windows Server since 2012. The file system is also available on Windows 10 Pro for Workstations, although it is not available on any nondevelopment versions of Windows 11. ReFS was developed to address some of the limitations of NTFS, especially when it comes to scalability and performance. However, ReFS does not support several NTFS features nor can Windows boot from a ReFS volume. It also consumes more system resources than NTFS.
Extended filesystem (ext)
Implemented in 1992, this file system was designed specifically for Linux and is still widely used on Linux systems. The current version, ext4, builds on ext3, which added journaling capabilities to reduce data corruption. The ext4 version provides better performance and reliability while supporting greater scalability. It is the default file system for multiple Linux distributions, including Ubuntu and Debian, and it is the primary files system used on Android devices.
B-tree filesystem (Btrfs)
Also referred to as butter FS or better FS, Btrfs combines a file system and file manager into a single solution for Linux systems. The solution offers advanced fault-tolerance and self-healing capabilities, resulting in greater reliability. It is also known for its efficiency and ease of administration. Btrfs has been making steady inroads into the Linux environment and is now the default file system in Fedora Workstation.
Global File System (GFS)
GFS is a Linux file system as well as a shared disk file system. GFS offers direct access to shared block storage and can be used as a local file system. GFS2 is an updated version with features not included in the original GFS, such as an updated metadata system. Under the terms of the GNU General Public License, both the GFS and GFS2 file systems are available as free software.
Hierarchical file system (HFS)
Also referred to as Mac OS Standard, HFS was developed for use with Mac operating systems. HFS was originally introduced in 1985 for floppy and hard disks, replacing the first Macintosh file system. It can also be used on CD-ROMs. HFS was eventually succeeded by Mac OS Extended, which has since given way to the Apple File System (APFS).
Apple File System
APFS has been the default file system on Mac computers since macOS 10.13. It is also used on iOS, iPadOS, tvOS and watchOS devices. APFS brought with it many important features, including snapshots, strong encryption, space sharing and fast directory sizing. The file system has also been optimized for the flash SSDs used in Mac computers, although it still supports traditional HDDs as well as external, direct-attached storage. As of macOS 10.13, APFS can be used for both bootable volumes and data volumes. The file system also supports a case-sensitive mode.
Universal Disk Format (UDF)
UDF is a vendor-neutral file system used for optical media. UDF replaces the ISO 9660 file system and is the official file system for DVD video and audio as chosen by the DVD Forum. The file system is also used for Blu-ray discs.
File system vs. database management system (DBMS)
Like a file system, a DBMS efficiently stores data that can be updated and retrieved. The two are not interchangeable, however. While a file system stores unstructured, often unrelated files, a DBMS is used to store and manage structured data that is usually related.
A DBMS creates and defines the restraints for a database. A file system allows access to single files and addresses each file individually. Because of this, functions such as redundancy are performed on an individual level, not by the file system itself. This makes a file system a much less consistent form of data storage than a DBMS, which maintains a single, highly controlled repository of data.
The centralized structure of a DBMS allows for easier data sharing than a file system and prevents anomalies that can occur when changes are made to different files in a file system.
Although files systems include file-level protections, a DBMS provides more robust security. Security in a file system is determined by the OS, and it can be difficult to maintain over time as files are accessed and authorization is granted to users.
A DBMS keeps security constraints high, relying on password protection, encryption and limited authorization. However, greater security means more obstacles when retrieving data. When it comes to simple-to-use file storage and retrieval, a file system is often preferred.
File systems definition evolves
While previously referring to physical files, the term file system has been used to refer to digital files since early 1961. By 1964, it had entered general use to refer to computerized file systems.
The term file system can also refer to the part of an OS or add-on program that supports a file system. Examples of such add-on file systems include the Network File System (NFS) and the Andrew File System.
In addition, the term has evolved to refer to the hardware used for non-volatile storage, the software application that controls the hardware and the architecture of both the hardware and software.
Learn the differences between FAT16, FAT32, NTFS and ReFS Windows file systems, each with its own unique capabilities and use cases. Compare block vs. file vs. object storage differences and uses. Find out how AWS implements its file services -- Amazon FSx and Amazon EFS -- based on Windows Server Message Block and NFS.







