What is interactive voice response (IVR)?
Interactive voice response (IVR) is an automated telephony system that interacts with callers, gathers information and routes calls to the appropriate recipients. An IVR system accepts a combination of voice input and touch-tone keypad selections and then provides the appropriate responses in the form of voice, fax, callback, email and other contact methods.
IVR systems can consist of telephony equipment, software applications, a database and a supporting infrastructure. An organization can run an in-house IVR system by purchasing the required software and hardware or opt to use an IVR hosting service that charges a monthly fee.
How interactive voice response works
An IVR application provides prerecorded voice responses for appropriate situations, keypad signal logic, access to relevant data and, potentially, the ability to record voice input for later use. Using computer telephony integration, IVR systems can hand off a call to a human being who can view data related to the caller on a display.
IVR systems also use dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) signals as a line of communication between a phone and a computer. The computer uses a telephony board or card to understand DTMF signals.
IVR software enables an organization to use prerecorded greetings or menu options that customers can access through a phone keypad. Advanced IVR systems might also include speech recognition software to let a customer communicate with a computer.
IVR systems are based on the programming language VoiceXML, which is an extension of Extensible Markup Language. The systems consist of several components -- including a telephone network, TCP/IP network, a VoiceXML telephony server, a web server and databases -- all working together to provide the best possible customer service.
Types of interactive voice response workflows and call flows
Among the interactive voice response systems deployed today, several distinct workflows can be found that are generally familiar to the public -- most everyone has had one or more of these interactions at this point. All customer support centers use one of the following:
- Touch-tone replacement. This is the oldest and most familiar form of IVR. Prerecorded voice messages prompt the customer to answer questions on the phone's keypad, such as "Press 1 for English, 2 for Spanish." This IVR type was originally a replacement for receptionists, designed to route phone calls, with IVR taking the role of auto attendant. Once call centers emerged, this technique presented a caller with service options.
- Directed dialogue. This IVR type is similar to touch-tone replacement but requires the caller to speak a requested response rather than touch a key. For example, "If you'd like to hear tonight's showings, say movie times or schedule."
- Natural language. As natural language processing and artificial intelligence (AI) have become ubiquitous, open-ended dialog between interactive voice response systems and customers has become increasingly common. In a typical scenario, the IVR system might prompt the caller with "How can I help you today?" and get a response like "I want to check on the status of my order." While this IVR service type is more complex and processing-intensive, it can also lead to shorter, more efficient interactions with customers, saving them time.
Uses of interactive voice response
There are many use cases for IVR systems. The most common use is to automate inbound and outbound calls and to route calls.
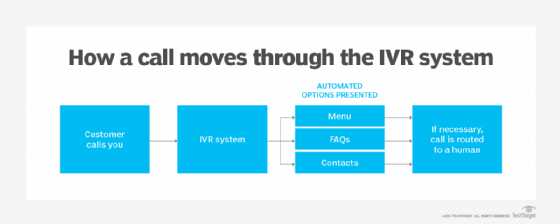
The IVR system eliminates the need for a switchboard operator to answer incoming calls. In this instance, the system presents a caller with a menu of options and can provide answers to frequently asked questions or contact information. It can also escalate calls to live agents.
A good example is when a customer calls the airline to check on their flight status. The IVR system communicates with the flight application to present the caller with updated flight information, helping eliminate call wait times and leading to greater customer satisfaction.
Organizations can also use IVR systems in the following ways:
- To enable customers to check their bank and stock account balances in real-time and make transfers.
- To route customer calls to the appropriate department.
- To help customers find a store's nearest location or business hours.
- To forward calls in a call center.
- For simple order entry or bill payment transactions.
- To help customers with selective information lookup or self-service options.
IVR systems can also be used in more complicated ways to simplify processes in other departments:
- Sales. IVR systems enable customers to fill out sales order forms with their phone keypad. They can input information, such as selected products, quantity and delivery address. The computer sends the completed form to a salesperson.
- Marketing. Marketers can use IVR systems to send surveys to gauge interest in a product or service.
- Medical records. Doctors can use an IVR system to transcribe notes and patient records and have a copy of the transcribed records sent to their office.
Benefits of interactive voice response
IVR technology can benefit both large and small organizations in the following ways:
- Time and money savings. IVR technology can replace the need for humans to provide commonly requested information -- such as directions and hours of operation -- that doesn't require critical thinking skills.
- Greater customer satisfaction. IVR technology eliminates wait times by responding to a caller immediately.
- 24/7 service. IVR technology operates without interruptions and is available to provide callers with information whenever they need it.
Disadvantages of interactive voice response
IVR also has its disadvantages, including the following:
- Limited functionality. These systems are limited in the type of questions they can answer and can leave callers frustrated and confused when IVR menus are too long.
- Poor customer service. IVR systems have been criticized for being too impersonal and for acting as a barrier between customers and live call center agents.
- Expensive. Establishing an IVR system requires an organization to invest in hardware, software and maintenance.
- Voice and language limitations. Some IVR systems can't recognize all voices or languages.
However, despite its limitations, IVR continues to evolve and improve to address these limitations.
Many companies have augmented or replaced IVR systems with automated speech recognition technologies that let callers speak their requests instead of punching numbers into their phones. However, these voice recognition systems can frustrate callers if they don't recognize a caller's questions.
History of interactive voice response
The core technology behind IVR has been around for decades but wasn't cost-effective for wide commercial deployment until the mid-1980s when hard drive storage technology dropped in price. At that point, digitizing and storing the speech used in an IVR interaction became affordable.
Call centers migrated from telephone-only to multimedia in the 1990s, prompting companies to integrate voice-computer interaction with a coordinating infrastructure to manage call handling and high call volumes. Queuing and call routing management led to greater efficiency and less caller frustration.
Since then, IVR systems have created stronger customer interactions by making routing logic and menus more intuitive and increasing security. For example, IVR voice verification is a biometric technique that provides additional security and protection from fraud resulting from social engineering attacks.
Interactive voice response advancements through AI
Despite the downsides, IVR software use is expected to increase in the coming years, thanks to improvements in conversational artificial intelligence and voice recognition technologies.
Natural language processing is being used to streamline and improve IVR systems because the technology can better analyze spoken language and, together with natural language generation applications, enables IVR to deliver a conversational response to callers.
In addition, IVR analytics software enables companies to analyze issues with their voice response systems and improve them to better meet customer needs.
Learn what advancements AI and generative AI are bringing to contact center technologies and how this benefits customers.






