Contact center compliance checklist for modern workforces
A contact center compliance checklist can serve as a starting point for contact center managers as they seek to comply with internal and external requirements.
The goal of a customer service organization is to provide service and support to current and potential customers. A significant number of these interactions occur in the contact center. To properly fulfill this role, contact centers must comply with regulatory bodies to provide accurate and effective support that protects the rights and well-being of customers. Contact centers can also develop internal rules and practices, such as call monitoring, to supplement external requirements and improve CX.
Adherence to these rules and practices goes beyond the scope of the contact center and requires a total company effort for successful compliance, whether staff works in the office or remotely.
Establishing and following a contact center compliance checklist helps to form good practices that lead to successful compliance.
What is contact center compliance and why is it important?
Compliance is critical to contact centers, as a failure such as a data breach can have a significant negative effect on a customer's life and potentially devastate an organization's brand image and reputation. Customers don't want to purchase services from an organization that can't protect their personal information from bad actors, and organizations do not want to pay fines and penalties to regulatory agencies.
Compliance requires participation from every individual in an organization. Contact center managers shouldn't assume that their processes always work or that agents always follow proper procedures. All employees must keep their eyes and ears open. Controls must be in place, and if something does not seem right, they must raise the issue with the appropriate individual.
Before the COVID-19 pandemic, most contact centers were on premises, which, in many ways, made compliance easier to implement and monitor. For example, employees had to swipe their key cards to enter the contact center. Compliance became more of a challenge when contact centers began to operate remotely, so checklists can help contact center managers follow proper guidelines.
Contact center compliance checklist
Organizations can't achieve compliance with a single tool or process. Compliance requires a multifaceted approach that integrates technology, processes and procedures.
The following contact center compliance checklist can serve as a starting point for contact center managers as they seek to comply with internal and external requirements.
1. Secure the network
Organizations should use network access control to limit who can physically and logically access system hardware and software. Physical security protects the physical components of a network, such as devices, modems or routers, from physical harm. Logical security uses passwords and system permissions to protect a network's software and data from unauthorized individuals.
Contact centers with remote agents might struggle to maintain physical security, as these agents don't always have secure workstations. Contact center managers should perform physical or virtual audit checks on their agents' remote workplaces to ensure they meet security standards.
2. Perform workstation audits
Physical workstation audits enable an organization to inspect both on-site and remote employees' work environments and ensure they support basic controls and meet compliance requirements. As physical visits to employees' remote workstations aren't always feasible, supervisors can use video conferencing to perform high-level audits. Beware: A video conferencing audit is limited in its scope and timing.
3. Authenticate customers
Customer authentication is a process where individuals prove they are who they claim to be. In some cases, single-factor authentication, where customers provide a single piece of information to confirm their identity, can suffice. However, many organizations have adopted multifactor authentication, which asks customers to provide distinct pieces of information, such as a password and a code sent to a mobile device, to confirm their identity. Additionally, some companies are using voice and facial recognition technologies to authenticate customers.
4. Record customer conversations
Call recording lets organizations review telephone conversations between customers and agents. Managers can review recordings through a QA program to determine if agents fulfilled external requirements, such as appropriate disclosures and authentication processes. Managers can also review recordings to determine if an agent fulfilled internal requirements, such as providing a customer with accurate information and/or following the correct internal procedures.
5. Provide mandatory disclosures
Contact center agents must provide mandatory disclosures, which are legal statements used to clearly explain specific processes, rules and options to callers. For example, if a contact center in the U.S. wants to record a customer call, it must be disclosed to the caller, and consent must be provided, which is passive consent in most cases. Regulations require mandatory disclosures when agents record customer calls, perform collection functions or make financial transactions.
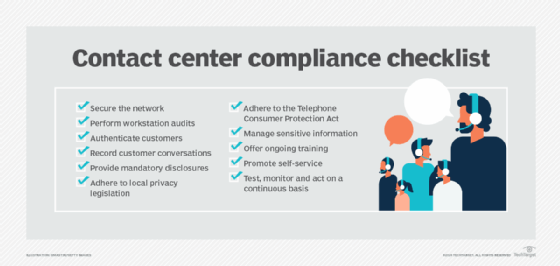
6. Adhere to local privacy legislation
Organizations must adhere to various global and local legislation on customer privacy, depending on the geographic reach of the business. Due to legislation, organizations can't manage all customer information in the same way. Data privacy laws vary by country and region, so organizations must know where each customer resides before they transmit, process and store customer information.
Location-based privacy legislation includes the following:
- General Data Protection Regulation. GDPR provides guidance on how organizations can collect and process personally identifiable information (PII) for individuals who live in the European Union.
- California Consumer Privacy Act. CCPA provides guidance on how organizations can collect and process personal and household information for individuals who live in California.
7. Adhere to the Telephone Consumer Protection Act
Organizations in the U.S. must adhere to the Telephone Consumer Protection Act, which sets rules for how an organization can use outbound calls for solicitation. TCPA regulations state that telemarketing contact centers cannot use predictive dialers to contact a wireless phone without prior consent from the customer. It also ensures telemarketers adhere to the National Do Not Call Registry and special regulations, which may include restricted calling hours in a particular geographic location after a natural disaster event.
8. Manage sensitive information
To comply with standards, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard and HIPAA, organizations must protect sensitive customer data at rest and in motion. Sensitive information can include PII, credit card numbers or protected health information. To protect sensitive information, organizations should encrypt all data, minimize the amount of stored data and use automation, such as interactive voice response, to perform sensitive transactions.
9. Offer ongoing training
Organizations should offer annual training on proper compliance procedures and guidelines to all employees. All employees should be up to date on specific compliance rules and understand how they can protect their organization and its customers.
10. Promote self-service
Organizations should maximize the ability for customers to self-service through secured portals to limit the sharing of information with other individuals and reduce security risks.
11. Test, monitor and act on a continuous basis
Organizations can implement all the previous items noted in the checklist, but that still might not be enough to assume everything is working properly or bad actors haven't found creative ways to bypass established controls. The testing and monitoring of the various compliance controls should occur on a continuous basis, whether through automated processes, such as reporting unauthorized attempts to access customer data, or human processes, like placing test calls.
When something doesn't seem right, it's important for the organization to analyze and potentially act to ensure the controls in place are performing as expected.
A contact center compliance checklist can help organizations avoid compliance failures. Contact center managers can use this checklist to evaluate their organization's current compliance protocols and ensure their teams follow proper guidelines.
Common contact center compliance issues and malpractices
If strong compliance controls and practices aren't in place, the following negative events can occur:
- Calling customers who requested not to be called, which violates outbound calling restrictions.
- Allowing PII to be stolen due to incorrectly accessing customer information.
- Improperly recording customer conversations by not adhering to call recording and consent rules.
- Providing incomplete information to customers by not adhering to scripting requirements.
When these types of events occur, an organization can be liable for financial penalties, along with other legal consequences. Just as important is the potential for negative customer perception, which can potentially lead to lower customer loyalty and customer defections.
A contact center compliance checklist might not stop all unauthorized activities, but it's a solid start to implementing a strategy that adheres to legal and organizational requirements.
Scott Sachs is president and founder of SJS Solutions, a consultancy that specializes in contact center strategy assessments and technology selection.








