What is first call resolution (FCR)?
First call resolution is when contact center agents properly address a customer's needs the first time they call so there is no need for the customer to follow up with a second call. FCR is a part of contact center customer engagement activities that embrace the tools, technologies and practices of customer relationship management (CRM).
Talk time, which is the average time an agent spends on each call, is a common call center and contact center performance metric. Lower talk time averages are usually desirable. However, low talk time averages accompanied by poor FCR rates are a sign that customer calls are not being answered satisfactorily.
Contact center managers carefully monitor follow-up calls from customers. In addition to being an indication of customer dissatisfaction, follow-up calls increase call volume and require more customer service agents. A contact center manager will accept an increase in talk time, as long as the first call resolution rate increases as well.
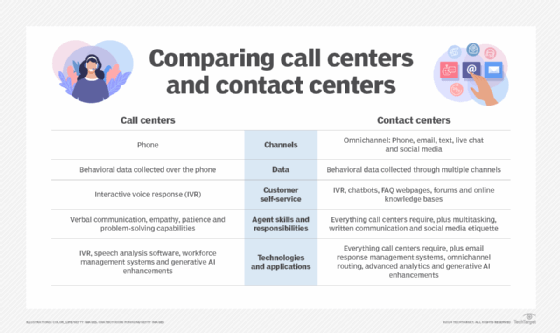
First call resolution is similar to first contact resolution. The first contact resolution rate involves all channels -- chats, texts, emails, social media and other avenues of support or help desk communications -- not just phone calls.
Why is FCR important?
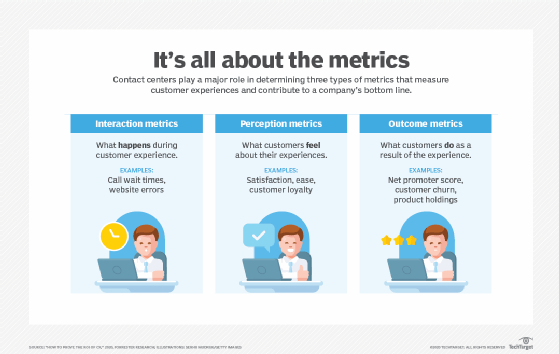
FCR is a measure of customer experience (CX), providing insight into ways to improve a company's CX strategy. It is also a good indicator of how responsive a company is and its operating cost efficiency. FCR drives other customer service-related metrics, such as customer satisfaction (CSAT), customer effort or the amount of effort a customer has to put in to interact with a business, customer interactions and average spend.
Companies that focus on high FCR rates often find that improving their first call resolution helps improve service speed and quality. Calls or contacts that are resolved on the first call help organizations live up to customer service expectations.
In general, contact center metrics such as FCR show organizations where issues occur and where their processes can be improved, which improves a business's bottom line. When processes are made more efficient, companies can cut down on customer support costs.
FCR can apply to all customer contact channels and first interactions. It can be used to measure a company's ability to provide service across all communication channels.
How to measure FCR
The FCR rate is considered one of the more significant key performance indicators to assess CSAT. The metric is calculated by taking the total number of customer service cases resolved on the first try divided by the total number of cases in the day and then multiplying the result by 100 to get a percentage.
First call resolution percent = (total cases resolved on first try ÷ total number of cases) x 100
For example, assume a software as a service (SaaS) vendor's customer support team received 2,345 calls in a single day. Of those calls, 894 were resolved in the first call. The SaaS vendor's FRC rate that day is just over 38%.

Calculating an FCR can get tricky because what constitutes a resolved call might vary among contact centers. Some of the questions that get raised when determining what calls will be counted as resolved include the following:
- Who determines if FCR was achieved -- the organization, customer or both?
- If the customer uses another channel, such as chat or email, to resolve their inquiry after an unresolved phone call, does it count as FCR?
- Are outbound callbacks considered an FCR?
- Are abandoned calls due to wait times considered non-FCR?
- Does escalation or call transfer count toward the FCR rate?
These issues are open to interpretation and must be evaluated and resolved to ensure consistent FCR calculations.

What is a good FCR rate?
The industry standard FCR is to resolve about three-quarters of all calls with the first contact. However, a lot of variables can affect the rate any one business or industry uses for its benchmark. What is considered a good FCR rate can differ based on the type of contact center, how the rate is measured, the type of business and the technology it has available.
A contact center in a highly technical field might have a lower FCR rate because more callbacks are required to collect the information needed and research solutions than in a less technical field.
Also, different call types require different timelines to determine when FCRs were achieved. For example, a claim call might take 30 days to process, whereas a status inquiry call might only require five days to determine whether FCR was a success.
The benefits of first call resolution
Some of the benefits of achieving a good FCR rate include the following:
- Customer retention. One reason customers stop engaging with a business is poor customer service. Good customer service motivates customers to keep coming back to the business.
- Customer satisfaction. Satisfied customers are more likely to provide repeat business.
- Willingness to spend. When customers are satisfied, they are more likely to spend more money with a business in single interactions.
- Improved efficiency. Good FCR maximizes agent productivity. Support agents spend less time dealing with repeat requests, can talk to more customers in a day and ultimately cut down on customer wait times.
- Decreased costs. A more efficient contact center achieved through good FCR enables companies to save time and money circling back to repeat calls and dealing with other customer dissatisfaction-related costs.
Challenges of first call resolution
FCR can be difficult to calculate and define. The two main challenges associated with FCR are the following.
When is a call resolved?
The first step in answering this question is determining who decides when resolution has happened: the customer, the organization or both. The organization must also establish criteria for a resolved call, which varies based on its industry and business.
Usually, some measurement of the customer's behavior is used to determine whether a call is resolved. For example, if a customer does not call back within 30 days to ask a follow-up question, the call might be considered resolved. In other cases, a post-call customer feedback survey is used.
How is FCR measured?
Even when the criteria for success are defined, it can be difficult to track and measure that criteria across all CX channels. For example, chat and email contacts in addition to phone contacts might have an effect on whether FCR was achieved.
How to improve FCR
To improve its FCR strategy, a company should do the following:
- Evaluate its existing FCR strategy.
- Determine what needs to be improved.
- Develop achievable goals to address deficiencies in the existing FCR strategy.
- Design a plan to reach the goals and implement it.
- Continually measure the performance of the new strategy by tracking key FCR performance metrics.
There are several steps a company can take to continually measure FCR metrics and improve upon them, including the following.
Add a customer service portal. A portal helps customer service team members with tracking and documentation. Implementing integrated CRM software to track tickets, calls and emails is easier than manually tracking them.
Use automation technology. Automation can help agents respond to inquiries and give them more accurate information to use in their responses. Interactive voice response systems are common and improving as artificial intelligence (AI) and voice recognition technology improves.
Define resolved. Outline concrete criteria for when a call can be considered resolved. Every company's definition of a resolved call will be a little bit different.
Follow up with customers. Use follow-up calls and emails to help gauge customer satisfaction. Such follow-up isn't necessary in a successfully resolved first call, but it is helpful from an analytics perspective.
Focus on staff. When assembling a customer staff, a company can take the following steps:
- Ensure it has adequate staff to deal with customer request volume. Long wait times can lead to dissatisfied customers.
- Train the customer support team. Agents should be continuously learning about the company's product or service, especially areas such as software as a service where the product is constantly changing.
- Structure the support team according to employees' strengths and weaknesses. In some cases, a team might consist entirely of generalists. In other cases -- as in companies with complex offerings -- teams might be diverse, with a mix of specialists and generalists.
- Motivate the customer service team. Create incentives that push employees to achieve and improve important metrics.
Use analytics. Analyze the results that come from customer service requests and responses. Look for common issues, ways to improve employee performance and common patterns in call intervals.
Leverage generative AI. The growth of generative AI might contribute to higher FCR rates. A March 2024 Customer Contact Week report on the state of generative AI found that 86% of contact center leaders see the technology as helping to increase speed and efficiency.
First call resolution best practices
For FCR success, follow industry standard best practices such as the following:
- Keep good documentation. Record answers to common problems that customers might have and make internal documentation easy to access. This is useful if customers call with the same question repeatedly. Some companies use a self-service customer service strategy that includes a knowledge base and frequently asked questions to provide accessible information for customers. Knowledge bases can include step-by-step instructions that can help customers resolve their issues.
- Route calls. Screen customer requests by content type and route calls to the appropriate department. Automated call routing cuts down on wait times for the customer and improves agent productivity.
- Respond to support inquiries quickly. Response time is a critical factor for providing a positive customer experience.
- Active listening. Agents should strive to get as much information as possible from a customer and confirm the details with them. Agents should aim to understand a customer's needs and help the customer meet them.
- Respond appropriately. Agents should respond with clear instructions for the customer and should be able to have tutorials or documentation for more complex customer issues. A call should always end with the agent asking if they solved the customer's problem.
Editor's note: This article was updated to include the latest information on call centers and contact centers.