What is direct marketing?
Direct marketing is a type of advertising campaign that seeks to elicit an action (such as an order, a visit to a store or website or a request for further information) from a selected group of consumers in response to communication from a marketer.
The communication itself might be in any of a variety of formats, including the following:
- Postal mail.
- Telemarketing.
- Direct email marketing.
- Point-of-sale interactions.
Customer responses should be measurable; for example, the marketer should be able to determine whether or not a customer who was offered a discount for online shopping takes advantage of the offer.
History of direct marketing
Montgomery Ward started direct marketing in the 19th century. In 1872, Ward pioneered mail-order catalogues for his business, successfully removing the middleman and benefiting the customer by reducing prices.
However, the term direct marketing wasn't coined until 1967 by Lester Wunderman. Wunderman is considered the father of contemporary direct marketing and is the man behind the creation of the toll-free 1-800 number, as well as many other customer loyalty programs.
Challenges and solutions for direct marketing
The main challenge with direct marketing is overcoming the image of junk or spam mail/email, which can result in ineffective and costly campaigns. In order to minimize frustration, companies can use opt-out lists or use a preference list that allows customers to have more control over what they receive.
Another solution is creating a targeted campaign with an accurate database, which also helps reduce advertising budget waste.
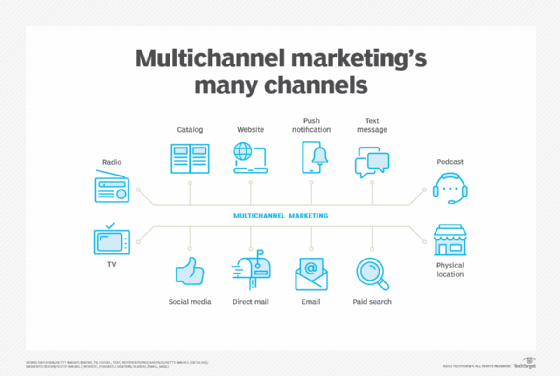
Direct marketing channels
The following are the most common forms of direct marketing channels:
- Email marketing.
- Mobile, such as SMS.
- Voicemail marketing.
- Direct mail.
- Insert mail, which lets users create content that is personalized for each recipient.
- Couponing.
- Telemarketing.
- Direct response marketing, which aims to get an immediate response from the customer.
- Direct selling, which directly offers products to customers rather than going through third parties, like retail stores or distributors.
- Grassroots/community marketing.
Effective audience for direct marketing
The most effective customers for direct marketing are customers who have opted into mailing lists or have expressed interest in a company's products. However, nontargeted blank mailings are also acted upon at a high percentage.
Editor's note: This article was originally published in 2021. Informa TechTarget editors revised it in 2025 to improve the reader experience.








