
What is customer intelligence (CI) and how does it help business?
Customer intelligence (CI) is the process of collecting and analyzing detailed customer data from internal and external sources to gain insights about customer needs, motivations and behaviors.
CI helps organizations understand customers better so they can improve interactions and deliver more personalized customer experiences. It also provides the crucial information organizations need to improve customer communications with segmentation strategies and optimal marketing campaign management planning. All of this can help improve customer journeys and drive the organization's future growth.
The need for customer intelligence
Improving the customer experience (CX) is becoming imperative for businesses to stay ahead of competitors. To deliver elevated CX, businesses need to gain critical insights into customer behaviors, including what they need and where they are in the buying journey. When available in real time, these insights provide a comprehensive view of customers that goes beyond their name, age, gender or other simple signals of purchasing intent or other targeted behavior. This is where CI comes in.
Customer intelligence data helps create a powerful, comprehensive, sophisticated customer analytics ecosystem that enables businesses to create dynamic customer profiles and deliver superior CX to each customer. When these capabilities lead to actionable recommendations, businesses can understand customers better and design tailor-made, cross-channel communications and marketing strategies at every stage of the customer journey. These strategies, when properly implemented, can increase conversion rates and customer retention.
What are the benefits of customer intelligence?
Besides boosting marketing effectiveness, CI is a linchpin in customer relationship management (CRM). Together, CI and CRM enable companies to more effectively manage interactions with their current customer base and new customer prospects. Further, they can deliver more relevant, timely and personalized campaigns that delight customers and deliver great results for the company. Additional benefits of CI include the following:
- It boosts sales efficiency and effectiveness while improving transparency in marketing return on investment.
- Businesses can strengthen customer loyalty by understanding customers better and improving the quality of their customer service programs.
- CI delivers actionable, data-driven insights that support and help optimize crucial product decisions.
- Companies can forecast campaign effectiveness and adjust their cross-channel marketing strategies to guide cross-sell and upsell strategies.
- By taking preemptive action to engage with at-risk customers through appropriate and personalized marketing campaigns, businesses can reduce customer attrition.
- With improved customer engagement comes greater customer retention.
- The forecasting improvements achieved via CI translate into improved conversion opportunities.
- Strong CI data can create new business opportunities and avenues for growth.
Types and sources of customer intelligence
CI is most effective when gathered from both internal and external sources. Combining these sources helps create a more complete picture of customer motivations and behaviors, which then enables organizations to take the right action to enhance CX.
Internal CI can be generated by any customer interaction. Usually, it's stored in the following locations:
- Corporate databases.
- Call center systems.
- Sales systems such as point-of-sale systems.
External CI can also emerge from many different sources. It typically falls into one of the following three categories:
1. Personal demographics. This includes data such as the following:
- Age.
- Gender.
- Income level.
- Debt level.
- Education.
- Marital status.
Such data might be analyzed to explore buying patterns of people in specific income brackets, changes in sales as people age or sales comparisons of homeowners and renters.
2. Geographic demographics. This includes data aggregated from specific locations that could be analyzed to explore regional buying patterns. What works best in rural areas, for example, might not perform as well in urban centers where most residents are young professionals.
3. Attitudinal data. This includes information about how an existing or potential customer perceives the company. This information can be gathered from the following:
- Customer satisfaction and market research surveys.
- Focus groups.
- Contact centers.
- Customer comments about a product or service on social media.
Some companies also use speech analytics to collect and examine voice recordings to understand customer sentiment and behaviors. Other organizations use website metrics, such as the following:
- Pageviews.
- Visits.
- Unique visitors.
- Time on site.
- Bounce rate.
External CI is particularly useful for sales and marketing teams in industries, including banking, retail, telecommunications and consumer goods.
Modern organizations use numerous technologies to gather and process both internally and externally collected CI. Examples include the following:
- Feedback management software.
- Social media monitoring tools and social CRM platforms.
- Natural language processing platforms.
- Mobile CRM.
The application of business analytics to customer data is called customer data mining.

The customer intelligence process
The CI process usually involves the following four steps:
1. Collect data
The CI process starts with the collection of customer information from multiple channels, including but not limited to emails, websites, phone calls, mobile apps, text messages, physical forms and contact center recordings. This data can be demographic -- personal or geographic -- or attitudinal. It can also be one of the following types:
- Transactional data involves customer purchase history.
- Behavioral data is about customer behaviors, such as in-store or on the e-commerce website. It's often collected via heat maps, eye tracking, market research surveys and website cookies.
- Psychographic data is information about what triggers customers' purchase decisions. This involves analysis of customer interests, attitudes and activities.
While demographic data is a key aspect of CI, organizations increasingly look to transactional and behavioral data to better understand user preferences and guide their marketing and branding decisions.
2. Categorize data
Once the organization collects customer data, the next step is to categorize it for better analytics and insights. Typically, collected data falls into one of the following three classes:
- Direct feedback is what customers provide directly to the business or a third party, such as a review aggregator. This feedback helps organizations identify and address issues, such as poor CX.
- Indirect feedback includes customer comments on social networks and complaints made to the Customer Service Department. This feedback enables companies to understand what customers think about the company and its offerings.
- Inferred feedback includes data collected from customer processes, including purchase history, cookies and location-based data.
3. Analyze data
A wide range of analytics tools and algorithms are available to analyze customer data collected from various channels. These tools facilitate the definition of customer segments based on similar patterns in the collected data. Examples of these technologies include the following:
- Customer lifetime value forecasting.
- Customer behavior modeling.
- Dynamic microsegmentation.
- Machine learning.
- Predictive customer analytics.
- Actionable insights.
4. Share insights
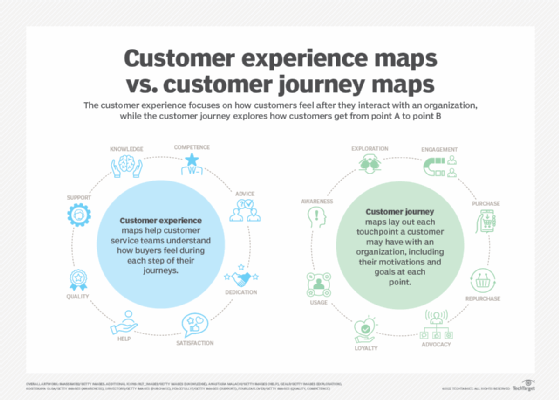
Once the analysis is complete, actionable insights are presented to relevant stakeholders in a comprehensible form, such as dashboards, alerts or customer journey maps. These insights help improve customer service workflows and guide future marketing campaigns to improve customer journeys, customer satisfaction and customer experiences.
Learn how organizations collect customer feedback to improve their experiences.






