
What is an AI assistant?
An AI assistant, or digital assistant, is software that uses artificial intelligence to understand natural language voice commands and complete tasks for the user.
Such tasks -- historically performed by a human personal assistant -- include taking dictation, reading text or email messages aloud, looking up phone numbers, scheduling and placing phone calls and reminding the user about appointments. Popular AI assistants include Amazon Alexa, Apple Siri and Google Assistant.
Types of AI assistants
Though this definition focuses on the digital form of AI assistants, the terms AI assistant and AI personal assistant are also commonly used to describe contract workers who work from home doing administrative tasks typically performed by executive assistants or secretaries.
With the evolution of chatbots and generative AI, various types of AI assistants have gained popularity. However, they serve different purposes for users and provide different levels of assistance.
This article is part of
What is enterprise AI? A complete guide for businesses
Common types of AI assistants include the following:
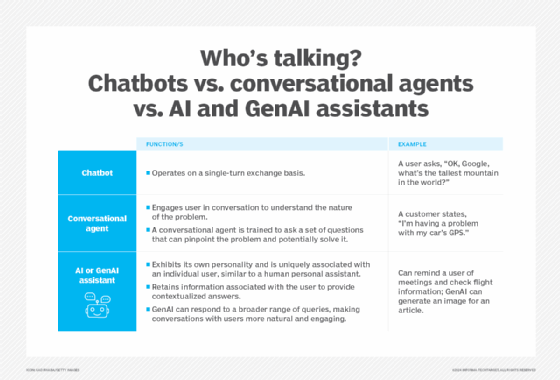
- Chatbots. Chatbots are computer programs that serve as AI assistants and communicate with users through text-based interfaces on websites, social media platforms and messaging apps. These chatbots can assist customers, respond to inquiries or start a discussion with them. AI chatbots employ natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML) algorithms to understand user input, produce pertinent responses and improve their performance over time by learning from these interactions.
- Conversational agents. Beyond text-based chatbots, conversational agents enable AI assistants to converse in a human-like manner through both text and voice interfaces. These AI-based systems are designed to comprehend intricate linguistic patterns, discern user intent and offer appropriate responses in each situation. Conversational AI can be used to build more sophisticated AI assistants that can handle various tasks and offer a more intuitive and natural user interface.
- AI digital assistants. These advanced AI digital assistants can perform various tasks, often across multiple devices and platforms. They frequently converse with users through voice-based interactions. With these AI digital assistants, users can easily and quickly access information, control smart home appliances and manage their calendars by integrating with a variety of services and applications.
A subcategory of AI assistants are generative AI (GenAI) assistants, such as OpenAI ChatGPT and its many siblings. They're rapidly gaining traction in the workplace as aides to content creation. A GenAI assistant can provide starter text for an email or report, generate artwork for an article, and condense text already written, making it more focused and concise.
AI assistant devices and technology
AI assistants are typically cloud-based programs that require internet-connected devices and applications to work. Most AI assistants can be found on devices such as smartphones, smart speakers or other platforms, including instant messaging apps.
AI chatbots that use GenAI -- such as Amazon Lex, ChatGPT and Google Cloud Dialogflow CX -- are also gaining popularity for their ability to generate human-like responses to text-based conversations.
Common AI assistant technologies and devices include the following:
- Amazon Alexa. Used mainly through Amazon's product line of hands-free speakers known as Amazon Echo, Alexa is a cloud-based voice service available on more than 100 million Amazon devices and third-party manufacturers. To use Alexa, users call out the wake word, Alexa and a light on the device signals to the user that it's ready to receive a command, which typically involves simple language requests, such as "Alexa, what is the weather today?" or "Alexa, play pop music." Alexa can also use GenAI with its own large language model to enable access to more than 200 smart home application programming interfaces. So, instead of saying "Alexa, turn on the air conditioning," users can say, "Alexa, I'm hot," and the assistant turns on the air conditioning using advanced contextual understanding that AI enables.
- Apple Siri. This built-in, voice-controlled personal AI assistant is available on devices using iOS, iPadOS, watchOS, macOS and tvOS. It uses voice recognition technology that's powered by AI.
- Google Assistant. Google developed this AI voice assistant software application for Android devices. Google Assistant can perform a variety of tasks, including answering questions, adjusting hardware settings on the user's device, scheduling events and alarms, and playing games.
- Microsoft Copilot. The Copilot AI assistant built into the Microsoft Windows 11 operating system (OS) can be used across all Windows apps and programs. It provides a natural user interface through AI-powered chat for interacting with the Windows OS.
- OpenAI ChatGPT. ChatGPT can create useful content across a broad range of tasks, generating human-like responses to queries of all kinds. Paid subscribers to the ChatGPT Plus and Teams plans can access the new ChatGPT Advanced Voice Mode by speaking to it instead of typing a prompt. Although ChatGPT has its Read-Aloud function, Advanced Voice Mode gives users a more human-like experience. Of its many features, it can say "Sorry I'm late" in more than 50 languages.
- Samsung Bixby. Samsung's AI assistant runs primarily on mobile devices but also some smart refrigerators. Bixby can be used for various tasks including texting, retrieving location-specific weather information, setting meeting reminders and reading news articles.
The technologies that power AI assistants require massive amounts of data, which feed AI platforms, including ML, NLP and speech recognition platforms. As the end user interacts with an AI assistant, the AI programming uses sophisticated algorithms to learn from data input and become better at predicting the end user's needs.
Capabilities of AI assistants
AI assistants typically perform simple jobs for end users, including the following:
- Adding tasks to a calendar.
- Providing information that could normally be searched in a web browser.
- Controlling and checking the status of smart home devices, including lights, cameras and thermostats.
- Making and receiving phone calls.
- Scheduling meetings and appointments.
- Creating text messages and rough drafts of emails.
- Creating images to embed in reports and articles.
- Revising text to make it more concise.
- Performing research.
- Providing real-time transcripts of meetings.
- Getting directions.
- Hearing news and weather reports.
- Finding hotels or restaurants.
- Checking flight reservations.
- Streaming podcasts.
- Setting reminders.
- Workflow management.
- Assisting in e-learning and training.
- Calling an Uber or Lyft.
- Listening to music.
- Playing games.
Privacy concerns
Some consumers have expressed privacy concerns about AI assistants, such as Amazon Alexa and Google Home. These AI assistants require large amounts of personal data and are always listening to respond to voice commands. Although voice assistants are only intended to begin recording when a user gives them the wake command, they can accidentally capture voice exchanges and private information without the user's knowledge.
AI assistant providers also maintain privacy policies, which define how each company uses and shares personal information. In most cases, companies don't share customer-identifiable information without a customer's consent but there have been concerns regarding how voice assistant providers use and handle user data.
Besides privacy policies practiced by providers, end users can also take the following security precautions:
- Change the settings of the AI assistant to enable sound notifications, which will alert the user when the assistant is accidentally triggered and begins to record voice interactions. By default, the notifications of certain voice assistants, such as Echo and a few Google devices, are set to silent.
- Opt out of recordings of commands and conversations as well as historical records saved on the devices, such as with Amazon Alexa. However, this step doesn't guarantee that the data won't be evaluated once the transcripts are deleted.
- Practice extra caution when sharing certain types of information with voice assistants. It's best to avoid giving voice assistants access to sensitive information.
Separating business and personal AI assistant profiles can also improve privacy. Most assistants -- including Alexa and Google Assistant -- support multiple accounts, enabling users to segregate their personal AI assistants from their professional ones.
The future of AI assistants
AI assistants are quickly evolving to provide more capabilities to users. As speech recognition and NLP have advanced, so has the AI assistant's ability to understand and perform requests. And as voice recognition technology continues to improve, AI assistant use will move deeper into business workflows.
As AI technology advances, AI assistants will continue to become humanistic and able to provide more personalized experiences. However, the widespread use of AI assistants doesn't obscure the growing worries about the privacy and security risks associated with them. Companies are being urged to address these concerns transparently in their policies to build trust with users. The future of AI assistants might also be tied to the metaverse, with companies exploring new ways of integrating these assistants into virtual reality environments.
AI and ML technologies are transforming businesses and society at large. Discover the top AI trends that businesses should look out for as AI continues to advance.






