
Getty Images/iStockphoto
Customer loyalty vs. brand loyalty: What's the difference?
Low prices can generate customer loyalty, whereas reliability and reputation foster brand loyalty. To maximize customer retention, organizations should strive for both.
Customer and brand loyalty can both encourage repeat business, but price can affect customer loyalty, whereas brand loyalty relies on trust.
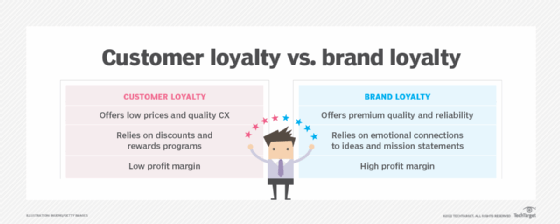
Organizations should devise strategies to retain their existing customers, as they typically generate the most profits from long-term patrons. Customer loyalty and brand loyalty can increase retention, but they work in different ways. Customer loyalty is a consumer's tendency to repeatedly buy from a brand due to price and convenience, whereas brand loyalty is a consumer's commitment to a brand based on trust and product quality.
While these approaches both drive customer retention, they differ in emotional connections, marketing strategies and profit margins. To increase retention, organizations should aim to boost both customer and brand loyalty.
3 differences between customer loyalty and brand loyalty
Customer and brand loyalty differ primarily in their emotional connections, marketing approaches and profit margins.
1. Emotional connections
The emotional connection that drives customer loyalty differs from the connection for brand loyalty. Low prices, loyalty programs and quality CX foster customer loyalty because they make customers feel like organizations listen to and appreciate their needs. Many people shop with set budgets, so when organizations offer items for prices consumers can afford, they can become repeat customers.
Also, loyalty programs reward repeat customers with additional -- often personalized -- offers, which helps consumers feel as though organizations value their commitments.
Brand loyalty, on the other hand, is less transactional and more emotional. It stems from trust between consumers and brands, rather than price. Customers might develop brand loyalty from the way they perceive an organization's reputation, product quality or mission statement.
For example, a customer who always buys the same brand of smartphone without considering other options represents brand loyalty. The customer trusts the brand's quality and reputation -- and likely won't consider an alternative.
Additionally, a customer might always buy the same coffee brand because it publicly supports and donates to a charitable cause. In this case, the customer's brand loyalty stems from an emotional connection to the brand's moral actions.
2. Marketing approaches
Given that customer loyalty centers around price, whereas brand loyalty focuses on trust, these two retention strategies often rely on distinct marketing approaches. To build customer loyalty, marketers can focus ads on cost savings, which appeal to customers with set budgets. Additionally, marketers can use rewards programs to incentivize frequent purchases.
For brand loyalty, marketing teams should work to connect with customers on an emotional level. For instance, marketing teams could link their brand to an idea or mission that might appeal to customers. An electric car company might associate itself with innovation and sustainability, or a whole foods store with health and wellness. Customers trust brands that share their own morals and values, which can boost brand loyalty.
3. Profit margins
Many organizations with high customer loyalty have lower profit margins because they offer products at low prices. However, these organizations typically make large numbers of sales, which makes up for the low margin.
Conversely, many organizations with brand loyalty have higher profit margins because their customers respect the brand and its values over prices. These organizations can charge premium prices for products because loyal customers are willing to pay. However, some organizations with high brand loyalty might sell fewer products and services than organizations with high customer loyalty.
What is customer loyalty?
Customer loyalty happens when customers make repeat purchases based on prices, discounts, rewards programs, service and overall CX. A person who shows customer loyalty to an organization doesn't necessarily have an emotional connection to that particular brand and may frequently shop from various brands in the same categories. Organizations like Amazon and Dominos have high customer loyalty.
What is brand loyalty?
Brand loyalty happens when customers make long-term commitments to brands based on product quality, trustworthiness and values. A customer who shows brand loyalty to an organization typically feels an emotional connection to that brand based on the quality of its products or its mission statement. In fact, customers with brand loyalty often remain loyal even when competitors offer lower prices. Organizations like Apple and Nike have high brand loyalty.
How to increase customer loyalty
Most consumers have budgets and look for value as they shop. They appreciate fair prices, convenience and rewards for their loyalty.
To retain these consumers, brands can take the following steps:
- Offer competitive pricing. Consumers prioritize value and often compare prices as they shop. Organizations that offer low prices can attract budget-conscious shoppers and retain them over time.
- Create loyalty programs. Rewards and personalized offers can incentivize people to repeatedly make purchases from the same brand.
- Offer convenient shopping experiences. Modern consumers have busy lives and expect quick and seamless interactions. Examples include simple check-out processes, fast shipping and reliable customer support.
How to increase brand loyalty
While many consumers prioritize low prices and convenience, others care more about product quality and an organization's mission statement. Brands that offer high-quality products and share the same values as their customers can generate trust and repeat business.
Organizations can take the following steps to increase brand loyalty:
- Offer a consistent brand identity. People tend to purchase from brands they recognize and trust. A consistent brand image across packaging and advertising helps consumers become familiar with an organization.
- Focus on quality. Many consumers remain loyal to brands that offer high-quality products and services. Quality builds trust, justifies premium pricing and encourages repeat purchases.
- Align the brand with a mission. Consumers want to support brands that share their values. Ethical business practices and social responsibility initiatives can strengthen emotional connections to a brand.
All organizations can devise strategies to maximize customer retention. Although some business models might favor customer loyalty and others lean toward brand loyalty, organizations can benefit from either strategy.
Editor's note: This article was originally published in 2023 and was updated to reflect changes in the CX industry.
Tim Murphy is associate site editor for Informa TechTarget's Customer Experience and Content Management sites.






