
What is C-level (C-suite)?
C-level, also called the C-suite, is a term used to describe high-ranking executive titles in an organization. The letter C, in this context, stands for "chief," as in chief executive officer and chief operating officer.
The C-Suite includes the senior executives and managers whose job titles start with "C," such as the chief executive officer (CEO), chief financial officer (CFO), chief information officer (CIO), chief technology officer (CTO), chief operating officer (COO), and so on.
In recent years, positions like chief diversity officer (CDO), chief compliance officer (CCO), chief risk officer (CRO) and chief information security officer (CISO) have also emerged as part of the C-suite.
Officers who hold C-level positions are typically considered the most powerful, influential members of an organization; consequently, they set the company's strategy, make high-stakes decisions, and ensure that daily operations align with fulfilling the company's strategic goals. They are also typically the highest-paid people in a company, often because their jobs involve a lot of stress and responsibility. In many companies, especially larger companies, the compensation of C-suite staff is tied to the company's revenues and profits. More and more companies and regulators also hold C-level leaders responsible for the company's regulatory mistakes or missteps, in which case, they could face legal or civil action in a court of law.
This article is part of
The evolving CIO role: From IT operator to business strategist
Which positions are part of the C-suite?
The number of positions and kinds of titles in the C-suite vary from company to company. This reflects the different sizes of companies, with larger ones often having more executive positions to distribute the correspondingly large workload.
Variations reflect each organization's missions and maturity. For example, a healthcare company might need a chief medical officer, while a company focused on developing cutting-edge technology products might have a chief innovation officer.
C-suite positions might also change over time. Some positions have evolved with business needs and have become widely accepted; the chief information officer role has evolved in the past several decades as businesses seized on technology -- first, to automate processes for efficiencies and cost-savings and, now, to transform the services they offer and how they are delivered.
Depending on the company type, size, country of operation and industry, the C-Suite might include some or all the following positions:
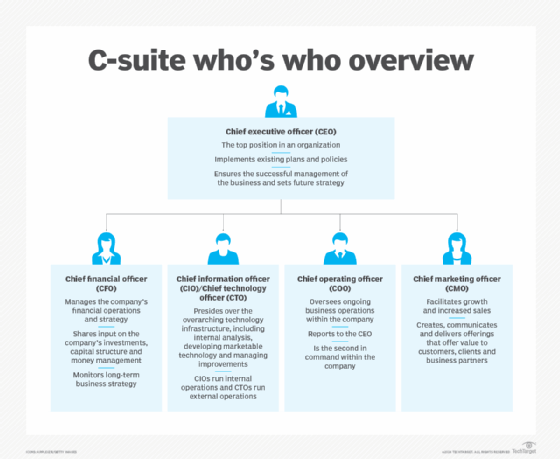
Chief executive officer (CEO). CEOs are responsible for the organization's success or failure, overseeing the entire operation at a high level. They set future strategies and implement plans and policies to ensure the successful management of the business. The CEO also hires other C-suite executives and typically can fire those who do not perform to set standards. As such, the CEO is the boss of all the other executives.
Chief operating officer (COO). COOs are generally second in command and might also sit on the board of directors with the CEO. They oversee the organization's daily operations, creating the governing policies and strategies. In the absence of a chief human resources officer (CHRO), the COO might also handle the firm's HR function.
Chief financial officer (CFO). The CFO oversees the organization's financial affairs, including developing annual budgets, managing cash flow and overseeing financial reporting and regulatory compliance.
Chief marketing officer (CMO). The CMO oversees marketing strategy. This includes advertising, brand management and market research. Responsibilities can also include overseeing a company's advanced technologies, such as business intelligence initiatives and mobility strategy. Some CMOs also have broadened their responsibilities to act as the voice of the company's customers.
Chief information officer (CIO) and chief technology officer (CTO). In the past, these titles were almost interchangeable. Now, they are increasingly separate functions and roles. The CTO commonly oversees the company's information systems and technologies. The CIO usually manages research and development, oversees the development of technologies into products and services, and ensures that all IT initiatives align with business goals.
Chief human resources officer (CHRO). The CHRO oversees human capital management. Their most important task is to set up and enable the talent strategy, encompassing talent acquisition and development, employee experience (EX) management, training and development, and succession planning.
Chief compliance officer (CCO). CCOs manage and oversee the organization's compliance responsibilities and issues. They ensure that the company complies with regulatory requirements and employees comply with internal policies and procedures.
Chief security officer (CSO) or chief information security officer (CISO). CSOs or CISOs are tasked with ensuring data and systems security. In general, a CSO is responsible for physical and digital security, while a CISO is only in charge of digital security, although these lines might be blurred depending on the company's requirements and structure.
Chief data officer (CDO) or chief digital officer (CDO). Chief data officers oversee an organization's data governance function. They might also help to aggregate and digitize the data required to demonstrate compliance.
Other examples of C-level job positions
Some C-suite positions are uncommon, appearing only in certain industries or in only a handful of companies. Such positions might become redundant when responsibilities are folded into other positions. They include the following:
Chief analytics officer (CAO). The CAO is responsible for data processing and analysis and insight-generation to support an organization's business functions.
Chief experience officer (CXO). The CXO ensures positive interactions between the organization and its external customers.
Chief green officer (CGO). The CGO is tasked with making an organization environmentally friendly, reducing its environmental and carbon footprint, and driving sustainability efforts. This includes energy-efficient construction, e-cycling and e-waste mitigation, recycling, LEED compliance, meeting OSHA standards, and ensuring clean production of the firm's products or services.
Chief IT architect (CITA). The CITA is responsible for syncing technology frameworks across the organization's business units and solving integration problems. This person might oversee and coordinate the efforts of other technology-specific architects, including the chief security architect, chief data architect, chief mobile architect and chief cloud architect.
Chief knowledge officer (CKO). The CKO gathers, organizes, shares and analyzes an organization's knowledge and manages the resources, documents and people involved in these activities.
Chief learning officer (CLO). The CLO ensures that a company's corporate learning program and strategy supports its overall business goals and talent management efforts.
Chief medical information officer (CMIO). The CMIO serves as the bridge between medical and IT departments at a healthcare organization and often leads teams that work on clinical programs or medical and scientific research.
Chief privacy officer (CPO). The CPO is charged with developing and implementing policies designed to protect employee and customer data from unauthorized access, cyberattacks and data breaches.
Chief process and innovation officer (CPIO). The CPIO identifies the business processes that could be improved and recommends ways to optimize them in terms of repeatability, consistency, efficiency or profitability.
Chief procurement officer (CPO). The CPO is responsible for the strategic acquisition of goods and services that support the company's functions and operations.
Chief reputation officer (CRO). The CRO oversees activities that could impact public perception of the organization or goodwill.
Chief risk officer (CRO). The CRO is tasked with assessing and mitigating significant threats to an enterprise's capital and earnings. These risks might be operational, competitive, regulatory, technological, environmental, and more.
Chief social scientist (CSS). The CSS is charged with developing policies that ensure a good work environment for employees while maintaining economic profitability for the company.
Chief strategy officer (CSO). The CSO helps formulate, facilitate and communicate an organization's plans for the future.
Chief trust officer (CTO). The CTO works to build confidence around the collection, storage, processing and use of customer information.
Essential skills and desirable qualities for C-level executives
Successful C-level executives have a combination of leadership, management and interpersonal skills. The first two are vital because they set the tone for how the company will function, plan and compete. Their critical thinking and decision-making skills will direct the firm toward success and strengthen its competitive posture. Additionally, their change management skills will help the organization adjust to positive or negative changes.
Strong leadership and communication skills are also critical for C-level staff, along with team-building abilities and experience, because they set the direction of the function they oversee and then hire staff to carry out established plans and policies. C-level leaders must also have strong conflict management skills; they're often required to resolve workplace issues that might arise from internal or external sources.
In larger organizations, C-level executives typically do not engage in daily management tasks. However, at small and medium-sized businesses or startup companies, these personnel are often required to wear multiple hats; they might take on some daily management and administrative duties.
In general, successful C-suite managers can do the following:
- Think strategically and play a strong role in shaping a vision for the organization's future.
- Develop a plan for how their functional area will support that strategic vision.
- Rally employees around the strategic vision and ensure they are well-aligned to achieving that vision.
- Prepare and motivate employees to successfully execute on tasks that will move their organizations toward the targeted future state.
- Persuade, influence and inspire their C-suite colleagues, as well as direct reports, managers and employees to make incremental and big improvements that could benefit the organization.
- Guide their departments through changes while minimizing the negative impact of disruptions.
- Draw on deep expertise in the functional areas they oversee.
- Effectively delegate management duties to their subordinates and line managers.
- Assess their direct reports against key metrics to ensure quality performance and improvement over time.
- Effectively communicate to a wide range of both managerial and rank-and-file employees in various settings and via various media, such as email, face-to-face meetings, company newsletters, and set the tone to promote ethical behaviors throughout the company.
- Work well with groups and in one-on-one settings to help create and strengthen the corporate culture and emulate the traits and behaviors of the organization's leadership values.

Corporate executive compensation
C-level executives typically receive the highest compensation within an organization. Pay varies greatly, depending on the size of the company, revenue, market performance and other factors. Compensation can range from hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars annually; it can also involve stock options and high-end perks like signing bonuses, loan forgiveness and even the use of a corporate plane.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual pay for C-suite leaders (specifically chief executives) in the U.S. as of May 2023 is $ 258,900. The hourly pay for these executives is $124.47. This figure varies by industry, with chief executives in local government earning $75.30 per hour, while chief executives working with management, scientific and technical consulting services firms earn as much as $132.17 per hour. The BLS has also observed salary variations by state, with chief executives in New Jersey earning as much as $449,370 annually, while those in North Carolina earn only $337,320.
Other sources report different figures than the BLS. ZipRecruiter, for example, puts the average annual salary for CEOs as of July 2024 at $142,683 ($68.60 an hour). Per Salary.com, this figure is much higher, with CEOs estimated to earn $754,713 per year. The median annual salary for other C-suite executives varies, with Salary.com estimating that COOs, CFOs and CMOs earning $457,468, $363,559 and $230,735, respectively.
How to become a C-level executive
People who get to be C-level executives typically build relationships internally and with executive search firms; they cultivate an extensive professional network that they draw upon when looking to land their next C-suite position. Due to the potential for earning a lot of money, competition for these roles is fierce and it's not easy to break into these upper echelons.
Executive search firms look for candidates who have been successful at other levels of management or in their existing C-level roles. Industry experience and management experience are essential for climbing the corporate ladder and advancing to the C-suite; experience in talent management and product management are also important for attaining a C-level position.
Would-be executive officers must also demonstrate most -- if not all -- the skills typically associated with those corporate titles. Often, they need to market themselves as experts and thought leaders, say, by maintaining a blog, writing articles for well-known websites or e-magazines, or contributing posts or articles to corporate networking platforms like LinkedIn.
Most C-suite leaders are often highly skilled in a specific functional area -- such as technology, in the case of CTOs -- as well as in management and business. Furthermore, successful executive officers often have held senior management positions in more than one line of business and sometimes even at companies in various industries, which broadens their experience and increases their chances of landing their next desired role.
Top executives generally have at least a bachelor's degree, with many companies requiring advanced degrees like MBAs or Ph.D.s to hire or promote personnel to the C-suite. However, many famous corporate titans do not have these degrees but are still successful. Examples include Meta (owner of Facebook) CEO Mark Zuckerberg; the late Steve Jobs, co-founder of Apple; former Microsoft CEO Bill Gates; Virgin Group CEO Richard Branson; and Vogue editor in chief Anna Wintour.
CIOs must work with other C-level executives to lead transformation and meet business goals. With an ever-expanding C-suite, the possibilities for collaboration are endless. Learn about overlooked relationships CIOs should build within the C-suite. Also, explore steps to create a CIO-CEO strategic partnership.







