3D (three dimensions or three dimensional)
What is 3D?
3D, or three dimensional, refers to the three spatial dimensions of width, height and depth. The physical world and everything that is observed in it are three dimensional.
While many flat images such as films and photographs register visually as two dimensional (2D) to the human brain, nothing can physically exist without all three dimensions. This is because everything that exists materially is comprised of atoms which, despite being invisible to the naked eye, are made up of all three spatial dimensions.
Human eyes have 3D perception, also known as depth perception. With depth perception, people see the world in all three spatial dimensions. The visual cortex in each human eye first perceives the three dimensions of space as 2D images. However, humans have stereoscopic vision, which means that the two eyes don't see the exact same image. The slightly different images register in each eye, enabling the brain to compare differences in visual information, process the image's depth and register all three dimensions at once.
What is 3D in computing?
In computing, a 3D image is a computer-generated graphic that provides the perception of depth similar to a real-world object. This technology is commonly used in movies, video games, graphics and virtual reality (VR) projects like the metaverse. However, industries of all types benefit from 3D technology, including real estate, architecture, healthcare, automotive, aeronautics, research and retail.
Computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-generated images (CGI) refer to the use of computer technology to create 3D images. These images can also be printed with 3D printing. 3D printers are able to produce high quality three-dimensional objects such as prosthetic legs.
2D vs. 3D explained
2D and 3D differ in many ways. While everything that exists is technically in 3D, 2D refers to images that appear flat such as paintings, drawings and images on a display screen.
Two dimensions
2D images appear flat because the dimension of depth in these images is so small compared to their width and height that the brain does not register it. 2D also refers to figures in mathematics, such as lines and polygons that have no dimension of depth.

2D images and figures can have the following characteristics:
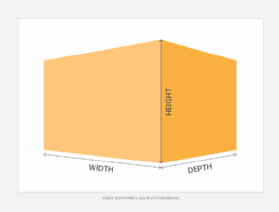
- They only possess the two dimensions of width and height. In graph theory, width and height are known as x and y coordinates, which refer to where a figure's vertices are located on the x-axis and y-axis of a graph.
- They are often referred to as flat, as they lie or are graphed on flat surfaces or planes.
- They are used to denote images that appear flat to the human eye, such as photographs and movies.
- The measure of the space they take up is referred to as area.
Three dimensions
3D images and objects have the following characteristics:
- They possess the added dimension of depth, or the z coordinate which is part of the z-axis.
- Everything that exists in the real world is 3D and has a property often referred to as thickness.
- They denote images or objects that have depth or the illusion of depth such as phones, computers and 3D films.
- The measure of the space 3D objects take up is referred to as volume.
How does 3D work?
The term 3D most often refers to the following three different visual experiences:
Human perception of reality
Human eyes observe the three spatial dimensions of reality, including the third dimension of depth, through depth perception. Depth perception relies on stereoscopic vision, in which the two human eyes see separate images and the brain compares the differences to ascertain information about depth.
Nonstereoscopic functions also give the brain information about depth. These include the phenomenon that objects further away appear smaller and slower than closer objects. Another similar function makes it so an object blocking another object registers in the brain as being closer.
For more on the metaverse, read the following articles:
Metaverse pros and cons: Top benefits and challenges
Metaverse interoperability challenges and impact
Metaverse privacy concerns and how to address them
The Metaverse Standards Forum: What you need to know
Metaverse vs. multiverse vs. omniverse: Key differences
2D graphics that simulate 3D to the naked eye
This happens with images rendered by CAD or CGI technology. CAD is typically used for creating computer models and prototypes that the creation of real-life objects are based on. For instance, the automotive industry uses CAD to build a 3D computer model of a car with more real life detail than a handmade model provides. A CAD model can then be rotated three-dimensionally on a screen, giving designers a sense of what the finished car might look like without having to physically build the model.
CGI is often used for delivering special effects in films and 3D video games. It enables designers to add layers of pixels with depth qualities, also known as textures, which make 3D images look more realistic. CGI also uses ray tracing, which re-creates how light interacts with solid objects in three-dimensional space.
2D graphics that require eyewear to simulate 3D
3D television shows and films are able to mimic stereoscopic perception by creating two different images in each eye. The most popular modern method of creating 3D stereoscopic images for film and television is light polarization. Polarization works by filming a movie on a 3D camera with two different lenses placed a short distance apart, similar to the distance between a pair of human eyes. One lens is polarized horizontally and the other vertically, creating two similar but different images.
To watch a movie with the 3D effect, a viewer must wear polarized glasses with one horizontally polarized lens and one vertically polarized lens. This allows only one image into each eye, forcing the brain to merge the two images together, projecting depth and simulating three dimensions.
How to create 3D images
The process of creating a 3D image depends on the type of graphic, how it will be deployed and what 3D modeling software will be used to create it. Both CAD and CGI use the following two steps to create 3D images:

1. Modeling. A computer-generated 3D model of a physical object provides a mathematical representation of the object, serving as a blueprint for producing the final image. Designers use various techniques with these models. A common technique is non-uniform rational B-spline, which provides mathematical representations of curve and surface geometries, including standard shapes, such as cubes or pyramids, as well as free-form objects, such as cars or medical equipment. A newer approach to modeling is digital sculpting, also called 3D sculpting. Digital sculpting approximates physical sculpting, providing tools that help make manipulating digital forms a more organic process.
2. Rendering. After a model has been completed, rendering is applied to create a realistic image that integrates effects such as lighting, shadow, reflections, textures, materials and other details to make the image as photorealistic as possible. Rendering can be done in advance or in real time. For example, rendering done in advance might be used for a website's graphics or a motion picture, whereas real-time rendering might be used for gaming or an interactive product catalog. Image creation products often support multiple rendering engines that offer different options for how an image is rendered. Rendering engines differ in terms of the underlying rendering methods they use and the features they offer.
Popular products for creating 3D images include the following:
- Autodesk's 3ds Max
- Blender
- Maxon's ZBrush
- NewTek's LightWave 3D
Blender is a free, open source product. Its GUI is based on the Open Graphics Library, an industry-standard application programming interface for rendering graphic images across different hardware and platforms. Tools like Google's artificial intelligence-powered Chimera Painter can also turn 2D images into 3D models.
Common 3D use cases and examples
The use of 3D computer images is fundamental to modern industries such as architecture, engineering, and film and entertainment. The following are some of the most popular types of 3D uses:
- 3D computer graphics. 3D graphics are often made with CAD or CGI technology. They let designers simulate 3D models on a computer before executing a design. They also enable television shows, such as Game of Thrones, to create 3D models for their special effects and to add photorealistic properties to 2D images.
- 3D printing. 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has reshaped modern manufacturing by allowing industries to create objects they weren't able to before with cost effective methods. Today, 3D printers are used to create everything from entire cars to chocolates and even human organs.
- 3D movies. The first 3D movie premiered in 1922, but it was 2009's Avatar that established 3D filmmaking in mainstream entertainment.
- 3D art. This use comprises traditional forms of art such as sculpture and modern techniques as well as 3D digital images that use the same technology as 3D films. 3D art is also created using 3D printers and traditional techniques of optical illusion, such as Edgar Mueller's The Crevasse.
- 3D gaming. This use is popular in VR environments such as the metaverse, where users are represented as 3D avatars and interact in a facsimile of reality. Games such as Axie Infinity are popular, where users can breed, raise and battle fantastical 3D pets.
History of 3D
3D technology is 100 years old and includes the simultaneous development of 3D film, computer graphics and printing. The major milestones include the following:
- 1922. The first recorded instance of a 3D film is the premiere of The Power of Love. It used stereoscopic imaging and required viewers to wear anaglyphic eyewear -- the first form of 3D glasses -- in order to perceive it.
- 1936. The first use of polarized light is demonstrated to the public using photographs printed with Polaroid filters.
- 1952. Bwana Devil, the first color 3D film, premieres and popularizes the well-known but now outdated red-and-blue 3D anaglyphic glasses.
- 1981. Hideo Kodama develops the first version of 3D printing using a layer-by-layer, or additive, manufacturing process, involving photosensitive resins polymerized by UV light.
- 1986. Charles Hull files a patent for the first 3D printing stereolithography (SLA) technology.
- 1988. Hull's company 3D Systems releases the first commercial SLA 3D printer and Scott Crump files the first patent for fused filament fabrication (FFF), today's most popular 3D printing technology which extrudes filaments from a nozzle instead of using light.
- 2000s. CAD technology becomes more widely available.
- 2006. Adrian Bowyer creates the RepRap Project, an open source project, allowing individuals to 3D print their own 3D printers.
- 2008. The first prosthetic leg is printed.
- 2009. The 1980s FFF patents fall into the public domain, giving companies more access to 3D printing technology, leading to innovation and lower-priced printers.
- 2016. Oculus Rift is released as the first consumer VR hardware.
- 2018. A family moves into a 3D printed home.

The future of 3D technology
Three-dimensional images are often associated with the entertainment and gaming industries, especially with the growing sophistication of CGI. 3D images and technologies have also become the bedrock of augmented reality- and VR-based projects like the metaverse. To participate in these AR or VR environments, users are represented by 3D avatars and the images are interactive, making users feel involved. Users often need special equipment or viewers to view and interact with 3D images.

3D printing technology is also revolutionizing the future of multiple industries. It works by adding layers of material on top of each other. 3D printed objects prevent the waste of excess materials and are faster and cheaper to produce.
3D printing's open source technology also makes it more accessible to individuals and small businesses. The technology is used to print apartment buildings, food including beef and body parts including prosthetic limbs, bone structures and even organs.
3D technology is critical to VR worlds like the metaverse. Learn what marketers need to know about staying in front of target audiences in the metaverse.