greenhouse gas
What is greenhouse gas?
A greenhouse gas lets the sun's rays warm the Earth's surface but restricts the heat from escaping into space. Specifically, these gases absorb infrared radiation from the sun in the Earth's atmosphere and release it. Some of the heat released reaches the Earth, along with heat from the sun that has penetrated the atmosphere. As such, greenhouse gas is a major contributing factor to global warming and climate change.
Greenhouse gases operate in much the same way as a physical greenhouse when it blocks heat from escaping a building. The Earth absorbs and releases the solar heat and radiated heat; greenhouse gases reabsorb some of that heat to perpetuate the cycle. The more of these gases that exist in the atmosphere, the more heat is prevented from escaping into space, and the more the Earth heats.
This increase in heat is called the greenhouse effect. Concerns about the greenhouse effect's contribution to global warming potential have prompted agreements among national governments on targets for the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
Examples of greenhouse gas
Common examples of greenhouse gases listed in order of abundance include water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and fluorocarbons, which are combinations of carbon and fluorine.
The presence of some degree of greenhouse gases in the Earth's environment is natural, and this natural greenhouse effect is needed to keep the global ecosystem running. However, too much of these gases has a negative effect on the average temperature of the Earth. Water vapor is the most abundant greenhouse gas. It differs from other gases in having concentrations linked, not to human activities, but to warming that is amplified by other gases with greater human influences.
Why are greenhouse gases important?
The proliferation of greenhouse gases from many sources threatens to increase the average global temperature. The threat of global warming has long-term consequences, such as rising sea water levels and increasingly severe weather.
Despite efforts underway to reduce greenhouse gases, most climate and environmental experts believe that more must be done, and action is needed faster than it's occurring. According to climate scientists, each year that passes without significant greenhouse gas reductions puts the world on a course toward a future with many climate-related problems.
Which greenhouse gases contribute to global warming?
The major greenhouse gases each affect the Earth's climate system in different ways. Contributors include the following:
- Water vapor. This is the most prevalent greenhouse gas in the atmosphere. However, it dissipates after a few days, rendering it less of a threat compared to carbon dioxide, which remains in the atmosphere for years.
- Carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide emissions are released from natural sources, including the exhaled breath of living creatures and events such as volcanic eruptions. Carbon dioxide is also produced by the burning of fossil fuels to produce electricity and run manufacturing and other industrial processes. As a result, these emissions have increased over 50% since the industrial revolution in the 18th century, making carbon dioxide one of the most prevalent greenhouse gases.
- Methane. Methane is produced naturally through undersea reservoirs and biological decomposition. It also results from human activities, such as raising farm animals, operating landfills, and producing oil and gas. Methane is the principal component of natural gas.
- Nitrous oxide. Nitrous oxide is also known as laughing gas. It's created from commercial fertilizers, the combustion of fossil fuels and the production of nitric acid.
- Ozone. When nitrous oxides and other fossil fuel gases interact with sunlight, it forms ozone low in the Earth's atmosphere. Low-level ozone is a component of smog and acts as a greenhouse gas.
- Fluorocarbons. The fluorocarbon gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include chlorofluorocarbons, or CFCs; hydrofluorocarbons, or HFCs; perfluorocarbons; and sulfur hexafluoride. They are commonly used to provide refrigerants. While each gas constitutes a tiny proportion of greenhouse gases, their propensity to trap heat makes them a key concern.
How can greenhouse gases be reduced?
The commonly recommended way to reduce the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases --particularly water vapor, carbon and methane emissions -- is to decrease fossil fuel combustion and replace it with environment-friendly renewable-energy technologies such as solar, wind and geothermal. Switching to electric vehicles, and increasing reuse and recycling are two other steps.
The United States and several other countries have adopted a mitigation strategy to cut global greenhouse gas emissions to a net-zero level by 2050. The U.S. commitment was expressed in an official White House document released in November 2021.
Green data centers are a way for companies and other organizations to cut their energy use and total emissions, and reduce their company's carbon footprint. These efforts include some simple actions, such as the following:
- Minimizing land use and building footprints.
- Using low-emission building materials, carpets and paints.
- Planting sustainable landscaping.
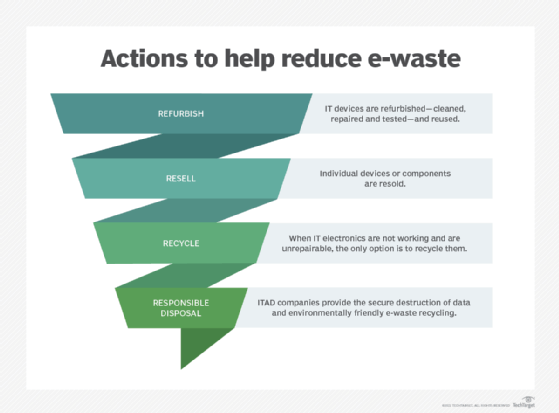
- Recycling e-waste.
- Installing catalytic converters on generators.
- Opting for photovoltaic, heat pump, evaporative cooling and other energy-efficiency technologies.
- Running hybrid or electric vehicles.
Learn more about the environmental impact of data centers and ways to reduce the damage.
