
Oracle Cloud
What is Oracle Cloud?
Oracle Cloud is a subscription-based public cloud services offering from database company Oracle. The global data centers in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) provide servers, storage, network, applications, data management and other services that support dedicated cloud, multicloud, hybrid cloud and on-premises environments. Customers use Oracle Cloud to build, deploy, automate and manage workloads and enterprise applications in the cloud.
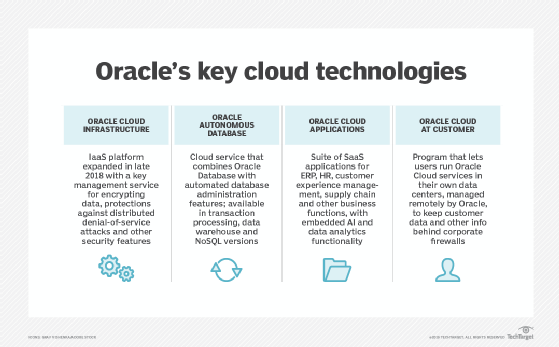
Oracle Cloud offers infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), software as a service and data as a service. These services can be accessed on demand over the internet. Oracle Cloud lets both virtualized multi-tenant deployment and bare-metal compute services connect with a single application programming interface (API). Oracle Cloud offerings also include machine learning and load balancer services and an autonomous database.
Oracle Cloud competes with the market-leading Amazon Web Services (AWS), as well as Google Cloud, IBM Cloud and Microsoft Azure. As of 2022, Oracle Cloud's global market share stood at 2%, according to Synergy Research Group.
How many cloud regions does Oracle Cloud have?
Oracle Cloud has a global network of managed data centers running its cloud offerings. As of December 2022, Oracle had data centers in 41 cloud regions spanning 22 countries. Oracle Cloud is also connected with Microsoft Azure cloud services in 12 cloud regions.
Oracle uses Oracle Cloud services to provide cloud apps, servers, storage and processing on its global network. The network itself is built on 25 Gb Ethernet. The nodes are no more than one hop from one another with the flat network topology, enabling Oracle to offer a strong service-level agreement.
Benefits of Oracle Cloud
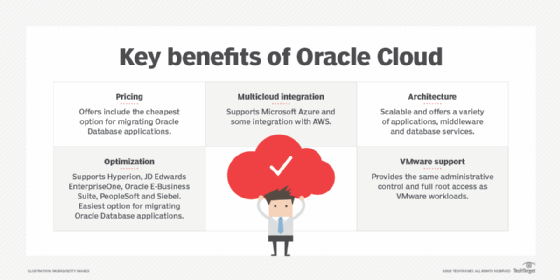
The benefits of Oracle Cloud include the following:
- Pricing. Oracle Cloud's cloud storage and data migration offerings are often cheaper than competitors such as AWS.
- Optimization for Oracle workloads. Oracle Cloud is based on the same IaaS technology as Oracle Database, making cloud migration from Oracle Database to Oracle Cloud easier than to other cloud offerings. Oracle Cloud also supports Oracle applications, such as Hyperion, JD Edwards EnterpriseOne, Oracle E-Business Suite, PeopleSoft and Siebel.
- Architecture. Oracle Cloud offers cloud-native applications, middleware and database services, making it unnecessary for users to seek third-party services. Oracle Cloud's high-performance computing architecture is scalable, enabling organizations to expand their IT platforms.
- Multicloud integration. According to Gartner's 2022 "Magic Quadrant for Cloud Infrastructure and Platform Services," one of Oracle's strengths is its multicloud approach in supporting Microsoft Azure and integration with AWS. For example, Oracle Exadata database platform runs on Oracle Cloud and Azure. Oracle can also be connected to AWS with native virtual private network services.
- VMware support. According to Oracle, OCI provides the same experience as on-premises VMware workloads in the Oracle Cloud, including the same administrative control and full root access. The difference is virtual machines in the cloud benefit from cloud elasticity, as well as the ability to integrate with over 50 Oracle Cloud platform services.
Drawbacks of Oracle Cloud
The drawbacks of Oracle Cloud include the following:
- Poor integration. While Oracle Cloud has tight integration with Microsoft Azure and VMware and limited integration with AWS, it doesn't integrate well with other non-Oracle offerings, according to the Gartner report.
- Lacks extensive third-party ecosystem. Oracle Cloud has less third-party support than AWS and Microsoft, which both have strong developer This is, in part, because Oracle's small market share is a disincentive to developers.
- The Oracle brand. According to Gartner's 2022 Magic Quadrant report, Oracle has a negative brand association due to years of "tough compliance enforcement and inconsistent sales and support." Because of this, most Oracle Cloud users integrate with Oracle Database applications.
- Difficult for small and midsize businesses (SMBs). OCI's architecture generally requires IT expertise to use and is aimed primarily at large enterprises. Therefore, it's not often used in the non-Oracle or SMB
Comparing Oracle Cloud to other cloud providers
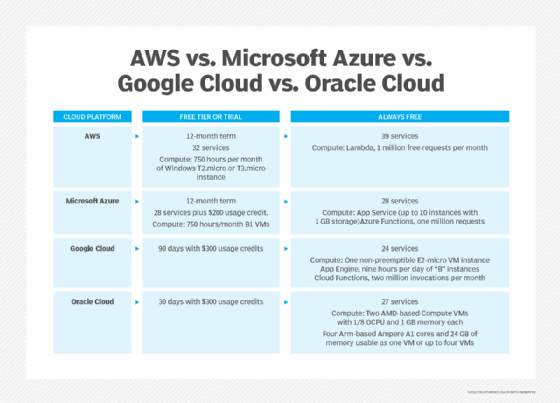
Oracle Cloud is often compared to AWS, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud and Microsoft Azure. Gartner categorized Oracle as visionary in its 2022 Magic Quadrant report, a step up from its 2021 categorization as a niche player. In the same report, Gartner analysts labeled AWS, Google Cloud and Azure as leaders and IBM as a niche player.
In contrast to competitors like AWS, Oracle Cloud has a more comprehensive multicloud integration wan innovative model with regards to sovereign clouds that enable developers in countries with strong data privacy laws to access the cloud and edge infrastructure.

However, with only 2% of the cloud infrastructure services market, Oracle isn't a major provider. The leading cloud providers are the following:
- AWS is the cloud computing market leader with 33% market share, according to Synergy Research Group. It has an extensive third-party developer ecosystem. However, it's not as aggressive with multicloud support as Oracle.
- Microsoft Azure, with 22% market share, is a leader in cloud-based data analytics, including data warehouses and data lakes. Azure also supports multicloud and hybrid cloud environments.
- Google Cloud, with 10% of the market, has a variety of IaaS, PaaS and sovereign cloud offerings.
- IBM Cloud has a smaller market share than the three cloud infrastructure services leaders. It focuses mostly on vertical markets, including regulated industries and retail.
Oracle Cloud is considered a cloud computing innovator. Learn the pros and cons of cloud computing and how the market has changed in the last few years.
