
What is AI (Artificial Intelligence)? Definition, Types, Examples & Use Cases
What is AI?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. It includes learning, reasoning, and self-correction. Examples of AI applications include expert systems, natural language processing (NLP), speech recognition, machine vision, and generative tools like ChatGPT and Perplexity.
As the hype around AI has accelerated, vendors have scrambled to promote how their products and services incorporate it. Often, what they refer to as "AI" is a well-established technology such as machine learning.
AI requires specialized hardware and software for writing and training machine learning algorithms. No single programming language is used exclusively in AI, but Python, R, Java, C++ and Julia are all popular languages among AI developers.
How does AI work?
In general, AI systems work by ingesting large amounts of labeled training data, analyzing that data for correlations and patterns, and using these patterns to make predictions about future states.
This article is part of
What is enterprise AI? A complete guide for businesses
For example, an AI chatbot that is fed examples of text can learn to generate lifelike exchanges with people, and an image recognition tool can learn to identify and describe objects in images by reviewing millions of examples. Generative AI techniques, which have advanced rapidly over the past few years, can create realistic text, images, music and other media.
Programming AI systems focuses on cognitive skills such as the following:
- Learning. This aspect of AI programming involves acquiring data and creating rules, known as algorithms, to transform it into actionable information. These algorithms provide computing devices with step-by-step instructions for completing specific tasks.
- Reasoning. This aspect involves choosing the right algorithm to reach a desired outcome.
- Self-correction. This aspect involves algorithms continuously learning and tuning themselves to provide the most accurate results possible.
- Creativity. This aspect uses neural networks, rule-based systems, statistical methods and other AI techniques to generate new images, text, music, ideas and so on.
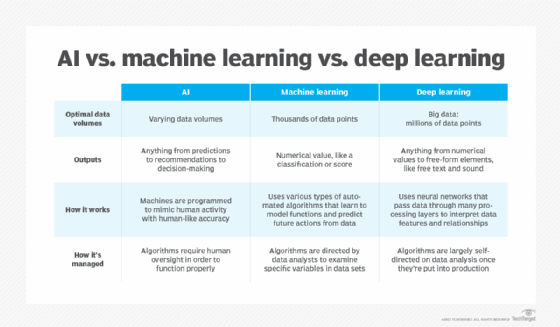
Differences among AI, machine learning and deep learning
The terms AI, machine learning and deep learning are often used interchangeably, especially in companies' marketing materials, but they have distinct meanings. In short, AI describes the broad concept of machines simulating human intelligence, while machine learning and deep learning are specific techniques within this field.
The term AI, coined in the 1950s, encompasses an evolving and wide range of technologies that aim to simulate human intelligence, including machine learning and deep learning. Machine learning enables software to autonomously learn patterns and predict outcomes by using historical data as input. This approach became more effective with the availability of large training data sets. Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, aims to mimic the brain's structure using layered neural networks. It underpins many major breakthroughs and recent advances in AI, including autonomous vehicles and ChatGPT.
Why is AI important?
AI is important for its potential to change how we live, work and play. It has been effectively used in business to automate tasks traditionally done by humans, including customer service, lead generation, fraud detection and quality control.
In a number of areas, AI can perform tasks more efficiently and accurately than humans. It is especially useful for repetitive, detail-oriented tasks such as analyzing large numbers of legal documents to ensure relevant fields are properly filled in. AI's ability to process massive data sets gives enterprises insights into their operations they might not otherwise have noticed. The rapidly expanding array of generative AI tools is also becoming important in fields ranging from education to marketing to product design.
Advances in AI techniques have not only helped fuel an explosion in efficiency, but also opened the door to entirely new business opportunities for some larger enterprises. Prior to the current wave of AI, for example, it would have been hard to imagine using computer software to connect riders to taxis on demand, yet Uber has become a Fortune 500 company by doing just that.
AI has become central to many of today's largest and most successful companies, including Alphabet, Apple, Microsoft and Meta, which use AI to improve their operations and outpace competitors. At Alphabet subsidiary Google, for example, AI is central to its eponymous search engine, and self-driving car company Waymo began as an Alphabet division. The Google Brain research lab also invented the transformer architecture that underpins recent NLP breakthroughs such as OpenAI's ChatGPT.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of artificial intelligence?
AI technologies, particularly deep learning models such as artificial neural networks, can process large amounts of data much faster and make predictions more accurately than humans can. While the huge volume of data created on a daily basis would bury a human researcher, AI applications using machine learning can take that data and quickly turn it into actionable information.
A primary disadvantage of AI is that it is expensive to process the large amounts of data AI requires. As AI techniques are incorporated into more products and services, organizations must also be attuned to AI's potential to create biased and discriminatory systems, intentionally or inadvertently.
Advantages of AI
The following are some advantages of AI:
- Excellence in detail-oriented jobs. AI is a good fit for tasks that involve identifying subtle patterns and relationships in data that might be overlooked by humans. For example, in oncology, AI systems have demonstrated high accuracy in detecting early-stage cancers, such as breast cancer and melanoma, by highlighting areas of concern for further evaluation by healthcare professionals.
- Efficiency in data-heavy tasks. AI systems and automation tools dramatically reduce the time required for data processing. This is particularly useful in sectors like finance, insurance and healthcare that involve a great deal of routine data entry and analysis, as well as data-driven decision-making. For example, in banking and finance, predictive AI models can process vast volumes of data to forecast market trends and analyze investment risk.
- Time savings and productivity gains. AI and robotics can not only automate operations but also improve safety and efficiency. In manufacturing, for example, AI-powered robots are increasingly used to perform hazardous or repetitive tasks as part of warehouse automation, thus reducing the risk to human workers and increasing overall productivity.
- Consistency in results. Today's analytics tools use AI and machine learning to process extensive amounts of data in a uniform way, while retaining the ability to adapt to new information through continuous learning. For example, AI applications have delivered consistent and reliable outcomes in legal document review and language translation.
- Customization and personalization. AI systems can enhance user experience by personalizing interactions and content delivery on digital platforms. On e-commerce platforms, for example, AI models analyze user behavior to recommend products suited to an individual's preferences, increasing customer satisfaction and engagement.
- Round-the-clock availability. AI programs do not need to sleep or take breaks. For example, AI-powered virtual assistants can provide uninterrupted, 24/7 customer service even under high interaction volumes, improving response times and reducing costs.
- Scalability. AI systems can scale to handle growing amounts of work and data. This makes AI well suited for scenarios where data volumes and workloads can grow exponentially, such as internet search and business analytics.
- Accelerated research and development. AI can speed up the pace of R&D in fields such as pharmaceuticals and materials science. By rapidly simulating and analyzing many possible scenarios, AI models can help researchers discover new drugs, materials or compounds more quickly than traditional methods.
- Sustainability and conservation. AI and machine learning are increasingly used to monitor environmental changes, predict future weather events and manage conservation efforts. Machine learning models can process satellite imagery and sensor data to track wildfire risk, pollution levels and endangered species populations, for example.
- Process optimization. AI is used to streamline and automate complex processes across various industries. For example, AI models can identify inefficiencies and predict bottlenecks in manufacturing workflows, while in the energy sector, they can forecast electricity demand and allocate supply in real time.
Disadvantages of AI
The following are some disadvantages of AI:
- High costs. Developing AI can be very expensive. Building an AI model requires a substantial upfront investment in infrastructure, computational resources and software to train the model and store its training data. After initial training, there are further ongoing costs associated with model inference and retraining. As a result, costs can rack up quickly, particularly for advanced, complex systems like generative AI applications; OpenAI CEO Sam Altman has stated that training the company's GPT-4 model cost over $100 million.
- Technical complexity. Developing, operating and troubleshooting AI systems -- especially in real-world production environments -- requires a great deal of technical know-how. In many cases, this knowledge differs from that needed to build non-AI software. For example, building and deploying a machine learning application involves a complex, multistage and highly technical process, from data preparation to algorithm selection to parameter tuning and model testing.
- Talent gap. Compounding the problem of technical complexity, there is a significant shortage of professionals trained in AI and machine learning compared with the growing need for such skills. This gap between AI talent supply and demand means that, even though interest in AI applications is growing, many organizations cannot find enough qualified workers to staff their AI initiatives.
- Algorithmic bias. AI and machine learning algorithms reflect the biases present in their training data -- and when AI systems are deployed at scale, the biases scale, too. In some cases, AI systems may even amplify subtle biases in their training data by encoding them into reinforceable and pseudo-objective patterns. In one well-known example, Amazon developed an AI-driven recruitment tool to automate the hiring process that inadvertently favored male candidates, reflecting larger-scale gender imbalances in the tech industry.
- Difficulty with generalization. AI models often excel at the specific tasks for which they were trained but struggle when asked to address novel scenarios. This lack of flexibility can limit AI's usefulness, as new tasks might require the development of an entirely new model. An NLP model trained on English-language text, for example, might perform poorly on text in other languages without extensive additional training. While work is underway to improve models' generalization ability -- known as domain adaptation or transfer learning -- this remains an open research problem.
- Job displacement. AI can lead to job loss if organizations replace human workers with machines -- a growing area of concern as the capabilities of AI models become more sophisticated and companies increasingly look to automate workflows using AI. For example, some copywriters have reported being replaced by large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT. While widespread AI adoption may also create new job categories, these may not overlap with the jobs eliminated, raising concerns about economic inequality and reskilling.
- Security vulnerabilities. AI systems are susceptible to a wide range of cyberthreats, including data poisoning and adversarial machine learning. Hackers can extract sensitive training data from an AI model, for example, or trick AI systems into producing incorrect and harmful output. This is particularly concerning in security-sensitive sectors such as financial services and government.
- Environmental impact. The data centers and network infrastructures that underpin the operations of AI models consume large amounts of energy and water. Consequently, training and running AI models has a significant impact on the climate. AI's carbon footprint is especially concerning for large generative models, which require a great deal of computing resources for training and ongoing use.
- Legal issues. AI raises complex questions around privacy and legal liability, particularly amid an evolving AI regulation landscape that differs across regions. Using AI to analyze and make decisions based on personal data has serious privacy implications, for example, and it remains unclear how courts will view the authorship of material generated by LLMs trained on copyrighted works.
Strong AI vs. weak AI
AI can generally be categorized into two types: narrow (or weak) AI and general (or strong) AI.
- Narrow AI. This form of AI refers to models trained to perform specific tasks. Narrow AI operates within the context of the tasks it is programmed to perform, without the ability to generalize broadly or learn beyond its initial programming. Examples of narrow AI include virtual assistants, such as Apple Siri and Amazon Alexa, and recommendation engines, such as those found on streaming platforms like Spotify and Netflix.
- General AI. This type of AI, which does not currently exist, is more often referred to as artificial general intelligence (AGI). If created, AGI would be capable of performing any intellectual task that a human being can. To do so, AGI would need the ability to apply reasoning across a wide range of domains to understand complex problems it was not specifically programmed to solve. This, in turn, would require something known in AI as fuzzy logic: an approach that allows for gray areas and gradations of uncertainty, rather than binary, black-and-white outcomes.
Importantly, the question of whether AGI can be created -- and the consequences of doing so -- remains hotly debated among AI experts. Even today's most advanced AI technologies, such as ChatGPT and other highly capable LLMs, do not demonstrate cognitive abilities on par with humans and cannot generalize across diverse situations. ChatGPT, for example, is designed for natural language generation, and it is not capable of going beyond its original programming to perform tasks such as complex mathematical reasoning.
4 types of AI
AI can be categorized into four types, beginning with the task-specific intelligent systems in wide use today and progressing to sentient systems, which do not yet exist.
The categories are as follows:
- Type 1: Reactive machines. These AI systems have no memory and are task specific. An example is Deep Blue, the IBM chess program that beat Russian chess grandmaster Garry Kasparov in the 1990s. Deep Blue was able to identify pieces on a chessboard and make predictions, but because it had no memory, it could not use past experiences to inform future ones.
- Type 2: Limited memory. These AI systems have memory, so they can use past experiences to inform future decisions. Some of the decision-making functions in self-driving cars are designed this way.
- Type 3: Theory of mind. Theory of mind is a psychology term. When applied to AI, it refers to a system capable of understanding emotions. This type of AI can infer human intentions and predict behavior, a necessary skill for AI systems to become integral members of historically human teams.
- Type 4: Self-awareness. In this category, AI systems have a sense of self, which gives them consciousness. Machines with self-awareness understand their own current state. This type of AI does not yet exist.
What are examples of AI technology, and how is it used today?
AI technologies can enhance existing tools' functionalities and automate various tasks and processes, affecting numerous aspects of everyday life. The following are a few prominent examples.
Automation
AI enhances automation technologies by expanding the range, complexity and number of tasks that can be automated. An example is robotic process automation (RPA), which automates repetitive, rules-based data processing tasks traditionally performed by humans. Because AI helps RPA bots adapt to new data and dynamically respond to process changes, integrating AI and machine learning capabilities enables RPA to manage more complex workflows.
Machine learning
Machine learning is the science of teaching computers to learn from data and make decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so. Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, uses sophisticated neural networks to perform what is essentially an advanced form of predictive analytics.
Machine learning algorithms can be broadly classified into three categories: supervised learning, unsupervised learning and reinforcement learning.
- Supervised learning trains models on labeled data sets, enabling them to accurately recognize patterns, predict outcomes or classify new data.
- Unsupervised learning trains models to sort through unlabeled data sets to find underlying relationships or clusters.
- Reinforcement learning takes a different approach, in which models learn to make decisions by acting as agents and receiving feedback on their actions.
There is also semi-supervised learning, which combines aspects of supervised and unsupervised approaches. This technique uses a small amount of labeled data and a larger amount of unlabeled data, thereby improving learning accuracy while reducing the need for labeled data, which can be time and labor intensive to procure.
Computer vision
Computer vision is a field of AI that focuses on teaching machines how to interpret the visual world. By analyzing visual information such as camera images and videos using deep learning models, computer vision systems can learn to identify and classify objects and make decisions based on those analyses.
The primary aim of computer vision is to replicate or improve on the human visual system using AI algorithms. Computer vision is used in a wide range of applications, from signature identification to medical image analysis to autonomous vehicles. Machine vision, a term often conflated with computer vision, refers specifically to the use of computer vision to analyze camera and video data in industrial automation contexts, such as production processes in manufacturing.
Natural language processing
NLP refers to the processing of human language by computer programs. NLP algorithms can interpret and interact with human language, performing tasks such as translation, speech recognition and sentiment analysis. One of the oldest and best-known examples of NLP is spam detection, which looks at the subject line and text of an email and decides whether it is junk. More advanced applications of NLP include LLMs such as ChatGPT and Anthropic's Claude.
Robotics
Robotics is a field of engineering that focuses on the design, manufacturing and operation of robots: automated machines that replicate and replace human actions, particularly those that are difficult, dangerous or tedious for humans to perform. Examples of robotics applications include manufacturing, where robots perform repetitive or hazardous assembly-line tasks, and exploratory missions in distant, difficult-to-access areas such as outer space and the deep sea.
The integration of AI and machine learning significantly expands robots' capabilities by enabling them to make better-informed autonomous decisions and adapt to new situations and data. For example, robots with machine vision capabilities can learn to sort objects on a factory line by shape and color.
Autonomous vehicles
Autonomous vehicles, more colloquially known as self-driving cars, can sense and navigate their surrounding environment with minimal or no human input. These vehicles rely on a combination of technologies, including radar, GPS, and a range of AI and machine learning algorithms, such as image recognition.
These algorithms learn from real-world driving, traffic and map data to make informed decisions about when to brake, turn and accelerate; how to stay in a given lane; and how to avoid unexpected obstructions, including pedestrians. Although the technology has advanced considerably in recent years, the ultimate goal of an autonomous vehicle that can fully replace a human driver has yet to be achieved.
Generative AI
The term generative AI refers to machine learning systems that can generate new data from text prompts -- most commonly text and images, but also audio, video, software code, and even genetic sequences and protein structures. Through training on massive data sets, these algorithms gradually learn the patterns of the types of media they will be asked to generate, enabling them later to create new content that resembles that training data.
Generative AI saw a rapid growth in popularity following the introduction of widely available text and image generators in 2022, such as ChatGPT, Dall-E and Midjourney, and is increasingly applied in business settings. While many generative AI tools' capabilities are impressive, they also raise concerns around issues such as copyright, fair use and security that remain a matter of open debate in the tech sector.
What are the applications of AI?
AI has entered a wide variety of industry sectors and research areas. The following are several of the most notable examples.
AI in healthcare
AI is applied to a range of tasks in the healthcare domain, with the overarching goals of improving patient outcomes and reducing systemic costs. One major application is the use of machine learning models trained on large medical data sets to assist healthcare professionals in making better and faster diagnoses. For example, AI-powered software can analyze CT scans and alert neurologists to suspected strokes.
On the patient side, online virtual health assistants and chatbots can provide general medical information, schedule appointments, explain billing processes and complete other administrative tasks. Predictive modeling AI algorithms can also be used to combat the spread of pandemics such as COVID-19.
AI in business
AI is increasingly integrated into various business functions and industries, aiming to improve efficiency, customer experience, strategic planning and decision-making. For example, machine learning models power many of today's data analytics and customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, helping companies understand how to best serve customers through personalizing offerings and delivering better-tailored marketing.
Virtual assistants and chatbots are also deployed on corporate websites and in mobile applications to provide round-the-clock customer service and answer common questions. In addition, more and more companies are exploring the capabilities of generative AI tools such as ChatGPT for automating tasks such as document drafting and summarization, product design and ideation, and computer programming.
AI in education
AI has a number of potential applications in education technology. It can automate aspects of grading processes, giving educators more time for other tasks. AI tools can also assess students' performance and adapt to their individual needs, facilitating more personalized learning experiences that enable students to work at their own pace. AI tutors could also provide additional support to students, ensuring they stay on track. The technology could also change where and how students learn, perhaps altering the traditional role of educators.
As the capabilities of LLMs such as ChatGPT and Google Gemini grow, such tools could help educators craft teaching materials and engage students in new ways. However, the advent of these tools also forces educators to reconsider homework and testing practices and revise plagiarism policies, especially given that AI detection and AI watermarking tools are currently unreliable.
AI in finance and banking
Banks and other financial organizations use AI to improve their decision-making for tasks such as granting loans, setting credit limits and identifying investment opportunities. In addition, algorithmic trading powered by advanced AI and machine learning has transformed financial markets, executing trades at speeds and efficiencies far surpassing what human traders could do manually.
AI and machine learning have also entered the realm of consumer finance. For example, banks use AI chatbots to inform customers about services and offerings and to handle transactions and questions that don't require human intervention. Similarly, Intuit offers generative AI features within its TurboTax e-filing product that provide users with personalized advice based on data such as the user's tax profile and the tax code for their location.
AI in law
AI is changing the legal sector by automating labor-intensive tasks such as document review and discovery response, which can be tedious and time consuming for attorneys and paralegals. Law firms today use AI and machine learning for a variety of tasks, including analytics and predictive AI to analyze data and case law, computer vision to classify and extract information from documents, and NLP to interpret and respond to discovery requests.
In addition to improving efficiency and productivity, this integration of AI frees up human legal professionals to spend more time with clients and focus on more creative, strategic work that AI is less well suited to handle. With the rise of generative AI in law, firms are also exploring using LLMs to draft common documents, such as boilerplate contracts.
AI in entertainment and media
The entertainment and media business uses AI techniques in targeted advertising, content recommendations, distribution and fraud detection. The technology enables companies to personalize audience members' experiences and optimize delivery of content.
Generative AI is also a hot topic in the area of content creation. Advertising professionals are already using these tools to create marketing collateral and edit advertising images. However, their use is more controversial in areas such as film and TV scriptwriting and visual effects, where they offer increased efficiency but also threaten the livelihoods and intellectual property of humans in creative roles.
AI in journalism
In journalism, AI can streamline workflows by automating routine tasks, such as data entry and proofreading. Investigative journalists and data journalists also use AI to find and research stories by sifting through large data sets using machine learning models, thereby uncovering trends and hidden connections that would be time consuming to identify manually. For example, five finalists for the 2024 Pulitzer Prizes for journalism disclosed using AI in their reporting to perform tasks such as analyzing massive volumes of police records. While the use of traditional AI tools is increasingly common, the use of generative AI to write journalistic content is open to question, as it raises concerns around reliability, accuracy and ethics.
AI in software development and IT
AI is used to automate many processes in software development, DevOps and IT. For example, AIOps tools enable predictive maintenance of IT environments by analyzing system data to forecast potential issues before they occur, and AI-powered monitoring tools can help flag potential anomalies in real time based on historical system data. Generative AI tools such as GitHub Copilot and Tabnine are also increasingly used to produce application code based on natural-language prompts. While these tools have shown early promise and interest among developers, they are unlikely to fully replace software engineers. Instead, they serve as useful productivity aids, automating repetitive tasks and boilerplate code writing.
AI in security
AI and machine learning are prominent buzzwords in security vendor marketing, so buyers should take a cautious approach. Still, AI is indeed a useful technology in multiple aspects of cybersecurity, including anomaly detection, reducing false positives and conducting behavioral threat analytics. For example, organizations use machine learning in security information and event management (SIEM) software to detect suspicious activity and potential threats. By analyzing vast amounts of data and recognizing patterns that resemble known malicious code, AI tools can alert security teams to new and emerging attacks, often much sooner than human employees and previous technologies could.
AI in manufacturing
Manufacturing has been at the forefront of incorporating robots into workflows, with recent advancements focusing on collaborative robots, or cobots. Unlike traditional industrial robots, which were programmed to perform single tasks and operated separately from human workers, cobots are smaller, more versatile and designed to work alongside humans. These multitasking robots can take on responsibility for more tasks in warehouses, on factory floors and in other workspaces, including assembly, packaging and quality control. In particular, using robots to perform or assist with repetitive and physically demanding tasks can improve safety and efficiency for human workers.
AI in transportation
In addition to AI's fundamental role in operating autonomous vehicles, AI technologies are used in automotive transportation to manage traffic, reduce congestion and enhance road safety. In air travel, AI can predict flight delays by analyzing data points such as weather and air traffic conditions. In overseas shipping, AI can enhance safety and efficiency by optimizing routes and automatically monitoring vessel conditions.
In supply chains, AI is replacing traditional methods of demand forecasting and improving the accuracy of predictions about potential disruptions and bottlenecks. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the importance of these capabilities, as many companies were caught off guard by the effects of a global pandemic on the supply and demand of goods.
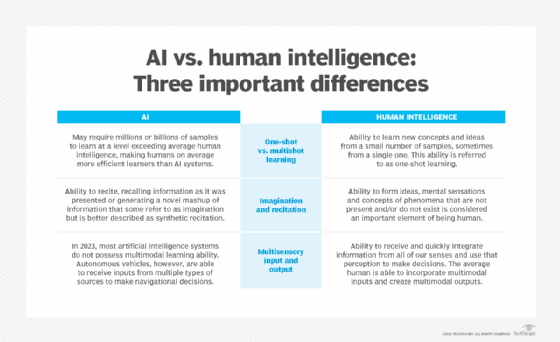
Augmented intelligence vs. artificial intelligence
The term artificial intelligence is closely linked to popular culture, which could create unrealistic expectations among the general public about AI's impact on work and daily life. A proposed alternative term, augmented intelligence, distinguishes machine systems that support humans from the fully autonomous systems found in science fiction -- think HAL 9000 from 2001: A Space Odyssey or Skynet from the Terminator movies.
The two terms can be defined as follows:
- Augmented intelligence. With its more neutral connotation, the term augmented intelligence suggests that most AI implementations are designed to enhance human capabilities, rather than replace them. These narrow AI systems primarily improve products and services by performing specific tasks. Examples include automatically surfacing important data in business intelligence reports or highlighting key information in legal filings. The rapid adoption of tools like ChatGPT and Gemini across various industries indicates a growing willingness to use AI to support human decision-making.
- Artificial intelligence. In this framework, the term AI would be reserved for advanced general AI in order to better manage the public's expectations and clarify the distinction between current use cases and the aspiration of achieving AGI. The concept of AGI is closely associated with the concept of the technological singularity -- a future wherein an artificial superintelligence far surpasses human cognitive abilities, potentially reshaping our reality in ways beyond our comprehension. The singularity has long been a staple of science fiction, but some AI developers today are actively pursuing the creation of AGI.
Ethical use of artificial intelligence
While AI tools present a range of new functionalities for businesses, their use raises significant ethical questions. For better or worse, AI systems reinforce what they have already learned, meaning that these algorithms are highly dependent on the data they are trained on. Because a human being selects that training data, the potential for bias is inherent and must be monitored closely.
Generative AI adds another layer of ethical complexity. These tools can produce highly realistic and convincing text, images and audio -- a useful capability for many legitimate applications, but also a potential vector of misinformation and harmful content such as deepfakes.
Consequently, anyone looking to use machine learning in real-world production systems needs to factor ethics into their AI training processes and strive to avoid unwanted bias. This is especially important for AI algorithms that lack transparency, such as complex neural networks used in deep learning.
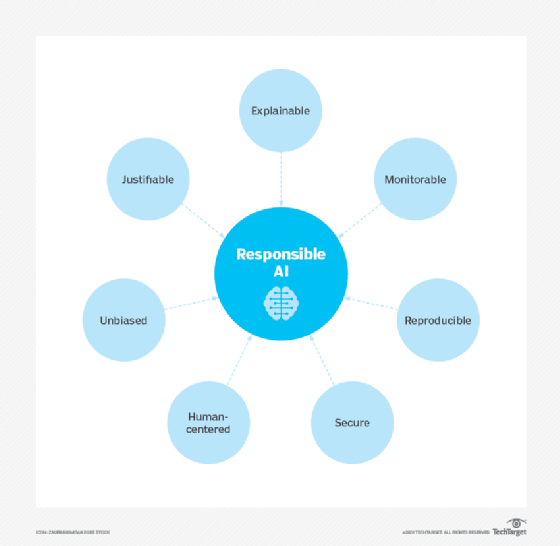
Responsible AI refers to the development and implementation of safe, compliant and socially beneficial AI systems. It is driven by concerns about algorithmic bias, lack of transparency and unintended consequences. The concept is rooted in longstanding ideas from AI ethics, but gained prominence as generative AI tools became widely available -- and, consequently, their risks became more concerning. Integrating responsible AI principles into business strategies helps organizations mitigate risk and foster public trust.
Explainability, or the ability to understand how an AI system makes decisions, is a growing area of interest in AI research. Lack of explainability presents a potential stumbling block to using AI in industries with strict regulatory compliance requirements. For example, fair lending laws require U.S. financial institutions to explain their credit-issuing decisions to loan and credit card applicants. When AI programs make such decisions, however, the subtle correlations among thousands of variables can create a black-box problem, where the system's decision-making process is opaque.
In summary, AI's ethical challenges include the following:
- Bias due to improperly trained algorithms and human prejudices or oversights.
- Misuse of generative AI to produce deepfakes, phishing scams and other harmful content.
- Legal concerns, including AI libel and copyright issues.
- Job displacement due to increasing use of AI to automate workplace tasks.
- Data privacy concerns, particularly in fields such as banking, healthcare and legal that deal with sensitive personal data.
AI governance and regulations
Despite potential risks, there are currently few regulations governing the use of AI tools, and many existing laws apply to AI indirectly rather than explicitly. For example, as previously mentioned, U.S. fair lending regulations such as the Equal Credit Opportunity Act require financial institutions to explain credit decisions to potential customers. This limits the extent to which lenders can use deep learning algorithms, which by their nature are opaque and lack explainability.
The European Union has been proactive in addressing AI governance. The EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) already imposes strict limits on how enterprises can use consumer data, affecting the training and functionality of many consumer-facing AI applications. In addition, the EU AI Act, which aims to establish a comprehensive regulatory framework for AI development and deployment, went into effect in August 2024. The Act imposes varying levels of regulation on AI systems based on their riskiness, with areas such as biometrics and critical infrastructure receiving greater scrutiny.
While the U.S. is making progress, the country still lacks dedicated federal legislation akin to the EU's AI Act. Policymakers have yet to issue comprehensive AI legislation, and existing federal-level regulations focus on specific use cases and risk management, complemented by state initiatives. That said, the EU's more stringent regulations could end up setting de facto standards for multinational companies based in the U.S., similar to how GDPR shaped the global data privacy landscape.
With regard to specific U.S. AI policy developments, the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy published a "Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights" in October 2022, providing guidance for businesses on how to implement ethical AI systems. The U.S. Chamber of Commerce also called for AI regulations in a report released in March 2023, emphasizing the need for a balanced approach that fosters competition while addressing risks.
More recently, in October 2023, President Biden issued an executive order on the topic of secure and responsible AI development. Among other things, the order directed federal agencies to take certain actions to assess and manage AI risk and developers of powerful AI systems to report safety test results. The outcome of the upcoming U.S. presidential election is also likely to affect future AI regulation, as candidates Kamala Harris and Donald Trump have espoused differing approaches to tech regulation.
Crafting laws to regulate AI will not be easy, partly because AI comprises a variety of technologies used for different purposes, and partly because regulations can stifle AI progress and development, sparking industry backlash. The rapid evolution of AI technologies is another obstacle to forming meaningful regulations, as is AI's lack of transparency, which makes it difficult to understand how algorithms arrive at their results. Moreover, technology breakthroughs and novel applications such as ChatGPT and Dall-E can quickly render existing laws obsolete. And, of course, laws and other regulations are unlikely to deter malicious actors from using AI for harmful purposes.

What is the history of AI?
The concept of inanimate objects endowed with intelligence has been around since ancient times. The Greek god Hephaestus was depicted in myths as forging robot-like servants out of gold, while engineers in ancient Egypt built statues of gods that could move, animated by hidden mechanisms operated by priests.
Throughout the centuries, thinkers from the Greek philosopher Aristotle to the 13th-century Spanish theologian Ramon Llull to mathematician René Descartes and statistician Thomas Bayes used the tools and logic of their times to describe human thought processes as symbols. Their work laid the foundation for AI concepts such as general knowledge representation and logical reasoning.
The late 19th and early 20th centuries brought forth foundational work that would give rise to the modern computer. In 1836, Cambridge University mathematician Charles Babbage and Augusta Ada King, Countess of Lovelace, invented the first design for a programmable machine, known as the Analytical Engine. Babbage outlined the design for the first mechanical computer, while Lovelace -- often considered the first computer programmer -- foresaw the machine's capability to go beyond simple calculations to perform any operation that could be described algorithmically.
As the 20th century progressed, key developments in computing shaped the field that would become AI. In the 1930s, British mathematician and World War II codebreaker Alan Turing introduced the concept of a universal machine that could simulate any other machine. His theories were crucial to the development of digital computers and, eventually, AI.
1940s
Princeton mathematician John Von Neumann conceived the architecture for the stored-program computer -- the idea that a computer's program and the data it processes can be kept in the computer's memory. Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts proposed a mathematical model of artificial neurons, laying the foundation for neural networks and other future AI developments.
1950s
With the advent of modern computers, scientists began to test their ideas about machine intelligence. In 1950, Turing devised a method for determining whether a computer has intelligence, which he called the imitation game but has become more commonly known as the Turing test. This test evaluates a computer's ability to convince interrogators that its responses to their questions were made by a human being.
The modern field of AI is widely cited as beginning in 1956 during a summer conference at Dartmouth College. Sponsored by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, the conference was attended by 10 luminaries in the field, including AI pioneers Marvin Minsky, Oliver Selfridge and John McCarthy, who is credited with coining the term "artificial intelligence." Also in attendance were Allen Newell, a computer scientist, and Herbert A. Simon, an economist, political scientist and cognitive psychologist.
The two presented their groundbreaking Logic Theorist, a computer program capable of proving certain mathematical theorems and often referred to as the first AI program. A year later, in 1957, Newell and Simon created the General Problem Solver algorithm that, despite failing to solve more complex problems, laid the foundations for developing more sophisticated cognitive architectures.
1960s
In the wake of the Dartmouth College conference, leaders in the fledgling field of AI predicted that human-created intelligence equivalent to the human brain was around the corner, attracting major government and industry support. Indeed, nearly 20 years of well-funded basic research generated significant advances in AI. McCarthy developed Lisp, a language originally designed for AI programming that is still used today. In the mid-1960s, MIT professor Joseph Weizenbaum developed Eliza, an early NLP program that laid the foundation for today's chatbots.
1970s
In the 1970s, achieving AGI proved elusive, not imminent, due to limitations in computer processing and memory as well as the complexity of the problem. As a result, government and corporate support for AI research waned, leading to a fallow period lasting from 1974 to 1980 known as the first AI winter. During this time, the nascent field of AI saw a significant decline in funding and interest.
1980s
In the 1980s, research on deep learning techniques and industry adoption of Edward Feigenbaum's expert systems sparked a new wave of AI enthusiasm. Expert systems, which use rule-based programs to mimic human experts' decision-making, were applied to tasks such as financial analysis and clinical diagnosis. However, because these systems remained costly and limited in their capabilities, AI's resurgence was short-lived, followed by another collapse of government funding and industry support. This period of reduced interest and investment, known as the second AI winter, lasted until the mid-1990s.
1990s
Increases in computational power and an explosion of data sparked an AI renaissance in the mid- to late 1990s, setting the stage for the remarkable advances in AI we see today. The combination of big data and increased computational power propelled breakthroughs in NLP, computer vision, robotics, machine learning and deep learning. A notable milestone occurred in 1997, when Deep Blue defeated Kasparov, becoming the first computer program to beat a world chess champion.
2000s
Further advances in machine learning, deep learning, NLP, speech recognition and computer vision gave rise to products and services that have shaped the way we live today. Major developments include the 2000 launch of Google's search engine and the 2001 launch of Amazon's recommendation engine.
Also in the 2000s, Netflix developed its movie recommendation system, Facebook introduced its facial recognition system and Microsoft launched its speech recognition system for transcribing audio. IBM launched its Watson question-answering system, and Google started its self-driving car initiative, Waymo.
2010s
The decade between 2010 and 2020 saw a steady stream of AI developments. These include the launch of Apple's Siri and Amazon's Alexa voice assistants; IBM Watson's victories on Jeopardy; the development of self-driving features for cars; and the implementation of AI-based systems that detect cancers with a high degree of accuracy. The first generative adversarial network was developed, and Google launched TensorFlow, an open source machine learning framework that is widely used in AI development.
A key milestone occurred in 2012 with the groundbreaking AlexNet, a convolutional neural network that significantly advanced the field of image recognition and popularized the use of GPUs for AI model training. In 2016, Google DeepMind's AlphaGo model defeated world Go champion Lee Sedol, showcasing AI's ability to master complex strategic games. The previous year saw the founding of research lab OpenAI, which would make important strides in the second half of that decade in reinforcement learning and NLP.
2020s
The current decade has so far been dominated by the advent of generative AI, which can produce new content based on a user's prompt. These prompts often take the form of text, but they can also be images, videos, design blueprints, music or any other input that the AI system can process. Output content can range from essays to problem-solving explanations to realistic images based on pictures of a person.
In 2020, OpenAI released the third iteration of its GPT language model, but the technology did not reach widespread awareness until 2022. That year, the generative AI wave began with the launch of image generators Dall-E 2 and Midjourney in April and July, respectively. The excitement and hype reached full force with the general release of ChatGPT that November.
OpenAI's competitors quickly responded to ChatGPT's release by launching rival LLM chatbots, such as Anthropic's Claude and Google's Gemini. Audio and video generators such as ElevenLabs and Runway followed in 2023 and 2024.
Generative AI technology is still in its early stages, as evidenced by its ongoing tendency to hallucinate and the continuing search for practical, cost-effective applications. But regardless, these developments have brought AI into the public conversation in a new way, leading to both excitement and trepidation.
AI tools and services: Evolution and ecosystems
AI tools and services are evolving at a rapid rate. Current innovations can be traced back to the 2012 AlexNet neural network, which ushered in a new era of high-performance AI built on GPUs and large data sets. The key advancement was the discovery that neural networks could be trained on massive amounts of data across multiple GPU cores in parallel, making the training process more scalable.
In the 21st century, a symbiotic relationship has developed between algorithmic advancements at organizations like Google, Microsoft and OpenAI, on the one hand, and the hardware innovations pioneered by infrastructure providers like Nvidia, on the other. These developments have made it possible to run ever-larger AI models on more connected GPUs, driving game-changing improvements in performance and scalability. Collaboration among these AI luminaries was crucial to the success of ChatGPT, not to mention dozens of other breakout AI services. Here are some examples of the innovations that are driving the evolution of AI tools and services.
Transformers
Google led the way in finding a more efficient process for provisioning AI training across large clusters of commodity PCs with GPUs. This, in turn, paved the way for the discovery of transformers, which automate many aspects of training AI on unlabeled data. With the 2017 paper "Attention Is All You Need," Google researchers introduced a novel architecture that uses self-attention mechanisms to improve model performance on a wide range of NLP tasks, such as translation, text generation and summarization. This transformer architecture was essential to developing contemporary LLMs, including ChatGPT.
Hardware optimization
Hardware is equally important to algorithmic architecture in developing effective, efficient and scalable AI. GPUs, originally designed for graphics rendering, have become essential for processing massive data sets. Tensor processing units and neural processing units, designed specifically for deep learning, have sped up the training of complex AI models. Vendors like Nvidia have optimized the microcode for running across multiple GPU cores in parallel for the most popular algorithms. Chipmakers are also working with major cloud providers to make this capability more accessible as AI as a service (AIaaS) through IaaS, SaaS and PaaS models.
Generative pre-trained transformers and fine-tuning
The AI stack has evolved rapidly over the last few years. Previously, enterprises had to train their AI models from scratch. Now, vendors such as OpenAI, Nvidia, Microsoft and Google provide generative pre-trained transformers (GPTs) that can be fine-tuned for specific tasks with dramatically reduced costs, expertise and time.
AI cloud services and AutoML
One of the biggest roadblocks preventing enterprises from effectively using AI is the complexity of data engineering and data science tasks required to weave AI capabilities into new or existing applications. All leading cloud providers are rolling out branded AIaaS offerings to streamline data prep, model development and application deployment. Top examples include Amazon AI, Google AI, Microsoft Azure AI and Azure ML, IBM Watson and Oracle Cloud's AI features.
Similarly, the major cloud providers and other vendors offer automated machine learning (AutoML) platforms to automate many steps of ML and AI development. AutoML tools democratize AI capabilities and improve efficiency in AI deployments.
Cutting-edge AI models as a service
Leading AI model developers also offer cutting-edge AI models on top of these cloud services. OpenAI has multiple LLMs optimized for chat, NLP, multimodality and code generation that are provisioned through Azure. Nvidia has pursued a more cloud-agnostic approach by selling AI infrastructure and foundational models optimized for text, images and medical data across all cloud providers. Many smaller players also offer models customized for various industries and use cases.
George Lawton also contributed to this article.







