
What is explainable AI?
Explainable AI (XAI) is artificial intelligence (AI) programmed to describe its purpose, rationale and decision-making process in a way that the average person can understand. XAI helps human users understand the reasoning behind AI and machine learning (ML) algorithms to increase their trust.
Explainable AI is often discussed in relation to deep learning models and plays an important role in the FAT -- fairness, accountability and transparency -- ML model. XAI is useful for organizations that want to adopt a responsible approach to developing and implementing AI models. XAI helps developers understand an AI model's behavior, how an AI reached a specific output and potential issues such as AI biases.
ML models are typically structured in a white box or black box format. White box models provide more visibility and understandable results to users and developers. Black box model decisions, such as those made by neural networks, are hard to explain even for AI developers.
Explainable artificial intelligence provides information in various areas on how an AI program makes decisions:
- The program's strengths and weaknesses.
- The specific criteria the program uses to arrive at a decision.
- Why a program makes a particular prediction or decision instead of alternatives.
- The level of trust appropriate for various types of decisions or predictions.
- The types of errors the program is likely to make.
- How errors can be corrected.
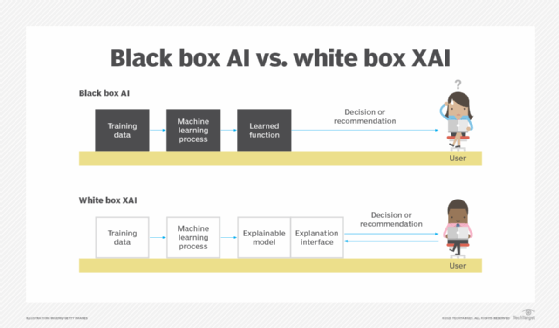
The importance of explainable AI
An important goal of XAI is to provide algorithmic accountability. AI systems used to be predominantly black boxes. Even if the inputs and outputs were known, the AI algorithms used to make decisions were often proprietary or weren't easily understood.
This article is part of
What is enterprise AI? A complete guide for businesses
With AI being used in industries such as healthcare and financial services, it's important to ensure that the decisions these systems make are sound and trustworthy. They must be free from biases that might, for example, deny a person a mortgage for reasons unrelated to their financial qualifications.
In healthcare, an AI-based system trained on a limited data set might not detect illnesses in patients of different races, genders or geographies. Insight into how the AI system makes its decisions is needed to facilitate monitoring, detecting and managing these issues.
As AI becomes increasingly prevalent, it's more important than ever to disclose how bias and trust are being addressed.
How does explainable AI work?
Explainable AI is based on some basic approaches to AI system design and deployment:
- Oversight. An AI governance committee can be created to set standards for AI explainability and guide development teams in creating AI models. Doing this from the start makes explainability one of the key principles of the organization's responsible AI guidelines.
- Data. The data used in training is also important for creating an explainable AI model. When designing an AI model, developers should pay close attention to the training data to ensure it has no bias. If the data is biased, developers should explore how to mitigate it. In addition, any irrelevant data should be excluded from training.
- Output. Some AI systems are designed to explain where the information for each out came from.
- Algorithms. Designing a model that uses explainable algorithms and produces explainable predictions is important. An explainable algorithm has a layered design, so it's clear how it reaches its output. Likewise, making an explainable prediction means the model's predictions are clearly defined.
Explainable AI techniques
Various techniques are used to explain how explainable machine learning models use input data to produce outputs:
- Decision trees. A decision tree maps a model's decision-making process using a tree-like structure where inputs lead to various outputs shown as branches.
- Feature importance. This technique identifies the most influential features that affect a model's output.
- Counterfactual explanations. This technique creates a list of what-if scenarios that show how small changes to a model's features cause different outcomes
- Shapley additive explanations. This technique, also known as SHAP, observes how all model features collectively influence its output.
- Local interpretable model-agnostic explanations. LIME alters inputs to a model and then observes the outputs resulting from each change.
- Partial dependence plots. This technique plots different model outputs on a graph based on gradual input changes.
- Visualization tools. Data analytics and visualization tools explain how models arrive at their predictions through charts and metrics.
Examples of explainable AI
Real-world XAI use cases can be found in various industries.
Healthcare
Explainable AI systems help doctors with patient diagnoses, providing insight into where and how the system arrives at a diagnosis. For example, AI is used to identify patient fractures in X-ray images. But even after an initial investment in an AI tool, doctors and nurses might still not fully trust it. An explainable system lets healthcare providers review the diagnosis and use the information to inform their prognosis.
Financial
XAI is used to assess financial qualifications for loans or mortgage applications and to detect financial fraud.
Military
Explainable AI-based systems build trust between military personnel and the systems they use in combat and other applications. The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, or DARPA, is developing XAI in its third wave of AI systems.
Autonomous vehicles
XAI in autonomous vehicles explains driving-based decisions, especially those that revolve around safety. If a driver can understand how and why the vehicle makes its decisions, they will better understand what scenarios it can or can't handle.
How does explainable AI improve decision-making and trust?
Traditional black box AI models have complex inner workings that many users don't understand. However, when a model's decision-making processes aren't clear, trust in the model can be an issue. An explainable AI model aims to address this problem, outlining the steps in its decision-making and providing supporting evidence for the model's outputs. A truly explainable model offers explanations that are understandable for less technical audiences.
Explainable AI secures trust not just from a model's users, who might be skeptical of its developers when transparency is lacking, but also from stakeholders and regulatory bodies. Explainability lets developers communicate directly with stakeholders to show they take AI governance seriously. Compliance with regulations is also increasingly vital in AI development, so proving compliance assures the public that a model isn't untrustworthy or biased.
Benefits of explainable AI
XAI provides more accountability and transparency in AI systems. Its benefits include the following:
- Builds trust. Individuals might be reluctant to trust an AI-based system if they can't tell how it reaches a conclusion. XAI is designed to give end users understandable explanations of its decisions.
- Improves the overall system. With added transparency, developers can more easily identify and fix issues.
- Identifies cyberattacks. Adversarial ML attacks attempt to fool or misguide a model into making incorrect decisions using maliciously designed data inputs. An adversarial attack against an XAI system would reveal the attack by showing unusual or odd explanations for its decisions.
- Safeguards against bias. XAI aims to explain attributes and decision processes in machine learning algorithms. This helps identify biases that can lead to suboptimal outcomes related to training data quality or developer biases.
Limitations of explainable AI
Despite benefits, XAI also has the following limitations:
- Oversimplification. An XAI system might oversimplify and misrepresent complex models compared to other transparency methods. A better approach might be to design AI systems with more interpretable models or models that can more accurately associate cause and effect.
- Lower model performance. XAI systems typically perform at lower levels than black box models.
- Training issues. Creating an AI system that explains its reasoning is more complicated than black box models.
- Lack of privacy. If an XAI system works with confidential data, CAI's transparent approach could expose the data.
- Mistrust. Although XAI should increase trust in AI, some users still might not trust a system, even with an understandable explanation behind its decisions.
Explainable AI vs. generative AI
Explainable AI and generative AI are different subsets of AI. Gen AI encompasses a growing list of tools that generate new content, including text, audio and visual content. Dall-E, ChatGPT and Google Gemini are examples of GenAI tools.
Explainable AI is a principle for developing and using AI systems in general. It's not a concrete list of tools and covers various types of AI systems. For example, explainable prediction models in weather or financial forecasting produce insights from historical data, not original content. If designed correctly, predictive methodologies are clearly explained, and the decision-making behind them is transparent.
Explainable AI concepts can be applied to GenAI, but they aren't often used with those systems. Generative AI tools often lack transparent inner workings, and users typically don't understand how new content is produced. For example, GPT-4 has many hidden layers that aren't transparent or understandable to most users. While any type of AI system can be explainable when designed as such, GenAI often isn't.
The history of explainable AI
Explainable AI systems are needed now more than ever because of their potential effects on people. AI explainability has been an important aspect of creating an AI system since at least the 1970s. In 1972, the symbolic reasoning system MYCIN was developed to explain the reasoning for diagnostic-related purposes, such as treating blood infections.
Throughout the 1980s and 1990s, truth maintenance systems (TMSes) were developed to extend AI reasoning abilities. For example, TMSes were used in rule- and logic-based inference systems. A TMS tracks AI reasoning and conclusions by tracing an AI's reasoning through rule operations and logical inferences. This process generates an explanation for each AI reasoning.
Starting in the 2010s, explainable AI systems became more visible to the general population. Some AI systems began exhibiting racial and other biases, leading to an increased focus on developing more transparent AI systems and ways to detect bias in AI.
Explainable AI vs. interpretable AI
Explainability and interpretability are two concepts in AI that are used interchangeably. However, they have different meanings.
Explainable AI is the ability to explain the AI decision-making process to the user in an understandable way. Interpretable AI refers to the predictability of a model's outputs based on its inputs. Interpretability is used to understand an AI model's inner workings. Interpretability is important if an organization needs a model with high levels of transparency and must understand exactly how the model generates its outcomes. However, this can slow performance.
Explainable AI vs. responsible AI
Explainable AI and responsible AI are both important concepts when designing a transparent and trustable AI system. Responsible AI approaches AI development and deployment from an ethical and legal point of view. Its goal is to use AI safely, truthfully and ethically. AI interpretability and explainability are both important aspects of developing responsible AI.
Principles that make up responsible AI include the following:
- Accountability and transparency.
- Explainability and interpretability.
- Fairness.
- Privacy.
- Security and resiliency.
- Validity and reliability.
- Safety.
Transparency and explainability continue to be important concepts in AI technologies. Learn more about why transparency in AI matters.