Essential business intelligence skills for BI analysts
Business intelligence analysts need various skills to succeed in the job. Here are nine key skills plus info on the responsibilities of BI analysts and current salaries.
The main purpose of business intelligence is to enhance a company's operations by analyzing data and generating insights into business processes. Business intelligence analysts play a central role in that process. What skills do you need to become a BI analyst? This article outlines the required ones and everything else you need to know about the position -- why a career as a BI analyst is worth pursuing, the primary responsibilities of one, ballpark salaries and how to go about finding a job.
First, let's look a little more deeply at what business intelligence is. It's a technology-driven analytics process that presents actionable information to decision-makers in an organization. BI data can include historical records in a data warehouse and new data gathered from operational systems. The BI process helps corporate executives, business managers and operational workers make more informed business decisions. It also accelerates their decision-making.
Business intelligence analysts do data analysis and create data visualizations, reports and BI dashboards for business users. To do so effectively, they must have a mix of business and IT skills, including the ability to work with the various tools, applications and methodologies in an organization's BI architecture. That enables them to collect data from internal systems and external sources, prepare it for analysis, develop and run queries against the data, and share the analytics results.
Working alongside the other members of a BI team, BI analysts with the right combination of technical skills and business acumen can lead the way to various benefits for a company. Their work helps organizations optimize business processes, increase operational efficiency, spot potential business problems, identify market trends and gain competitive advantages over business rivals, ultimately resulting in higher productivity, revenue and profits.
Why would you want a career as a BI analyst?
Aside from the personal or monetary reasons why you might want to get into business intelligence, there are other incentives for pursuing a BI career path. For example, BI professionals are integral to business operations as organizations increasingly look to capitalize on all the data they collect. That makes BI analysts and other business intelligence roles key contributors to business success.
Also, the demand for business intelligence analysts continues to grow, creating ample job opportunities. In many areas, there aren't enough skilled BI pros to satisfy the demand. This can work to your advantage if you're interested in BI -- companies are always on the hunt for qualified job candidates with business intelligence skills.
BI analyst might be the ideal career if you answer yes to the following questions:
- Do you like the idea of extracting, wrangling, organizing and analyzing complex data to help a company's management make better business decisions?
- Do you also look forward to providing operational employees with data, benchmarks, metrics and insights to help them be successful in their roles?
- Do you strive to support optimization and continuous improvement of business processes?
- Are you flexible, creative and detail-oriented, with the ability to stay focused on the big picture while working on individual projects?
Because BI is rooted in both business strategy and computer science, it also provides you with a lot of flexibility. It's a varied field, with lots of different areas to focus on. If you find your current focus isn't right for you, or if you just want to change what you're doing, it won't take an extreme effort to shift to another area of expertise in BI. For example, if a programming-oriented BI analyst role turns out to be too isolated, you could switch to one that's more face-to-face with business users -- or vice versa.
In addition, there are many options for finding a job in business intelligence. The insights a BI analyst can pull from data -- and the actions they enable -- are valuable across different industries. There's also a need for BI analysts and related positions in both small and large organizations. Whether you prefer a startup culture, the smaller scale of an SMB or the established structure of a large company, there should be job openings available to you.
Responsibilities of BI analysts and related roles
Not surprisingly, given their title, the primary duty of business intelligence analysts is analyzing data. But that isn't the only task they handle. The typical responsibilities of a BI analyst include the following:
- Analyzing data to find useful information, patterns and trends. BI analysts typically dive into large data sets to find relevant information about a company as a whole or for different departments and business processes. They also need to be proficient in interpreting the data so they can discover new insights based on data-driven inferences and strategic thinking.
- Collaborating with business users and other BI team members. BI analysts must work closely with business managers, department heads and other end users to identify key KPIs and the data that needs to be analyzed to meet business goals. This includes gathering requirements for BI projects and communicating clearly with users throughout the BI process. Collaboration with the other BI professionals in an organization is also part of the job.
- Creating reports and dashboards. Reports and interactive dashboards should present data visualizations and relevant insights to assist business users in decision-making processes. They can also include suggestions from BI analysts on how to improve business processes and strategies based on data analysis results.
- Supporting self-service BI strategies. Many organizations have deployed self-service BI environments that enable business users to analyze data and build reports themselves. Business intelligence analysts often are tasked with training self-service BI users, monitoring their work and supporting them as needed.
- Maintaining compliance, data privacy and data security. BI data needs to be protected and used properly. BI analysts are expected to work with security and IT teams to ensure that the data used in BI applications is secure. They're also responsible for helping to make sure that data collection and analysis processes, especially ones involving sensitive data, comply with data privacy laws and other regulatory requirements.
Other BI roles have their own set of responsibilities, although there's often some overlap on duties between different roles. The following are some of the key positions that commonly work with BI analysts on business intelligence initiatives:
BI developers. They're responsible for developing, deploying and maintaining business intelligence systems, including the tools that help BI analysts do their work. Many BI developers also get involved in gathering BI requirements, running queries requested by business users, and designing dashboards and reports.
BI architects. They lead the process of designing and building the overall BI architecture. That typically includes BI systems and the data warehouse platforms that store BI data, as well as the extract, transform and load (ETL) processes used to pull operational data sets into a warehouse for analysis.
BI engineers. In some organizations, BI engineers are akin to BI architects, with responsibility for the development, implementation and management of data warehouses and BI systems. In other cases, they function more like BI developers and handle tasks that include designing applications and delivering insights.
BI consultants. They help an organization devise new strategies to manage and analyze data. For example, BI consultants might help improve existing BI systems or implement new ones to enable more efficient analytics operations. Their goals could also include assisting with budget planning and creating project timelines.
Some other common business intelligence titles include BI administrator, BI manager, BI project manager and BI specialist.
9 business intelligence skills that BI analysts need
A BI analyst should possess a combination of hard skills and soft skills to succeed in the position. That includes the following essential skills:
1. Knowledge of data warehousing
Understanding how BI data is stored in and retrieved from large data repositories provides a solid foundation for the various steps in the BI process. In addition to data warehouses, the repositories used in BI applications might include data lakes, which often store a mix of structured, unstructured and semistructured data, as well as data lakehouses that combine elements of data lakes and data warehouses.
2. Data management
BI analysts should also have foundational abilities to manage data. Key data management skills include knowledge of ETL functions for data integration; data quality improvement techniques; and data modeling capabilities for creating visual representations of data sets and mapping them to different business processes.
3. Data preparation
Being able to prepare data for analysis is a must-have skill for a BI analyst. Core data preparation tasks include data collection; data preprocessing; data cleansing to remove errors and other issues in data sets; and data transformation and enrichment to optimize data sets for BI uses.
4. Data analysis
The ability to analyze and interpret data is central to the BI analyst role. That starts with basic data querying and descriptive analytics capabilities to track KPIs. But more advanced skills are often required, too. For example, BI analysts commonly must be proficient in data mining to find patterns, relationships and correlations in large data sets. Knowledge of statistical analysis methods and predictive analytics techniques is also called for in many cases. Helpfully, AI-enabled business intelligence tools that provide augmented analytics features are increasingly becoming available from BI vendors.
5. Data visualization
A BI analyst must be able to create charts and other graphics that visualize data in an informative, easy-to-understand way. Engaging dashboard and report design that effectively incorporates data visualizations is also a vital skill. Another related one is data storytelling, which uses visualizations and text to create a narrative about analytics results.
6. Programming
BI analysts should also have some familiarity and experience with programming languages. The most common one that's required is SQL, the industry standard language for managing relational databases and data warehouses and writing queries to run against them. Other languages that can be useful to know include Python, R, C++ and C#.
7. Communication
Being able to explain insights gleaned from data in a clear manner, both verbally and in written form, is a must. In addition, BI analysts must communicate effectively with business users when gathering requirements for BI projects and working with them on self-service BI initiatives.
8. Critical thinking, problem-solving and curiosity
To get valid and relevant results, BI analysts need to think critically about the data analysis work they do and the findings it produces. Strong problem-solving skills are also needed to identify and address issues in BI projects. Being curious by nature is another important attribute -- much of a BI analyst's work often involves exploring data to find useful information.
9. Attention to detail
Being detail-oriented is a key trait for BI analysts, too. It helps them ensure that analytics results are accurate, valid and comprehensive, with all data issues caught and no valuable information overlooked. Paying attention to the details also keeps BI projects on schedule and focused on meeting business needs.
What else do you need to become a BI analyst?
According to jobs site Indeed, it typically takes at least four years to become a business intelligence analyst, although it could be less for someone who already has a suitable college degree and decides they want to go into the BI field. Having the following should help prospective BI analysts find a job:
- A bachelor's degree or higher. Most BI analysts have at least a bachelor's degree in fields like computer science, business analytics, data science or statistics. Specific BI undergraduate degree programs are also available from some universities. A master's degree, whether it's an MBA or one in BI, analytics or a related discipline, can further help job candidates.
- Some form of hands-on experience. This is typically gained through internships or freelance work. Previous experience in IT or business positions might help, too. Either way, BI analysts should develop technical and analytical skills they can showcase. Industry-specific knowledge, such as experience in healthcare or financial services, can also be a useful part of their skill sets.
- Familiarity with specific BI tools. Knowing how to use particular BI software technologies is another valuable asset for landing jobs that involve them. For example, that might include being proficient on Microsoft platforms, such as Excel and Power BI, or on Tableau, Qlik and other popular BI tools.
- Certifications. Although not always required, certifications are a good way to demonstrate required competencies. Some relevant examples include the Microsoft Certified Power BI Data Analyst Associate, the Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate and the Certified Business Intelligence Professional designation from education and research organization TDWI. Certifications in business administration or computer programming might be helpful as well.
- A portfolio. Job seekers should create a portfolio that showcases their skills in data analysis, reporting, visualization and other aspects of being a BI analyst. This can include examples of BI projects from previous work experiences or college programs.
Business intelligence analyst salaries
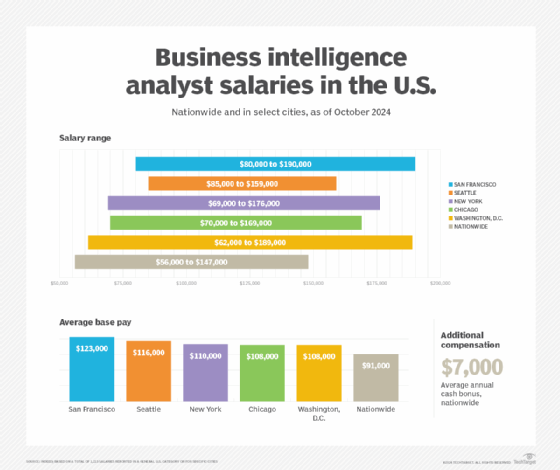
Salaries for BI analyst positions vary depending on factors such as location, industry and company size. There can also be multiple job levels, with senior BI analysts earning more than junior ones. In addition, general salary estimates differ on some of the well-known websites that report average salaries. Indeed, for example, estimates the average base salary for BI analysts in the U.S. is nearly $91,000 per year, with a range from about $56,000 to almost $147,000. PayScale estimates an average annual salary of about $76,000, while Glassdoor's average is about $97,000.
As you'd expect, salaries also differ based on the type of BI position, with BI analysts often at the low end of the scale. For comparison, the four other roles mentioned previously make the following average annual salaries, according to PayScale:
- BI developer: $88,000.
- BI consultant: $90,000.
- BI engineer: $93,000.
- BI architect: $119,000.
How to find a BI analyst job
A good way to get started on finding a BI analyst job is to reach out to some BI professionals on LinkedIn and ask if they can offer any advice. Even better, if you already know someone in the industry, you'll have an easier time getting tips -- and maybe help on getting your foot in the door at companies. In addition to Indeed, Glassdoor and LinkedIn, you can look for available jobs on websites such as Dice, Monster and Wellfound. You can also engage a hiring consultant to help with the job search process.
There's no general BI analyst resume template available. But when writing your resume, you should focus on your most relevant skills; BI and analytics tools you know how to use; your current job, if you have one; any certifications you've obtained; related side projects; and your educational background. Do your best to sound skilled, with a unique set of capabilities.
Your cover letter should also emphasize the BI and data analytics skills you've used in previous jobs, if applicable. Providing examples of past issues you were able to overcome on BI projects is also a good idea. Make sure as well to mention the skills and requirements listed in the job posting.
Learn more about the responsibilities of a business intelligence analyst and how the job differs from other BI roles.
Editor's Note: This article, originally published in 2020, was updated in October 2024 for timeliness and to add new information.
Alexander S. Gillis is a technical writer for WhatIs. He holds a bachelor's degree in professional writing from Fitchburg State University.







