30 of the best large language models in 2026
Behind the scenes influencing search for years, large language models have proliferated since the debut of ChatGPT and other chatbot interfaces. Wade through the LLM waters.
Large language models are the dynamite behind the generative AI boom.
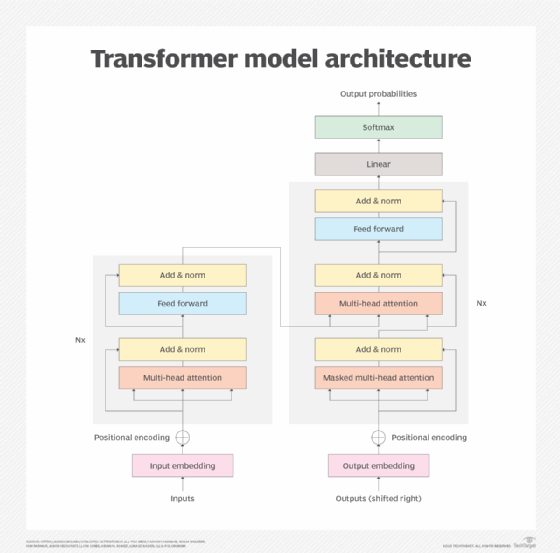
LLMs are black box AI systems that use deep learning on extremely large data sets to understand and generate new text. Modern LLMs began taking shape in 2014 when the attention mechanism -- a machine learning technique designed to mimic human cognitive attention -- was introduced in a research paper titled "Neural Machine Translation by Jointly Learning to Align and Translate." In 2017, that attention mechanism was honed with the introduction of the transformer model in another paper, "Attention Is All You Need."
Some of the most well-known language models today are based on the transformer model, including the generative pre-trained transformer series of LLMs and the Claude series of LLMs. ChatGPT, which runs on a set of language models from OpenAI, attracted more than 100 million users just two months after its release in 2022. Since then, many competing models have been released. Some belong to big companies such as Google, Amazon and Microsoft, while others are open source or open weight.
Constant developments in the field can be difficult to track. Here are some of the more influential models, past and present, including models that paved the way for today's leading models as well as ones that could have a significant future impact.
Best LLMs to know in 2026
The most relevant large language models today do natural language processing and influence the architecture of future models.
Claude
The Claude LLM focuses on constitutional AI, which shapes AI outputs guided by a set of principles that aim to make the AI assistant it powers helpful, harmless and accurate. Claude was created by the Anthropic PBC. Claude's latest iterations understand nuance, humor and complex instructions better than earlier versions of the LLM. They also have broad programming capabilities that make them well-suited for application development.
This article is part of
What is GenAI? Generative AI explained
There are three primary branches of Claude -- Opus, Haiku and Sonnet. The Claude Sonnet 4 and Claude Opus 4 models debuted in early 2025. Opus 4, the premium model, can perform long-running tasks and agentic workflows. Sonnet 4, the efficiency-focused model, shows continued improvement in coding, reasoning and instruction-following compared to previous iterations. Both models also include several features, including extended thinking with tool-use, improved memory and instruction-following, integrations with IDEs and APIs, code execution, MCP connector, files API and prompt caching.
In late 2025, Anthropic released Claude 4.5 models and began piloting a Claude extension for Chrome that lets the model "see" and interact with the user's browser.
Cohere
Cohere is an enterprise AI platform that provides several LLMs, including Command, Rerank and Embed. These LLMs can be custom-trained and fine-tuned to a specific company's use case. Command comes with several specialized models -- Command A Vision, Command A Reasoning and Command A Translate. Cohere's LLMs are designed for enterprise use cases and can be deployed on-premises, which offers a benefit to organizations that handle sensitive data. Cohere was founded by one of the authors of the paper "Attention Is All You Need."
DeepSeek
DeepSeek-R1 is an open source reasoning model for tasks requiring complex reasoning, mathematical problem-solving and logical inference. The model uses reinforcement learning techniques to refine its reasoning ability and solve complex problems. DeepSeek-R1 can perform critical problem-solving through self-verification, chain-of-thought reasoning and reflection. In August 2025, DeepSeek released V3.1, which lets the system switch between thinking and reasoning modes, augmenting the speed and complexity of responses.
Ernie
Ernie is Baidu's LLM powering the Ernie chatbot, which was released in August 2023 and has garnered more than 45 million users. Near the time of its release, it was rumored to have 10 trillion parameters, which turned out to be an overestimation -- later models have parameter counts in the billions. More recent versions of the chatbot include Ernie 4.5 and Ernie X1. The recent models are based on a mixture-of-experts architecture. Baidu open sourced it's Ernie 4.5 LLM series in 2025.
Falcon
Falcon transformer-based models developed by the Technology Innovation Institute is open source and has multilingual capabilities. Falcon 2 is available in an 11-billion-parameter version that provides multimodal capabilities for both text and vision. Falcon 3 is available in several sizes ranging from 1 to 10 billion parameters.
The Falcon series also includes a pair of larger models with Falcon 40B and Falcon 180B as well as several specialized models. Falcon models are available on the Hugging Face platform and cloud providers like Amazon.
Gemini
Gemini is Google's group of LLMs that power the company's chatbot of the same name. The model replaced Palm to power the chatbot, which was rebranded from Bard to Gemini upon the model switch. Gemini models are multimodal to handle images, audio and video as well as text. Gemini is also integrated in many Google applications and products. It comes in several sizes -- Ultra, Pro, Flash and Nano. Ultra is the largest and most capable model, Pro is the mid-tier model, Flash prioritizes speed for agentic systems and real-time applications, and Nano is the smallest model, designed for efficiency with on-device tasks. Gemini also powers Google's AI mode in Google search and integrates with many Google applications.
Among the more recent models is Gemini 3, released in November 2025. Gemini 3's top tier is now Pro, which replaces the Ultra tier and works in tandem with a reasoning capability called "Deep Think." It was a top performer on several benchmark leaderboards at the time of its release.
Gemma
Gemma open weight language models from Google were trained on the same resources as Gemini. Gemma 2 was released in June 2024 in two sizes: a 9-billion-parameter model and 27-billion-parameter model. Gemma 3 was released in March 2025, with 1B, 4B, 12B and 27B versions, and has expanded capabilities. Gemma models can run locally on a PC and are available in Google Vertex AI.
GPT-3.5
GPT-3.5 is an upgraded version of GPT-3, which was retired by OpenAI and is no longer available in the API or in ChatGPT. GPT-3.5's training data extends back to September 2021. It was fine-tuned using reinforcement learning from human feedback. It was also integrated into the Bing search engine but was replaced with GPT-4. GPT-3.5 is considered a legacy model and is expected to be phased out.
GPT-4
GPT-4 was released in 2023. Like the others in the OpenAI GPT family, it's a transformer-based model. Unlike the other models, GPT-4's parameter count was not released to the public, though there were rumors that the model's parameter count exceeds 1 trillion. OpenAI describes GPT-4 as a multimodal model that can process and generate both language and images as opposed to being limited to language-only.
GPT-4 demonstrated human-level performance in multiple academic exams. At the model's release, its was speculated that GPT-4 came close to artificial general intelligence -- as smart or smarter than a human -- which was unfounded. GPT-4 is considered a legacy model no longer available in ChatGPT and is expected to be phased out.
GPT-4o
GPT-4 Omni (GPT-4o) is OpenAI's successor to GPT-4 and offers several improvements over the previous model. GPT-4o creates a more natural human interaction for ChatGPT and is a large multimodal model, accepting various inputs such as audio, image and text. The conversations let users engage as they would in a normal human conversation, and the real-time interactivity can also read human emotions. GPT-4o can see photos or screens and ask questions about them during interaction. GPT-4o is available to paying ChatGPT users and through the API.
GPT-5
OpenAI's GPT-5 was released in August 2025. It contains two models -- one for speed and high throughput and the other for deeper "reasoning." ChatGPT routes users between the two models depending on the intent and complexity of user interaction with the application.
GPT-5 is the default model in the ChatGPT UI and currently available to free and paying users. It's also available in the API.
GPT-OSS
GPT-OSS is OpenAI's series of open weight models. Designed for reasoning and agentic tasks, the series consists of a 120b and 20b parameter version. It enables local deployment, with the smaller of the two models more suitable for consumer hardware and the larger more suitable for enterprise hardware. Both models use a mixture-of-experts architecture and have agentic capabilities. They were the first to be released by OpenAI in 2025 under an open license since GPT-2's release in 2019. GPT-OSS is primarily for local hosting and cloud infrastructure -- it's not exposed in the ChatGPT UI.
Granite
The IBM Granite models are fully open source under the Apache v.2 license. The first iteration of the open source model debuted in May 2024, followed by Granite 3.0 in October 2024, Granite 3.1 in December 2024, Granite 3.2 in February 2025 and Granite 3.3 in April 2025.
There are multiple Granite model variants, including general-purpose models (8B and 2B variants), guardrail models and mixture-of-experts models. Beyond general purpose deployments, IBM is focused on deployment and optimization for enterprise use cases like customer service, IT automation and cybersecurity.
Grok
Grok is an LLM from xAI that powers a chatbot of the same name. Released in May 2025, Grok 3 mini is a smaller, more cost-efficient version of Grok 3, which provides two modes that augment the chatbot's default state: Think mode and DeepSearch mode. In Think mode, Grok uses chain-of-thought reasoning, explaining outputs in step-by-step detail. DeepSearch delves more deeply into internet research to produce an output. Grok performs particularly well on reasoning and mathematics benchmarks such as GPQA and AIME. Grok 3 is closed source and uses primarily Rust and Python in the training stack. Grok 4.1 was released in November 2025.
Grok's training infrastructure includes the Colossus supercomputer, which contains more than 10,000 GPUs from Nvidia. The supercomputer was built in a repurposed Electrolux factory near Memphis, Tenn. xAI and Colossus have drawn criticism from residents and activists for a lack of transparency on the environmental impact of the facility's emissions.
The name Grok comes from Robert Heinlein's 1961 science fiction novel Stranger in a Strange Land to describe the ability to thoroughly comprehend something.
Kimi
The Kimi LLM series is developed by Moonshot AI. Released in July 2025, the Kimi K2 open weight, 1-trillion-parameter, mixture-of-experts model drew attention for its competitive performance and pricing. In October 2025, Moonshot AI released Kimi Linear, which uses a more efficient attention method to reduce memory usage and improve the speed of generation for larger context windows. Kimi also has an agentic feature called OK Computer -- named after the Radiohead album -- which can create detailed web applications.
Lamda
Lamda (Language Model for Dialogue Applications) LLMs were developed by Google Brain in 2021. It used a decoder-only transformer language model and was pre-trained on a large corpus of text. In 2022, it gained widespread attention when then-Google engineer Blake Lemoine went public with claims that the program was sentient.
Llama
Llama (Large Language Model Meta AI) is Meta's LLM first released in 2023. The Llama 3.1 models. released in July 2024, include an 8-billion- and 70-billion-parameter model, with a 405-billion parameter model released later as part of the same generation. These models use a dense transformer architecture and are trained on a variety of public data sources, including webpages from CommonCrawl, GitHub, Wikipedia and Project Gutenberg.
The most recent version, Llama 4, released in April 2025, is two main models -- Llama 4 Scout and Llama 4 Maverick. Llama 4 is the first iteration of Llama to use a mixture-of-experts architecture. Earlier versions of Llama were effectively leaked and spawned many descendants, including Vicuna and Orca. Lllama models are available in many locations, including llama.com and Hugging Face.
Mistral
Mistral is a group of mixture-of-experts and dense architecture models from Mistral AI. Mistral Large 2, first released in July 2024, operates with a 128k context window, supporting dozens of languages including French, German, Spanish and Italian, along with more than 80 coding languages. In November 2024, Mistral released Pixtral Large, a multimodal model designed to handle text and visual data. Mistral Medium 3, released in May 2025, is touted as a "frontier-class multimodal model." Mistral models are available via Mistral's API to those with a Mistral billing account.
Nemotron
Nemotron open source LLMs are developed by Nvidia. The latest generation, Nemotron-4, is built on the Llama-3 architecture and comes in a range of sizes, including 340B, 70B and 15B, along with smaller mini models for edge and local deployment. The larger Nemotron-4 models deliver performance competitive with leading proprietary systems, while smaller variants are used for PC and single-GPU inference. Nemotron models are available through Nvidia inference microservices as well as standard open model distribution channels.
Nova
Nova is a series of foundation models from Amazon, hosted and served on Amazon Bedrock, the company's platform for building generative AI applications and agents. Nova video and image generation models come in several sizes: Micro text-only and low-latency model; Lite multimodal and low-latency model; Pro, a slightly higher cost, more performant version; Premier, the most capable version; Canvas image generation model; and Reel video generation model.
o1
OpenAI o1, first introduced in September 2024, is focused on providing what OpenAI calls reasoning models that can reason through a problem or query before offering a response. o1 models excel in STEM fields, with strong results in mathematical reasoning (scoring 83% on the International Mathematics Olympiad compared to GPT-4o's 13%), code generation and scientific research tasks. They operate more slowly than previous models due to their thorough reasoning processes and come with certain limitations, such as restricted access features and higher API costs. o1 is a deprecated model, having been largely replaced by newer o-series models.
o3
OpenAI introduced the successor model, o3, in December 2024. According to OpenAI, o3 is designed to handle tasks with more analytical thinking, problem-solving and complex reasoning and will improve o1's capabilities and performance. The o3 model became available to the public in June 2025.
o4-mini
Like others in the o-series, o4-mini is a reasoning model that aims to excel at tasks that require complex reasoning and problem-solving. It comes in o-4-mini and o4-mini-high, which uses more extensive reasoning for complex problems. Designed to be cost-efficient, the model uses a technique called deliberative alignment to identify attempts to exploit the system and create unsafe content.
Orca
Developed by Microsoft, the Orca LLM has 13 billion parameters. Primarily a research model, it aims to improve on advancements made by other models by imitating their reasoning procedures. The research surrounding Orca involved teaching smaller models to reason the same way larger models do. Orca 2 was built on top of the 7-billion- and 13-billion-parameter versions of Llama 2.
Palm
The Pathways Language Model is a 540-billion-parameter transformer-based model from Google powering its AI chatbot Bard. It was trained across multiple TPU 4 pods, Google's custom hardware for machine learning. Palm specializes in reasoning tasks such as coding, math, classification and question answering as well as decomposing complex tasks into simpler subtasks.
Palm gets its name from a Google research initiative to build Pathways to create a single model that serves as a foundation for multiple use cases. In October 2024, the Palm API was deprecated, and users were encouraged to migrate to Gemini.
Phi
Phi is a transformer-based language model from Microsoft. The Phi 3.5 models were first released in April 2024. Phi-4 models were released in late 2024 and early 2025. The series includes the base model, Phi-4-reasoning, Phi-4-reasoning-plus and Phi-4-mini. Released under a Microsoft-branded MIT license, the models are available for developers to download, use and modify without restrictions, including for commercial purposes.
Qwen
Qwen is large family of open models developed by Alibaba Cloud. The newest set of models, Qwen 3, was pre-trained on a significantly larger number of tokens that its predecessor was trained on. These models are suited for a wide range of tasks, including code generation, structured data understanding, mathematical problem-solving, general language understanding and generation.
StableLM
StableLM is a series of open language models developed by Stability AI, the company behind image generator Stable Diffusion. StableLM 2 debuted in January 2024 initially with a 1.6-billion-parameter model and was expanded to include a 12-billion-parameter model. StableLM 2 supports seven languages: English, Spanish, German, Italian, French, Portuguese and Dutch. The 1.6B model is suitable for specific, narrow tasks and faster processing while the 12B model provides more capability but requires more computational resources.
Tülu 3
The Allen Institute Tülu 3 is an open source 405-billion-parameter LLM that combines supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning at a larger scale. Tülu 3 uses a reinforcement learning from verifiable rewards (RLVR) framework for fine-tuning tasks with verifiable outcomes, such as solving mathematical problems and following instructions.
Vicuna 33B
Vicuna LLM, derived from Meta's original Llama models and developed by the nonprofit LMSYS Corp., was fine-tuned using data from sharegpt.com. Early evaluations suggested it was smaller and less capable than GPT-4 according to several benchmarks but was strong relative to other comparable models. Vicuna comes in several sizes, ranging from 7 to 33 billion parameters.
LLM precursors paved the way for today's entries
Although LLMs are a recent phenomenon, their precursors can date back years to decades and set the stage for modern LLMs.
BERT
BERT is a language model that Google introduced in 2018. Unlike generative LLMs, BERT is a transformer-based model that processes sequences of data to produce contextual embeddings. BERT's architecture is a stack of transformer encoders and features 342 million parameters. BERT was pre-trained on a large corpus of data, then fine-tuned to perform specific tasks along with natural language inference and sentence text similarity. It was used to improve query understanding in the 2019 iteration of Google search. BERT is still widely used in research but has been superseded by more advanced transformer models.
Seq2Seq
Seq2Seq is a deep learning approach used for machine translation, image captioning and natural language processing. It was developed by Google and underlies some more modern LLMs, including Lamda. Seq2Seq also underlies AlexaTM 20B, Amazon's LLM. It uses a mix of encoders and decoders.
Eliza
One of the earliest examples of a language model, Eliza was a natural language processing program created in 1966. It is. It simulated conversation using pattern matching and substitution. By running a certain script, Eliza could parody the interaction between a patient and therapist by applying weights to certain keywords and responding to the user accordingly. The creator of Eliza, Joshua Weizenbaum, wrote a book on the limits of computation and artificial intelligence.
Ben Lutkevich is a site editor for Informa TechTarget. Previously, he wrote definitions and features for WhatIs.
Sean Michael Kerner is an IT consultant, technology enthusiast and tinkerer. He has pulled Token Ring, configured NetWare and been known to compile his own Linux kernel. He consults with industry and media organizations on technology issues.






