What is UCaaS? Unified communications as a service guide
Unified communications as a service (UCaaS) is a cloud delivery model that offers a variety of communication and collaboration applications and services.
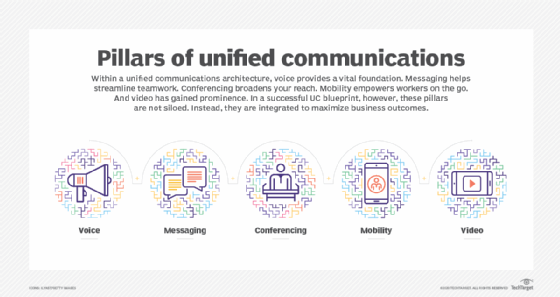
UCaaS features include enterprise messaging, presence technology, online meetings, team collaboration, telephony and video conferencing. UCaaS has become increasingly popular among businesses of all sizes as they upgrade legacy communications systems and support increasingly distributed workforces.
How does UCaaS work?
UCaaS, like its on-premises and hosted unified communications alternatives, integrates software that supports synchronous and asynchronous communication from any device, enabling consistent collaboration among teams. UCaaS is known for providing flexibility and scalability for core business tasks.
In a single, cloud-based platform, UCaaS delivers several communications features, including cloud telephony, video conferencing, meetings, team collaboration and app integrations. UCaaS offers VoIP for telephony, which enables companies to migrate from using hardware devices to software applications.
UCaaS is a subscription-based service offered through a UCaaS provider, MSP or reseller partner. The management and security of the technology are outsourced to a provider that owns the underlying infrastructure, including the data center and network.
UCaaS offerings typically have three main components:
- Application servers run by UCaaS providers in their data centers, hosted in third-party data centers or on public cloud platforms such as AWS, Google Cloud or Microsoft Azure.
- Software clients downloaded onto user devices or accessed via web browsers using WebRTC or a plugin.
- Endpoints, such as phones and video conferencing gear, that allow customers to access their UCaaS providers via the public internet or private WAN links.
Companies can deploy UCaaS relatively easily as compared with on-premises alternatives because no complex hardware installations are necessary. UCaaS, which fosters business agility, also enables organizations to shift IT staff away from tedious tasks around siloed, legacy communications platforms to more strategic roles that directly help the business. Perhaps most important, however, are employee benefits that primarily include improved collaboration and productivity.
Why should you use UCaaS?
Many companies use UCaaS to avoid the Capex and Opex associated with deploying UC on their own. Small businesses were early UCaaS adopters, as they often lack the staff and resources to maintain and support on-premises UC. Large enterprises are increasingly deploying UCaaS to streamline their communications services, enhance business continuity and support dispersed workforces. Here are some additional reasons UCaaS may be a good option for businesses:
- Scalability. UCaaS offers greater flexibility for organizations that need to quickly add and remove users, such as seasonal employees, without major infrastructure changes. The growth of the hybrid workforce has driven a greater need for organizations to support employee communication and collaboration across corporate and home networks. Cloud-based communications enables users to access features regardless of location, which provides a more consistent UX for remote and mobile workers.
- Disaster recovery. Organizations can also use UCaaS for disaster recovery and business continuity, as they no longer need to buy and maintain multiple public branch exchanges (PBXs) and UC platforms in case of an outage. Also, with UCaaS, users don't need to use a VPN to access calling and other features.
- Advanced, integrated communications. UCaaS providers often include advanced communications capabilities, such as mobility and text messaging, as part of their calling feature set. Some UCaaS providers are adding support for calling using a mobile device's native dialer or messaging app, so users don't need to switch apps to place business calls. Organizations can also integrate their contact center platform or buy contact center services directly from their UCaaS provider to create more integrated communications across the business.
- Improved productivity. Organizations looking to enhance employee productivity can do so through key UCaaS features. Support for third-party app integrations, for example, enables employees to connect the UCaaS platform with other business apps. Integrated team messaging also enables employees to treat their UCaaS platform as a one-stop shop for collaboration and business workflows.
Types of UCaaS architectures
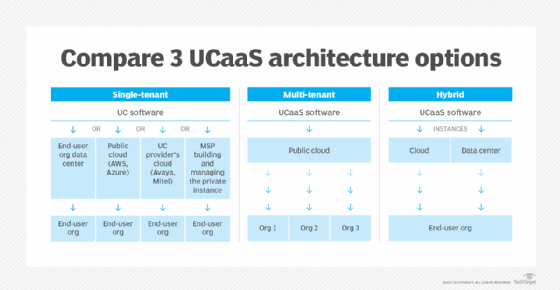
UCaaS has two primary architecture options: single-tenant and multi-tenant. Increasingly, providers are offering a hybrid of the two.
- Single-tenant. In this scenario, each customer has a single, dedicated software instance that can be customized to fits its needs. The customer maintains control of the data, where the data resides and what features are rolled out, in addition to security policies and integrations. Companies that opt for a single-tenant architecture are often in highly regulated industries, such as healthcare, government and financial services.
- Multi-tenant. In this scenario, multiple customers use the same software instance, which can reduce costs but also limits flexibility. Management and security of the platform are offloaded to the UCaaS provider. Updates and maintenance costs are all shared by the tenants, which reduces overall subscription costs as compared with a single-tenant infrastructure. A multi-tenant architecture also enables UCaaS providers to quickly deploy new features to users, but it limits customizability for individual customers.
- Hybrid. In a hybrid infrastructure, the UCaaS provider puts the software instance in a customer's network or data center. This enables providers to offer the flexibility of a single-tenant architecture with access to the variety of features offered by a multi-tenant architecture. Organizations maintain control over data residency and choose the data they want to keep on internal networks.
An organization's choice of UCaaS architecture will depend on factors including security and privacy. Organizations with significant requirements around those factors may choose a single-tenant architecture to maintain control over security, privacy and data retention. Organizations that want to lower cloud costs, on the other hand, may opt for a multi-tenant architecture.
What are the benefits of UCaaS?
Organizations can reap several benefits when implementing a UCaaS platform.
By contrast, on-premises UC, where servers are located on the corporate LAN, often requires proprietary hardware and higher upfront costs as compared with UCaaS. On-premises models also require greater dependency on in-house IT skills for maintenance and management.
While hosted UC, another option, alleviates some of the maintenance and management woes, organizations still have the upfront hardware and infrastructure costs, mainly for private WAN links.
UCaaS, on the other hand, eliminates those upfront costs, moving UC budgets from Capex to Opex. In addition, UCaaS often is easier to manage, which reduces the need for in-house IT skills. Ultimately, by moving to cloud-based UC, businesses can realize numerous benefits for both IT and end users. The most noteworthy UCaaS benefits include the following:
- Reduced costs. By migrating to UCaaS, businesses don't need to buy server hardware or manage in-house data centers.
- Offloading management. When administration responsibilities shift to the service provider, IT teams can focus on other business-specific technology goals.
- Improved scalability. The cloud model makes communications scalability faster and more efficient. The ability to scale licenses up or down provides organizations with a great deal of flexibility.
- Support for distributed work. With UCaaS, end users can access communications services from almost anywhere, which is great for supporting hybrid and remote work.
- Enhanced security and platform updates. Much like management offloading, enterprises can rely on UCaaS providers to handle security maintenance and routine platform updates to protect against software vulnerabilities.
- Better access to features. In addition to security patching, other UCaaS features are routinely updated, providing enterprises with a full suite of communications tools, along with newly added functions like generative AI.
What are the challenges of UCaaS?
Despite the promising benefits of UCaaS, the cloud-based communications technology also has some challenges. Interestingly, for some businesses, benefits such as shifting management to the service provider and using an Opex cost structure can also be seen as drawbacks.
Potential challenges of UCaaS include the following:
- Loss of control. Not all enterprises want to fully relinquish control of their communications platform to a service provider. A loss of quality control could also be problematic: Most UCaaS platforms use the internet for connectivity, which means quality of service can't be applied once communications traffic hits the internet edge.
- Carrier coverage for telephony. If organizations have a bring-your-own-carrier (BYOC) environment, they could experience problems with integration, configuration and troubleshooting.
- Interoperability issues. Different UCaaS platforms from different vendors don't always play nicely with each other, especially for collaboration sessions like meetings. But vendors are making integration improvements.
- Cost structure. While the Opex cost structure of monthly payments seems enticing, for example, the licensing expenditures over the long term could be challenging for some organizations.
- Security concerns. UC-specific security threats, especially toward voice and video applications, always pose challenges for organizations. With UCaaS, organizations lose some control over data security and might prefer to manage their own security risk.
Much like any other technology investment and implementation, enterprises need to weigh both the benefits and challenges of UCaaS.
UCaaS vs. CCaaS vs. CPaaS
At one point, UCaaS was separate from contact center as a service, or CCaaS, and communications platform as a service, or CPaaS. Over time, the apparent barriers among these technologies have faded, however. Some providers now even bundle UCaaS, CCaaS and CPaaS offerings.
UCaaS has long served the needs of office workers. CCaaS is a cloud delivery model for contact center infrastructure serving the needs of contact center agents with features such as interactive voice response and workforce management. The differences between UCaaS and CCaaS have dwindled as organizations look for a platform that can address the needs of both end-user groups.
Ideally, a consolidated platform that melds UCaaS and CCaaS features would provide contact center agents access to the same UC tools as the rest of the organization and, therefore, improve communication throughout the company.
When weighing UCaaS vs. CCaaS, organizations need to consider their unique environments to see whether a combined deployment is justified or whether the two platforms should remain siloed. For instance, office workers can probably handle the frequent upgrades and feature integrations common in many UCaaS offerings. These platform changes, however, could create service disruption to customers that contact centers can't endure.
Organizations need to realistically assess what their current architecture can support. For example, an organization using end-of-life hardware might be more agreeable to cloud migration than one that just invested in new on-premises equipment.
The decision between UCaaS vs. CPaaS has different considerations, since the two technologies are more distinct. In UCaaS, all functions and applications reside within the platform, while CPaaS has more of a build-your-own-communications model. CPaaS is a cloud delivery system organizations can use to embed communications into business apps with tools such as APIs, SDKs and the .NET Framework.
Despite their differences, UCaaS and CPaaS are, in fact, converging. UCaaS providers have incorporated open APIs into their platforms to enable tighter integration with CRM and other business applications.
How to choose the right UCaaS platform
UCaaS is a mature market, which means most providers have standardized their platforms on key features, including telephony, meetings and messaging. But that doesn't mean any UCaaS platform will work for an organization. UCaaS isn't a one-size-fits-all deployment. But using key evaluation criteria can help organizations choose the right platform for their current and future communications needs. Evaluation criteria should include the following:
1. Evaluate incumbent UC provider
Organizations already using some form for VoIP or on-premises or hosted UC should examine whether their current provider can provide UCaaS capabilities. If not, organizations should consider migrating to a new provider to access the full suite of capabilities they need.
2. Evaluate features
Organizations should determine the key features they require in a UCaaS platform. Some UCaaS providers may prioritize VoIP and calling over other collaboration features, while others offer a larger suite of features, plus contact center, email and calendaring. Most providers offer team messaging, but support for text messaging and mobility varies.
Organizations should also evaluate whether providers offer features that support specific vertical needs, such as integrating calling with appointment management for healthcare.
3. Examine potential costs
Subscription and licensing costs vary by provider, as some offer flexible, a la carte licensing, while others offer bundles. Companies with more advanced communication requirements, such as contact center or internal calling, may incur additional licensing costs. Some providers also enable organizations to continue with existing carrier contracts through BYOC.
Migration costs should also be considered. These could range from costs to upgrade the network to support UCaaS traffic to purchasing new hardware and endpoints, like phones, if current hardware isn't supported by the UCaaS vendor.
4. Review service-level agreements
Most UCaaS providers guarantee a minimum of four-nines -- 99.99% -- availability, while some offer five-nines -- 99.999% -- reliability. Some providers may only guarantee best-effort services, however. UCaaS providers that use over-the-top services may lack visibility and control into the underlying network as compared with providers that also offer network services.
Organizations must also evaluate service-level agreements to understand where provider responsibility falls in the case of an outage, as well as how the provider manages support and service delivery, such as moves, adds and changes, as well as 911 routing.
5. Establish security, compliance and governance requirements
Organizations -- particularly those in regulated industries -- have strict requirements they must meet for security, compliance and governance. UCaaS providers vary in how they offer security and compliance features, including end-to-end encryption, single sign-on and data archiving. Organizations should also evaluate providers based on their support for security standards such as ISO 27001 and SOC 2.
6. Evaluate integrations and bundled services
Most UCaaS providers integrate with common office productivity suites. More advanced providers will also support third-party integrations with popular business apps, such as Salesforce, Jira and Miro, as well as APIs to enable organizations to create their own custom integrations. Some UCaaS providers will also include CPaaS and CCaaS as a bundled suite to meet a wide array of communication needs across the organization.
How to implement UCaaS, step by step
Once an organization has chosen to adopt UCaaS and selected a provider, the next step is to create an implementation strategy. The following best practices can ensure the success of a UCaaS migration:
1. Determine the migration approach
Organizations should decide if they want to migrate to the new platform all at once or take a phased approach. Those that choose a phased approach must decide their migration path. Organizations could choose to migrate only a few services, like IP telephony to replace an aging PBX, to the new platform, and then migrate the rest at a later date. They could also migrate users to the new platform based on job role or description.
2. Examine the network
Evaluate WAN investments to ensure enough bandwidth supports cloud-based services on the corporate network -- particularly bandwidth-sensitive services like video. Consider software-defined WAN, which is layered on top of network services, to provide increased reliability and app performance. BYOC may also come into play when evaluating network support for telephony.
IT departments are facing the new challenge of supporting both corporate and home networks as more organizations employ distributed workforces. Home Wi-Fi must also be adequate enough to support cloud-based, real-time communication tools. Some UCaaS providers, like Cisco, bundle home networking devices with their platforms. Consider supporting new networking technology, like Wi-Fi 6, for home users or providing stipends that enable them to upgrade their home internet service.
3. Prepare end users
End-user buy-in is critical to the success of a UCaaS implementation. Organizations should involve end users early on in the implementation process through pilot programs to test the new system and make sure it meets their communication and collaboration needs.
Train end users to ensure they understand the full suite of features and capabilities provided by the new platform. The UCaaS provider may offer on-site or web-based user adoption and training programs. Users should be trained not only on how to use the new platform, but also on how it can improve and streamline workflows and business process.
4. Monitor and evaluate post-deployment
Implementing UCaaS doesn't stop once the platform is rolled out to end users. Organizations must monitor the UCaaS environment to ensure apps are performing well and to detect issues that negatively affect users. Use the monitoring and performance capabilities built into the UCaaS platform, and consider third-party monitoring services.
Organizations should also evaluate usage patterns and gain user feedback to identify areas that need to be addressed. Consider deploying employee experience platforms that can provide insight into how employees are using the platforms to identify areas where additional training is needed.
UCaaS future and trends
The growth of the hybrid workforce will continue to drive UCaaS adoption. Organizations will seek to consolidate their communications services in order to provide a single, unified platform that can address all of their communications needs. Tightly integrating CPaaS and CCaaS will become a greater priority in order to achieve this goal.
AI will also drive further advancements for enterprise communications. UCaaS providers are already implementing AI for features like real-time meeting transcriptions and translations. The introduction of generative AI will provide more advanced communication and collaboration capabilities, including the following:
- Digital assistants that manage and automate workflows for employees, as well as perform increasingly complex tasks, such as writing emails and attending meetings. In UCaaS platforms integrated with productivity suites, generative AI can access a wide range of user data to help with content and idea generation.
- Intelligent meeting capabilities, such as meeting recaps and action items tailored to a user's role, chapters for meeting recordings, and even facial and gesture recognition for sentiment analysis.