Common Service Center (CSC)
What is Common Service Center (CSC)?
Common Service Center (CSC) is an initiative by the government of India to establish locations with computers that are freely available for citizens to use. These centers allow the citizens in rural areas to access digital government resources and business services. It is also spelled Common Service Centre.
A CSC is essentially a kiosk with a personal computer (PC), an internet connection and other ICT (information and communications technology equipment) and services. The CSCs provide access to e-governance, education, health, entertainment and other government and private services. Other services available include computer training, telemedicine, office applications, compact disk burning, scanning, printing and digital imaging.
History of Common Service Centers
In 2006, the government of India passed a plan to introduce an e-governance initiative for its citizens. This would allow all its citizens to access government programs electronically.
Many locations in India are rural though and many people do not have access to computers nor the internet. Common Service Centers were envisaged as a way to bridge this digital divide to give everyone in the country fair access to government programs.
According to their website, CSCs offer access to e-services, delivering essential government and public utility services, social welfare schemes, financial inclusion services, healthcare and agriculture services, apart from a host of B2C services. CSCs have also been trying to bridge the gaps in digital literacy and skills of rural citizens through a range of literacy initiatives focused on digital, financial and legal literacy and e-learning and skill development courses.
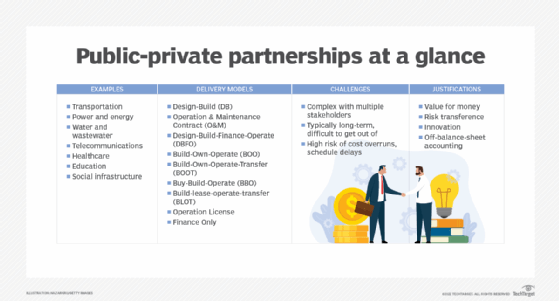
CSC would go on to be built as a public-private partnership (PPP) paid for primarily by private financiers with additional national and state government funding. The initial scope included building 100,000 CSCs spread throughout rural villages in India.
Common Service Centers 2.0
Digital India is an ambitious plan by the Indian government to establish fully digital services, identity and literacy among its citizens. In 2015 the plan for CSC 2.0 was approved. It called for modernizing the existing CSCs and building new ones for a total of 250,000 CSCs.
The goal is for each CSC to be self-funded by a village level entrepreneur (VLE). The VLE would earn a share of the revenue gained by the CSC from filling services. It is also hoped to empower more women to be VLEs and take technical roles. The CSC will also be able to help people in their local languages.
The CSC 2.0 guidelines list the types of equipment that should be available at each CSC. It will consist of a computer or laptop and a printer, scanner, web camera, broadband internet, biometric scanner and an uninterruptable power supply (UPS). The specifics of the hardware are left up to the VLE.
See how HR can help with a digital divide in the U.S. and learn how techno-nationalism links technology and technological innovation to national identity.
