Toyota Way
What is the Toyota Way?
The Toyota Way is a comprehensive expression of the company's management philosophy, which is based on the two foundational pillars of Continuous Improvement, also known as kaizen, and Respect for People. Toyota documented its management philosophy in 2001 but has not made the document publicly available.
The Toyota Way is based on 14 principles and aims to remove obstacles to perfection in everyday business processes.
Background of the Toyota Way
Dr. Jeffrey Liker, a professor of industrial and operations engineering at the University of Michigan, analyzed the philosophy and principles in his 2004 book, The Toyota Way. Liker characterizes the approach as "a system designed to provide the tools for people to continually improve their work."
The Toyota Way is based on the Toyota Production System (TPS). Toyota developed the TPS in the 1950s as a response to automaker Ford's mass production systems. Eiji Toyoda, a member of the Toyota Group founding family, studied Ford's production system and realized Toyota couldn't achieve Ford's speed and scale of production. As a result, he worked with industrial engineer Taiichi Ohno to create the TPS, using machines right-sized for production demand and self-monitoring machines.
The TPS went on to inspire lean manufacturing decades later, which then informed the Toyota Way in 2001.
What are the Toyota Way principles?
The 14 principles of the Toyota Way, as detailed by Liker, are the following:
- Build a long-term philosophy. Management should focus on extended sustainability rather than short-term financial gain. Fostering a sense of purpose in employees is also part of this principle.
- Create a continuous process flow. The thinking behind this principle is that the right process will produce the right results. Continuous improvement is promoted by eliminating the seven wastes -- known as muda in Japan -- that Ohno identified: overproduction, waiting, unnecessary transport or conveyance, overprocessing or incorrect processing, excess inventory, unnecessary motion and defects.
- Use pull systems to avoid overproduction. This involves minimizing the work in progress. It relies on initiating production based on downstream demand or signals, as in the kanban visual production system.
- Balance the workload. This is sometimes referred to by the Japanese word heijunka, which means "leveling the production process." It aims to reduce unevenness -- or mura -- in a production process and mitigate the risk of overburdening -- or muri -- parts of the production system.
- Stop to fix problems or get quality right the first time. Companies should build a culture where problems are addressed immediately. Any employee can halt production when a problem is detected. The thinking behind this principle is that quality drives value. Jidoka -- meaning "machines with human intelligence" -- is the foundation for building quality into a system.
- Use standardized tasks and processes for continuous improvement and employee empowerment. Stable, repeatable methods should be used wherever possible to maintain predictable timing and output.
- Use visual controls to illuminate problems. Visual indicators should be easy to understand so employees can determine whether they are in compliance with standards.
- Use reliable, thoroughly tested technology. Technology should be used to support rather than replace people. This can be done by working out a process manually before applying technology to expediate it.
- Grow leaders who teach the philosophy to others. Leaders should thoroughly understand the work and the philosophy behind it to effectively teach future leaders about it.
- Develop teams that follow the philosophy. A strong company culture features teams of exceptional people who champion the company's philosophy, values and beliefs over many years.
- Respect extended network. Treat partners and suppliers as extensions of the business so they grow and develop as well.
- Solve problems by going directly to the source. This principle is sometimes called genchi genbutsu, meaning "go and see" in Japanese. Go and personally observe, verify and speak based on personally verified data.
- Make decisions deliberately and by consensus. Consider all options, decide carefully and implement decisions quickly.
- Continually learn and become a learning organization. Use continuous improvement and relentless reflection to address process inefficiencies and apply countermeasures.
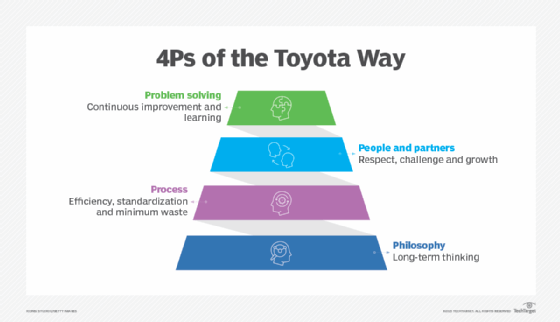
The Toyota Way's 14 principles can be framed using the 4P model:
- Philosophy. This encompasses the first principle.
- Process. This encompasses principles 2 through 8 and is related to process optimization and technical aspects of the Toyota Way.
- People and partners. This encompasses principles 9 through 11 and emphasizes culture.
- Problem solving. This encompasses the last three principles and deals with continuous process improvement.
What are the Toyota Way pillars?
The 14 principles of Toyota's management philosophy are categorized under two main pillars:
- Continuous Improvement. This pillar emphasizes small, ongoing positive changes, cooperation and commitment. It is also referred to as kaizen, which is a compound of two Japanese words that mean "good change." Continuous improvement is built on its own set of principles, which include letting go of assumptions and proactive problem solving.
- Respect for People. The Respect for People pillar has two components: respect and teamwork. Teams should strive to understand each other, take responsibility and build mutual trust. They should also stimulate personal and professional growth as well as share development opportunities to maximize team and individual performance.

Uses of the Toyota Way
Elements of the Toyota Way have been widely adopted in business areas, including the following:
- lean production
- lean management
- Agile software development
- project management
- just-in-time manufacturing
In lean project management, the Toyota Way is used to maximize efficiencies. It uses bottleneck analysis, which looks for places where process flow is constrained and tries to find the root causes. This helps companies conform with the principles in the process and problem-solving sections of the Toyota Way.
Industries where the Toyota Way might be useful include manufacturing, software production and healthcare. Any team tasked with performing a series of processes can use the approach to its benefit.
The Toyota Way vs. lean manufacturing
The Toyota Way and lean manufacturing are easily confused concepts. They focus on many of the same points and influence each other, but they aren't interchangeable.
Lean manufacturing is based on five principles laid out in the foundational book Lean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation by James P. Womack and Daniel T. Jones. The principles are value, the value stream, flow, pull and perfection.
The Toyota Way is divided into 14 principles that take ideas from lean manufacturing and apply them specifically to Toyota's management principles and organizational culture. For example, principle 14 in the Toyota Way draws from principal five of lean -- pursuing perfection. Both the Toyota Way and lean are based on the TPS.
Agile takes the lean concepts that inspired the Toyota Way and applies them to software development. Learn about Agile, how it differs from other methodologies and how software methodologies have their roots in manufacturing methodologies.