What is a web server?
A web server is software and hardware that uses HTTP and other protocols to respond to client requests made over the World Wide Web. Its main job is to display website content, such as text, images, videos and applications, to users by storing, processing and delivering webpages. Web servers are also used in web hosting, i.e., the hosting of data for websites and web-based applications.
Computers that host websites must have web server software to be able to store, process and, most importantly, display web content, like documents, images or videos.
A web server usually refers to hardware and software working together.
The web server hardware is connected to the internet and enables data to be exchanged with other devices connected to the web. It is a computer that stores web server software and other files related to a website, such as Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) documents, images and JavaScript files, and is installed with web server software. The computer includes numerous components, including processor, RAM, high-capacity storage drive, and one or more network interface cards.
Web server software controls how a user accesses hosted files. Its primary function is to display the content of hosted websites on a user's device, e.g., computer, smartphone, tablet, etc. The software is accessed through the domain names of websites -- multiple domains can be hosted on one web server -- and ensures the delivery of the site's content to the requesting user.
The web server understands web addresses, also known as URLs. Like web server hardware, web server software is also composed of several components. Also, most of them support and use HTTP to view webpages. Besides HTTP, some web servers support Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) and File Transfer Protocol (FTP) for email, file transfer and storage.
What are web servers used for?
Web servers often come as part of a larger package of internet- and intranet-related programs that are used for the following:
- Building and publishing webpages.
- Web hosting.
- Sending and receiving emails.
- Downloading requests for FTP files.
Some web servers also provide platforms for developing web applications, thus contributing to the growth of the web's global infrastructure.
How web servers work
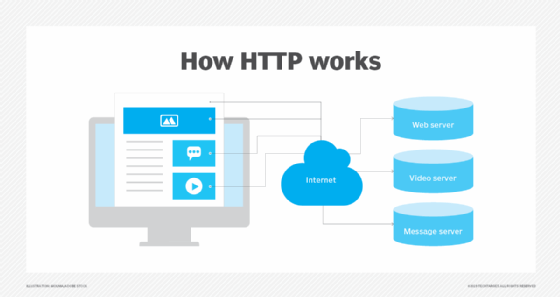
The web server process is an example of the client-server model. In this model, a client -- usually an end user's device -- requests a server for some information. The server acknowledges the request and then provides the requested information to the client.
When a user's device needs a file that's hosted on a web server, it initiates the request via a web browser, such as Google Chrome or Firefox. The user types the URL of the site where the required file is hosted. The browser requests the file by HTTP. When the request is received by the web server, the HTTP server accepts the request, finds the content and sends it back to the browser through HTTP.
Thus, when a browser requests a page from a web server, this series of steps plays out:
- The user specifies a URL in a web browser's address bar.
- The web browser obtains the IP address of the domain name -- either by translating the URL through the domain name system (DNS) or by searching for it in its cache. This brings the browser to a web server.
- The browser requests the specific file from the web server by an HTTP request.
- The web server responds, sending the browser the requested page, again, through HTTP. The browser is then able to display the webpage.
- If the requested page does not exist or if something goes wrong, the web server responds with an error message: 404 Not Found.
What is an example of a web server?
There are a number of web servers available, including the following:
- Apache HTTP Server. Developed by Apache Software Foundation, it is a free and open source web server for Windows, macOS and Unix operating systems (OSes). Launched in 1995, the web server is secure and extensible, and it aligns with HTTP standards. In July 2024, the Apache Foundation released the latest version of the web server: Apache httpd 2.4.62.
- Lighttpd. This flexible web server is designed to efficiently use the central processing unit and memory and includes features like FastCGI, Common Gateway Interface, authentication, output compression and URL rewriting, making it suitable for high-performance environments.
- Microsoft Internet Information Services. Developed by Microsoft, IIS for Windows Server provides a scalable and open architecture to host websites and web applications. The web server is flexible and easy to manage and includes capabilities to securely publish web content, delegate site configuration management, centralize web farm management, reduce server footprint, enable high-speed dynamic caching and compression, and deliver high-fidelity user experiences. Website owners can try IIS with a free trial edition of Windows Server.
- Nginx. Pronounced "engine X," this popular open source HTTP web server is known for its light resource utilization and scalability. It provides automatic load balancing and high fault tolerance, and it accelerates reverse proxying with caching and supports Post Office Protocol 3, Internet Message Access Protocol and SMTP for authentication. In addition, it supports multiple protocols, including HTTP/2, HTTP/3, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security Server Name Indication.
Dynamic vs. static web servers
A web server can be used to serve either static or dynamic content. Static refers to the content being shown as is, while dynamic content can be updated and changed. A static web server consists of a computer and HTTP software. It is considered static because the server sends prewritten hosted files as is to a browser. Also, every user sees the same content since the server only delivers the stored files. There is no server-side processing, database interaction or real-time generation of dynamic, user-specific content.
A dynamic web browser consists of a web server and other software, such as an application server and database. It is considered dynamic because the application server can be used to update any hosted files before they are sent to a browser. The web server can generate content by requesting it in real time from the underlying database. Also, this content is delivered based on a user's specific input or other variables.
This makes it possible to deliver interactive features on the website, such as login forms and shopping carts. These features, generated dynamically and on the fly, can enhance user experiences. However, the increased flexibility of the process also makes it more complicated to design and implement.
Server-side scripting in web servers
Many basic web servers also support server-side scripting, which is used to employ scripts that run on the server. The goal is to customize the response to the client's request and dynamically generate and deliver web content in real time.
Server-side scripting runs on the server machine and typically has a broad feature set, which may include database access, identity authentication, push notifications, etc. The server-side scripting process also uses Active Server Pages, PHP and other scripting languages. This process also enables HTML documents to be created dynamically.
Server-side scripting is useful because it enables dynamic content generation. Its drawback is that it introduces a lot of latency because every request from every client has to travel to the server before it can be processed. For this reason, many web developers run more code on the client side for modern web applications. Including client-side processes in the application architecture can reduce latency, while still displaying dynamic content.
How to choose a web server
Site owners and administrators should consider numerous factors when choosing a web server, including the following:
- What the website is used for and whether the web server can support those needs.
- How well it works with the OS and other servers.
- Its hosting environment.
- Its ability to handle server-side programming.
- Whether it can handle sudden spikes in workloads without impacting performance (scalability).
- Security characteristics.
- Publishing, search engine and site-building tools that come with it.
It's also important to check whether the provider offers responsive customer support, frequent data backups and assurance of uptime above 99%. Web servers may also have different configurations and set default values. To create a high-performance web server, high throughput and low latency help.
Web server security practices
Comprehensive security practices can make for more secure web servers and safer web experiences for users. These may include the following:
- Reverse proxy, which hides an internal server and acts as an intermediary for traffic originating on an internal server.
- Access restrictions by limiting the web host's access to infrastructure machines or by using Secure Shell.
- Patched and up-to-date web servers to minimize vulnerabilities and susceptibility to cyberattacks.
- Network monitoring to detect unauthorized or potentially malicious activity.
- SSL to encrypt sensitive data and make it inaccessible to anyone other than the intended recipient.
- Firewalls to monitor HTTP traffic, block malicious traffic and malware, and ensure that only authorized users are allowed to access web resources.
Explore the differences between Tomcat vs. Apache HTTP Server and HTTP vs. HTTPS. Also, a DNS server resolves the hostnames of websites into Internet Protocol addresses. Learn how to troubleshoot common name resolution issues on Windows, Linux and macOS.