microchip
What is a microchip?
A microchip -- also called a chip, computer chip or integrated circuit (IC) -- is a unit of integrated circuitry that is manufactured at a microscopic scale using a semiconductor material, such as silicon or, to a lesser degree, germanium. Electronic components, such as transistors and resistors, are etched into the material in layers, along with intricate connections that link the components together and facilitate the flow of electric signals.
Microchip components are so small they're measured in nanometers (nm). Some components are now under 10 nm, making it possible to fit billions of components on a single chip. In 2021, IBM introduced a microchip based on 2 nm technology, smaller than the width of a strand of human DNA. A nanometer is one-billionth of a meter or one-millionth of a millimeter. At that scale, it is possible to fit up to 50 billion transistors on a microchip the size of a fingernail.
How are microchips made?
Microchip manufacturers rely on silicon for their chips because it is abundant, inexpensive and easy to work with. Also, it has proven to be a reliable semiconductor in a variety of devices. However, silicon might be reaching its practical limits as microchip technologies become smaller and more components are squeezed into the microchip in an effort to meet the ever-increasing demands for greater performance and more data. Researchers are actively working on a variety of solutions that they hope will be able to carry electronics into the future.
Microchips typically include the following types of components, which can number into the millions or even billions, depending on the type and function of the microchip:
- Transistors. Transistors are active components that control, generate or amplify electric signals within the circuitry, acting as a switch or gate. Multiple transistors can be combined into a single logic gate that compares input currents and produces a single output according to the specified logic.
- Resistors. Resistors are passive components that limit or regulate the flow of electrical current or that provide a specific voltage for an active device. Resistors control the electric signals that move between transistors.
- Capacitors. Capacitors are passive components that store electricity as an electrostatic field and release electric current. Capacitors are often used along with transistors in dynamic RAM (DRAM) to help maintain stored data.
- Diodes. Diodes are specialized components with two nodes that conduct electric current in one direction only. A diode can permit or block the flow of electric current and can be used for various roles, such as switches, rectifiers, voltage regulators or signal modulators.
What are the types of microchips?
Microchips drive all of today's electronics. Not only do these include computers, but also smartphones, network switches, home appliances, car and aircraft components, televisions and amplifiers, internet of things devices and countless other electronic systems. Microchips generally fall into one of the following two categories:
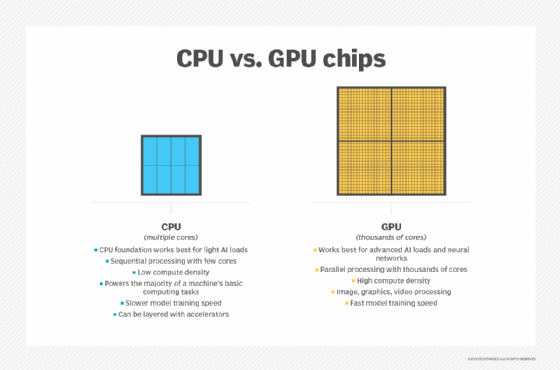
- Logic. This type of microchip does all the heavy lifting, processing the instructions and data that are fed to the device and subsequently to the chip in that device. The most common and widely used type of logic microchip is the central processing unit (CPU). However, this category also includes more specialized chips, such as graphical processing units (GPUs) and neural net processors.
![CPUs vs. GPUs]()
Logic microchips include the central processing unit (CPU), a category of integrated circuit that also includes more specialized chips, like graphical processing units (GPUs) and neural net processors. - Memory. This type of microchip stores data. Data storage is either volatile or non-volatile. volatile memory chips require a constant source of power to retain their data. DRAM is a common example of a volatile memory chip. A non-volatile chip is one that can persist data even if the power supply is disrupted. A good example of non-volatile memory is NAND flash. Volatile memory devices tend to perform much better than non-volatile devices, although a number of efforts are underway to bridge the gap between the two, such as storage class memory.
Although many microchips focus on logic or memory only, other types of chips incorporate both, along with other capabilities. For example, system-on-a-chip (SoC) ICs are now widely used in devices such as smartphones and wearable technology and have begun making headway into the computer market, as evidenced by the Apple silicon series of chips. Another example is the application-specific IC, which can also include logic, memory and other capabilities, much like the SoC chip, except that the ASIC chip is customized for a specific purpose, such as medical equipment or an automotive component.

Learn the differences between CPU vs. microprocessor, and explore how CPU, GPU and DPU differ from one another.