What is a communication service provider (CSP)?
Communication service provider (CSP) is a broad category of companies that deliver telecommunications, including broadcast and two-way communications services.
Types of communication service providers
Types of providers under the umbrella of CSP include wireless and landline telecommunications providers, as well as cable and satellite communications providers that own their infrastructure. Also included are over-the-top (OTT) content providers and cloud communications providers; these companies operate through a bring-your-own-bandwidth business model, which requires customers to have existing internet service from another provider to access the product.
Infrastructure providers
Most CSPs that own their infrastructure no longer focus on only a single type of service. They will package several services together to maximize revenue. This will often include internet, cellular and television services.

- Telecommunication/telephony providers. These companies focus on voice service. Historically, this largely comprised plain old telephone service (POTS), but voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is now the predominant service in most markets. Due to this shift, most of these providers have essentially become internet service providers (ISPs).
- ISPs. These providers primarily offer internet access. They can deliver it through fiber optics, coaxial cable, cellular, satellite or other technologies. Most specialize in either home or business use.
- Mobile network operators. MNOs provide wireless voice, data and text message services via technologies such as 4G and 5G. They own the base station and supporting infrastructure.
- Television providers. These companies deliver content over cable and satellite networks. Today, this also includes other streaming media over broadband networks.
OTT providers
OTT providers deliver their content, application or service using a customer's existing internet access.
- Video content providers. These companies deliver streaming video, such as movies and TV shows, directly to the consumer.
- Cloud communication providers. These offer voice and video chat services. This might be pure VoIP services, and internet meeting services.
- Mobile virtual network operators. MVNOs don't own cell towers or infrastructure, but instead lease service from an MNO and resell it under their own brand.
The evolution of CSPs
Communication service providers have evolved over the years in response to changes in the regulatory landscape, market trends and new technologies.
Era of monopolies
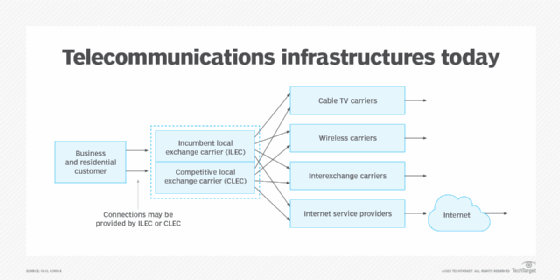
Telecom providers once monopolized communication infrastructures, as the large capital investment required to lay cables limited competition. Some companies were treated as utilities with government monopolies, such as incumbent local exchange carriers in the United States. This limited ownership made for low competition and high-cost, high-margin communications, especially where international communications were concerned. There was also little overlap between communication services such as cable, satellite, wireless and traditional landlines.
Deregulation and new competition
Deregulation in the 1980s and the increase in new technologies caused legacy providers in the United States to offer a larger selection of services, disrupting the delineated categories of traditional communication services.
Common carrier rules also required incumbent providers to allow newer competitors access to their networks. These upstarts, known as competitive local exchange carriers, could now operate alongside ILECs and would be given direct access to the same equipment panels and service poles.
The digital revolution
The advent of IP telephony and regulatory changes have eroded the margins on communications services and lowered costs, resulting in greater competition. As a result, legacy providers have been forced to expand and innovate, as access alone is no longer a differentiator and competitors offer similar services at lower prices or even for free.
OTT providers have supplanted historically lucrative markets, such as cable television. Net neutrality rules prevent infrastructure providers from abusing their market position to keep out new content providers by purposefully slowing or blocking their traffic.
Future communication service provider trends
Today, CSPs are focused on the digital transformation of the industry. Shrinking margins and new competition requires innovation to keep pace. Customers now expect inexpensive internet service as a means to access streaming media services. Technologies like artificial intelligence, analytics and automation can help providers improve service and prevent outages.
CSPs can leverage their infrastructure to boost revenue through new business services. For instance, private 5G can give an enterprise secure, dedicated access for their devices. Many CSPs can also offer edge computing with lower latency than major cloud providers because they connect directly to the customer network.
