empirical analysis
What is empirical analysis?
Empirical analysis is an evidence-based approach to the study and interpretation of information. Empirical evidence is information that can be gathered from experience or by the five senses. In a scientific context, it is called empirical research.
Empirical analysis requires evidence to prove any theory. An empirical approach gathers observable data and sets out a repeatable process to produce verifiable results. Empirical analysis often requires statistical analysis to support a claim.
The word empirical comes from the ancient Greek word empeiria, meaning experience.
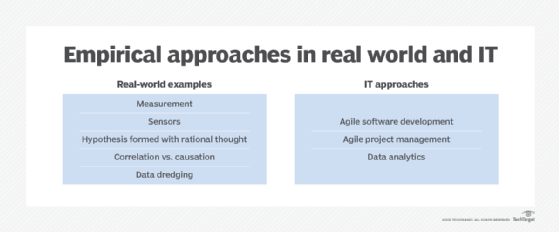
How to conduct empirical analysis
Empirical analysis is based on observable data. It is mainly concerned with what can be experienced and directly observed. Well-conducted empirical analysis sets out what was initially observed, what it expects to observe during testing and what was observed during testing. If the observed results do not match the expected result, then the hypothesis is not supported by the observed data. Empirical research is concerned only with what is observed, not with what makes sense or follows logically. It is closely related to the scientific method.
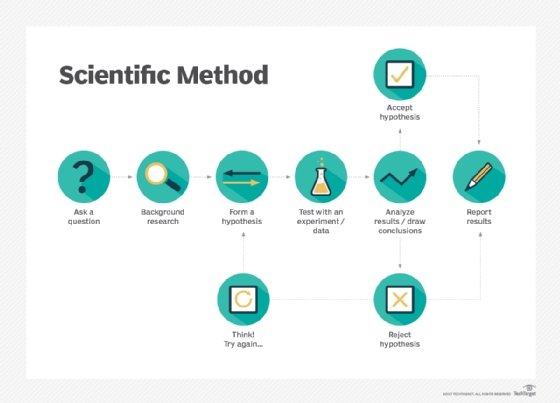
Empiricism vs. rationalism
Empiricism is often contrasted with rationalism. Rationalism is a school of thought that truth can be determined by starting from simple truths, or axioms, and using logic and reasoning alone to build up to larger truths without needing to verify the truths with reality. A strictly empirical approach is limited to only what can be observed and can only produce results that support, disprove or are neutral to a theory.
Both an empirical and rational approach are needed to produce practical results. A purely rational approach can produce ideas that do not agree with observable reality, while relying on empirical data alone cannot produce new ideas and insights. Making good use of both is the cornerstone of the scientific method.
Quantitative and qualitative research in empirical analysis
Empirical analysis relies on gathering data through quantitative research, qualitative research or a mix of the two.
Quantitative research is related to things that can be quantified or assigned numbers. It deals with things that can be counted or measured. It may also use multiple-choice or closed-ended questions. In quantitative research, if two different people made the same measurements, they would get the same results.
Qualitative research is related to human perception. It deals with likes, dislikes, opinions, thoughts and behavior. It is often gathered in interviews, focus groups or open-ended surveys. Qualitative research can give excellent insight into data, but due to human nature and the difficulty of gathering large amounts of unstructured information, it may not always be reliable.
As an example of quantitative and qualitative research, imagine a firm wanted to determine if its new product was easier to use then its old one, so it observes people using the product. Examples of quantitative data it can gather would be how many people successfully completed the task, how long it took the person to finish, the age of the person and a survey with a rating of one to five of how difficult the person thought the task was. Examples of qualitative data would be what an observer saw while the person was doing the task and an interview afterward.

Empirical research cycle
In 1969, Dutch researcher A.D. de Groot published his five-step empirical research cycle. It has been widely adopted as the most concise way to conduct empirical research. Each step must be conducted in sequence and is as important as the last:
- Observation. Initial observations of a phenomena are made. This sparks an idea or a line of inquiry. Initial empirical data and research into existing information can be done.
- Induction. A probable explanation of the observed phenomenon is proposed. Inductive reasoning is used to take the specific example from step one and infer a generalized explanation for it.
- Deduction. A testable hypothesis is proposed that can support the explanation. Deductive reasoning is used to take the generalized explanation and make a specific prediction that can be tested and observed.
- Testing. Quantitative and qualitative empirical data are gathered. The data is examined, often with statistical analysis. The results can support, refute or be neutral to the hypothesis. Because of the limits of empirical data and human perception, it is not said that the results prove or disapprove the hypothesis, only that they support or don't support it.
- Evaluation. The reasoning, methodology and findings of the experiment are written down, and the conclusions of the researcher are presented. Information relating to any difficulties, challenges and limits of the test are also included. It may also include further possible avenues of research.
As a simple example of the empirical research cycle, imagine you start sneezing when you visit your sister.
- Observation. I do not sneeze at home, I do sneeze at my sister's home and my sister owns a cat, while I do not have a cat.
- Induction. I may be allergic to cats.
- Deduction. I hypothesize that, if I go to the pet store and pick up a cat, I will start sneezing.
- Testing. I went to the pet store, and when I picked up the cat, I started sneezing.
- Evaluation. My trip to the pet store supports the idea that I am allergic to cats. But it was a different type of cat, and it was the same season, So, it may have been hay fever. If I wanted to gather more evidence, I should visit another person with a cat.

Empirical analysis in IT and business
Using empirical analysis is highly effective in IT and in business. These areas can be highly complex, have interrelated factors or delve into human behavior. Because of this, the behaviors of systems or why things happen can be unclear, hard to find, or even counterintuitive or seemingly irrational. Using the evidence-based approach of empirical analysis can help to remove uncertainty in the decision-making process.

Data warehouses and data lakes can create vast amounts of empirical information. By applying empirical analysis methods to this data, new insights can be found. This can include information about customer behavior or business efficiencies. Data analytics falls in this category.
Using A/B testing is a common way to do empirical research on usability. Different users are presented different designs, and by monitoring metrics, such as click-through, the best one can be found.
See also: data collection, data mining, data cleansing, data curation, data validation, big data, quantitative analyst and field of view.
