scientific method
What is the scientific method?
The scientific method is the process of objectively establishing facts through testing and experimentation. The basic process involves making an observation, forming a hypothesis, making a prediction, conducting an experiment and finally analyzing the results. The principals of the scientific method can be applied in many areas, including scientific research, business and technology.
Steps of the scientific method
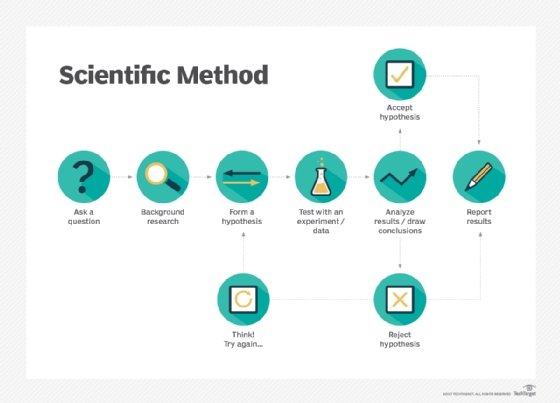
The scientific method uses a series of steps to establish facts or create knowledge. The overall process is well established, but the specifics of each step may change depending on what is being examined and who is performing it. The scientific method can only answer questions that can be proven or disproven through testing.
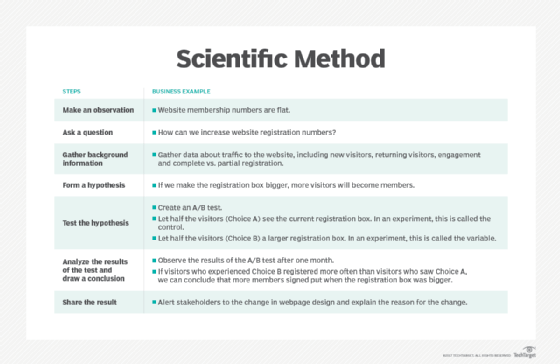
Make an observation or ask a question. The first step is to observe something that you would like to learn about or ask a question that you would like answered. These can be specific or general. Some examples would be "I observe that our total available network bandwidth drops at noon every weekday" or "How can we increase our website registration numbers?" Taking the time to establish a well-defined question will help you in later steps.
Gather background information. This involves doing research into what is already known about the topic. This can also involve finding if anyone has already asked the same question.
Create a hypothesis. A hypothesis is an explanation for the observation or question. If proven later, it can become a fact. Some examples would be "Our employees watching online videos during lunch is using our internet bandwidth" or "Our website visitors don't see our registration form."
Create a prediction and perform a test. Create a testable prediction based on the hypothesis. The test should establish a noticeable change that can be measured or observed using empirical analysis. It is also important to control for other variables during the test. Some examples would be "If we block video-sharing sites, our available bandwidth will not go down significantly during lunch" or "If we make our registration box bigger, a greater percentage of visitors will register for our website than before the change."
Analyze the results and draw a conclusion. Use the metrics established before the test see if the results match the prediction. For example, "After blocking video-sharing sites, our bandwidth utilization only went down by 10% from before; this is not enough of a change to be the primary cause of the network congestion" or "After increasing the size of the registration box, the percent of sign-ups went from 2% of total page views to 5%, showing that making the box larger results in more registrations."
Share the conclusion or decide what question to ask next: Document the results of your experiment. By sharing the results with others, you also increase the total body of knowledge available. Your experiment may have also led to other questions, or if your hypothesis is disproven you may need to create a new one and test that. For example, "Because user activity is not the cause of excessive bandwidth use, we now suspect that an automated process is running at noon every day."
Using the scientific method in technology and computers
The scientific method is incredibly valuable in technology and related fields. It is obviously used in research and development, but it is also useful in day-to-day operations. Because almost everything can be quantified, testing hypotheses can be easy.
Most modern computer systems are complicated and difficult to troubleshoot. Using the scientific method of hypothesis and testing can greatly simplify the process of tracking down errors and it can help find areas of improvement. It can also help when you evaluate new technologies before implementation.
Using the scientific method in business
Many business processes benefit when using the scientific method. Shifting business landscapes and complex business relationships can make behaviors hard to predict or act counter to previous history. Instead of using gut feelings or previous experience, a scientific approach can help businesses grow. Big data initiative can make business information more available and easier to test with.
The scientific method can be applied in many areas. Customer satisfaction and retention numbers can be analyzed and tested upon. Profitability and finance numbers can be analyzed to form new conclusions. Making predictions on changing business practices and checking the results will help to identify and measure success or failure of the initiatives.
Common pitfalls in using the scientific method
The scientific method is a powerful tool. Like any tool, though, if it is misused it can cause more damage than good.
The scientific method can only be used for testable phenomenon. This is known as falsifiability. While much in nature can be tested and measured, some areas of human experience are beyond objective observation.
Both proving and disproving the hypothesis are equally valid outcomes of testing. It is possible to ignore the outcome or inject bias to skew the results of a test in a way that will fit the hypothesis. Data in opposition to the hypothesis should not be discounted.
It is important to control for other variables and influences during testing to not skew the results. While difficult, not accounting for these could produce invalid data. For example, testing bandwidth during a holiday or measuring registrations during a sale event may introduce other factors that influence the outcome.
Another common pitfall is mixing correlation with causation. While two data points may seem to be connected, it is not necessarily true that once is directly influenced by the other. For example, an ice cream stand in town sees drops in business on the hottest days. While the data may look like the hotter the weather, the less people want ice cream, the reality is that more people are going to the beach on those days and less are in town.
History of the scientific method
The discovery of the scientific method is not credited to any single person, but there are a few notable figures who contributed to its development.
The Greek philosopher Aristotle is considered to be one of the earliest proponents of logic and cycles of observation and deduction in recorded history. Ibn al-Haytham, a mathematician, established stringent testing methodologies in pursuit of facts and truth, and he recorded his findings.
During the Renaissance, many thinkers and scientists continued developing rational methods of establishing facts. Sir Francis Bacon emphasized the importance of inductive reasoning. Sir Isaac Newton relied on both inductive and deductive reasoning to explain the results of his experiments, and Galileo Galilei emphasized the idea that results should be repeatable.
Other well-known contributors to the scientific method include Karl Popper, who introduced the concept of falsifiability, and Charles Darwin, who is known for using multiple communication channels to share his conclusions.
See also: falsifiability, pseudoscience, empirical analysis, validated learning, OODA loop, black swan event, deep learning.