World Wide Web (WWW)
What is the World Wide Web (WWW, W3)?
The World Wide Web -- also known as the web, WWW or W3 -- refers to all the public websites or pages that users can access on their local computers and other devices through the internet. These pages and documents are interconnected by means of hyperlinks that users click on for information. This information can be in different formats, including text, images, audio and video.
The term World Wide Web isn't synonymous with the internet. Rather, the World Wide Web is part of the internet.
How does the World Wide Web work?
Paving the way for an internet revolution that has transformed the world in only three decades, the World Wide Web consists of multiple components that enable users to access various resources, documents and web pages on the internet. Thus, the WWW is like a vast electronic book whose pages are stored or hosted on different servers worldwide.
These pages are the primary component or building blocks of the WWW and are linked through hyperlinks, which provide access from one specific spot in a hypertext or hypermedia document to another spot within that document or a different one. Hyperlinks are another defining concept of the WWW and provide its identity as a collection of interconnected documents.
Hypertext is a method for instant information cross-referencing that supports communications on the web. Hypertext makes it easy to link content on one web page to content on another web page or site. Hypertext and HTTP enable people to access the millions of websites active on the WWW.
This article is part of
What is Web 3.0 (Web3)? Definition, guide and history
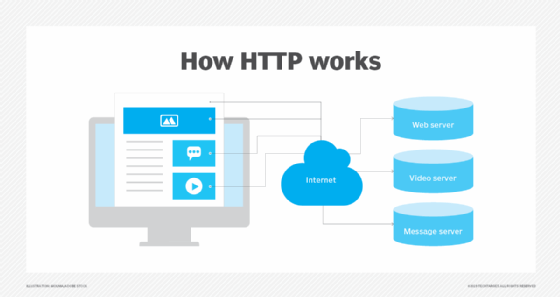
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is another key component of the WWW. It enables users to access web pages by standardizing communications and data transfer between the internet's servers and clients.

Most web documents and pages are created using Hypertext Markup Language (HTML), a text-based way of describing how content within an HTML file is structured. HTML describes the structure of web pages using elements or tags and displays the content of these pages through a web browser.
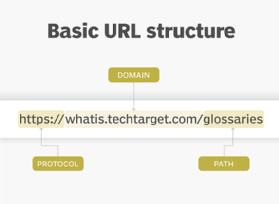
To access one of these pages, a user and their client machine supply a universal identifier to the web server via a browser. This identifier may be a uniform resource locator (URL) or uniform resource identifier (URI) and is unique to each web page.
A collection of web pages belonging to a URL is called a website. For example, www.techtarget.com is a website, while https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/definition/World-Wide-Web is a web page.
The browser accepts the URL or URI provided by the user and communicates it to the web server. The server then retrieves the web page associated with that URL or URI and presents it to the user in the browser window of their client machine.
History of the World Wide Web
British physicist Tim Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web. Along with colleagues at Geneva-based CERN -- the European Organization for Nuclear Research -- Berners-Lee had been working on the concept since 1989. Their goal was to combine available technologies and data networks to create a user-friendly system for global communication and information sharing. At the time, they began work on the first WWW server, which they called httpd. They also dubbed the first client WWW.
Originally, WWW was a what you see is what you get (WYSIWYG) hypertext browser/editor that ran in the NextStep environment. In 1990, Berners-Lee demonstrated the first web server and browser at CERN to explain his idea of a World Wide Web. The web then entered the public eye in 1991 when Berners-Lee, who also developed hypertext, announced his creation on the alt.hypertext newsgroup; at the same time, he created the world's first web page with the address http://info.cern.ch/hypertext/WWW/TheProject.html.
This page, which remains operational as of 2022, includes information and links about the WWW project and web servers. In 1993, CERN made the W3 technology publicly available on a royalty-free basis.
Web browser evolution and the growth of the World Wide Web
Berners-Lee and his team developed a text-based web browser that was released in early 1992. However, it took the release of the more user-friendly Mosaic browser in 1993 to kickstart the rapid acceptance and adoption of the WWW. Mosaic provided a point-and-click graphical interface that people had been using in personal computers for a few years. This familiarity increased public interest in WWW and led to its rapid growth all over the world.
Entrepreneur and software engineer Marc Andreessen and others developed Mosaic in the United States. They also developed the Netscape Navigator browser that quickly became the dominant browser in 1994, until it was displaced by Microsoft's Internet Explorer in 1995. IE dominated the web browser space until it was challenged by browsers like Mozilla Firefox -- released in 2004 -- and Google Chrome -- released in 2008. In 2015, Microsoft discontinued IE and replaced it with the Microsoft Edge browser.
After inventing the web, Tim Berners-Lee also founded the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), a nonprofit international consortium that aims to standardize the web through specifications and reference software.
World Wide Web versus the internet
The web is often confused with the internet even though they're different. While the two are intricately connected, the web is just one of many applications built on top of the internet, a vast, global network of multiple smaller networks. The internet incorporates supporting infrastructure and other technologies that connect networks, websites and users to each other. In contrast, the web is a communications model or platform that enables the retrieval or exchange of information over the internet through HTTP. Through the WWW, users can access web pages over the internet by following a series of HTTP links. To retrieve and view these pages, users need to use a browser installed on the computer, such as Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox.
Both the internet and the web operate within a client-server model. A server is a program that accepts requests from other computers, known as clients, on the network to store and transmit documents. Clients request documents from a server when a user asks for them and then displays them on the user's screen.
The world's first web server went online in 1991 in the U.S. By the end of the year, there were only 10 web servers around the world. Two years later, there were 500 operational web servers; by 2016, the number of web servers had grown to more than 100 million.
Since the release of CERN's first web browser, the WWW has evolved into a massive ecosystem of websites and users. As of 2022, approximately 5 billion people -- or 63% of the world's population -- use the web, which is believed to contain approximately 1.88 billion websites.
What will Web 3.0 look like compared to Web 1.0 and 2.0?
The World Wide Web continues to evolve. The first generation of the Web, Web 1.0, which Berners-Lee originally defined in 1989, had no video content and a page format similar to that of a printed page. Web 1.0 was primarily static and focused on providing information.
Around the beginning of the 21st century, Web 2.0 ushered in a new era that was more interactive and dynamic than its predecessor and focused on user collaboration, universal network connectivity and communications channels. As smartphones, mobile internet access and social networks spurred the growth of Web 2.0, applications -- such as Airbnb, TikTok, Twitter and Uber -- which increased online interactivity and utility, became increasingly popular.
With a lofty goal of creating more intelligent, connected and open websites, Web 3.0 is still in its infancy and has yet to be defined fully. Unlike Web 2.0, which includes applications and websites that entail user-generated content, Web 3.0 is expected to be fully decentralized; this places content creation in the hands of the creators rather than platform owners.

Smarter and more autonomous technology, including artificial intelligence and machine learning, are expected to define Web 3.0. Encrypted digital currencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum may be used to pay for transactions. As peer-to-peer technologies, such as blockchain, and security technologies become more important, Web 3.0 is expected to gain momentum.
Explore what Web 3.0 means for your business, if long URLs are better for security than short URLs, common and avoidable HTML5 mistakes and how to mitigate an HTTP request smuggling vulnerability.
