Chief Medical Information Officer (CMIO)
What is a Chief Medical Information Officer (CMIO)?
A Chief Medical Information Officer, or CMIO, essentially serves as the bridge between medical and information technology (IT) departments at a healthcare organization. This person may also be referred to as the director of medical informatics or health informatics.
The CMIO is responsible for the design, implementation and use of healthcare IT in a healthcare organization. The CMIO is a critical member of the leadership team and plays a key role in ensuring that IT is used to improve patient care, safety and outcomes.
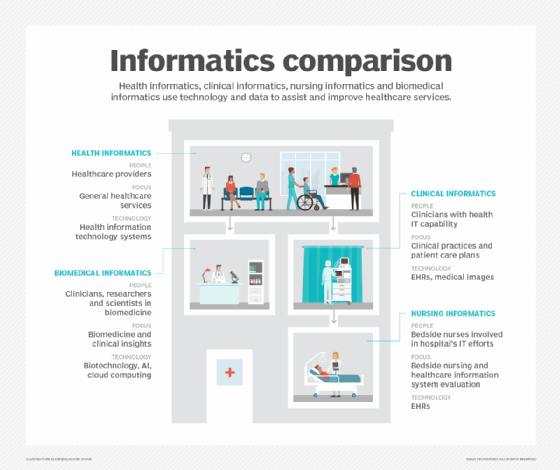
Responsibilities of a CMIO
The responsibilities of a CMIO vary depending on the size and complexity of the healthcare organization. However, some common responsibilities include the following:
- Developing and implementing the organization's IT strategy. Identifying the organization's IT needs, developing a plan to meet those needs and overseeing the implementation of the plan.
- Overseeing the organization's IT infrastructure. Ensuring the organization's IT infrastructure is secure, reliable and up to date.
- Managing the organization's IT security program. Developing and implementing security policies and procedures that ensure the organization's IT systems are protected from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification or destruction.
- Overseeing the organization's IT compliance program. Requires due diligence in complying with all applicable laws and regulations that pertain to the organization's IT systems.
- Working with clinical staff to develop and implement IT solutions that improve patient care. This includes working with physicians, nurses and other healthcare professionals to identify their IT needs, and developing and implementing solutions that meet those needs.
- Educating clinical staff on the use of IT in healthcare. Providing training on how to use IT systems to facilitate care of patients, their safety and ultimate outcomes.
- Representing the organization to the public and to other healthcare organizations. Speaking at conferences, publishing articles and participating in other activities that promote utilizing IT in healthcare.
Qualifications for a CMIO
The qualifications required for a CMIO can vary significantly based on the organization. However, there are some common qualifications that tend to be sought across the board.
First and foremost, a medical degree is required. This reflects the need for comprehensive medical knowledge in this role. Additionally, a background in IT is often essential due to the significant integration of technology in healthcare processes.
Experience in healthcare administration is another common prerequisite, as it equips candidates with a grasp of the broader organizational context. Strong leadership and communication skills are paramount, as they are necessary for facilitating effective coordination, team management and decision-making.
Finally, the ability to work harmoniously with both clinical staff and IT professionals is crucial, given the cross-functional nature of the role that demands a cohesive approach to healthcare IT solutions.
The future of the CMIO role
The role of the CMIO is evolving as healthcare organizations increasingly rely on IT to improve patient care. In the future, it is expected that CMIOs will play an even more important role in leading the adoption and implementation of new IT technologies.
Learn how health informaticians weave medicine tech and science together and see how CIOs can help alleviate electronic health record issues.






