runtime
What is runtime?
Runtime is a piece of code that implements portions of a programming language's execution model. In doing this, it allows the program to interact with the computing resources it needs to work. Runtimes are often integral parts of the programming language and don't need to be installed separately.
Runtime is also when a program is running. That is, when you start a program running in a computer, it is runtime for that program. In some programming languages, certain reusable programs or "routines" are built and packaged as a "runtime library." These routines can be linked to and used by any program when it is running.
Programmers sometimes distinguish between what gets embedded in a program when it is compiled and what gets embedded or used at runtime. The former is sometimes called compile time.
How does runtime work?
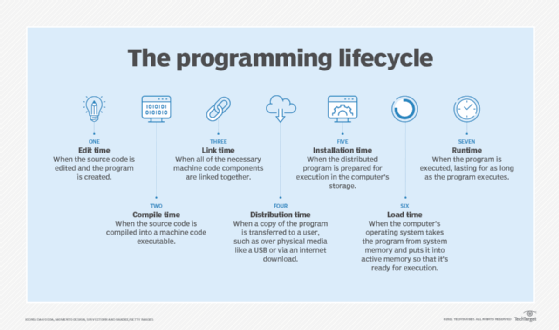
Runtime is a stage of the programming lifecycle. It is the time that a program is running alongside all the external instructions needed for proper execution. Some of these external instructions are called runtime systems or runtime environments and come as integral parts of the programming language.
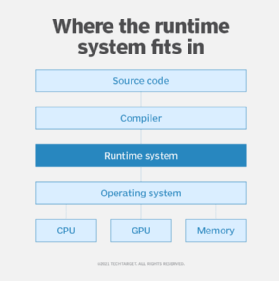
A runtime system creates a layer over the operating system (OS) that contains other programs that handle the tasks needed to get the main program running. These other programs handle tasks such as allocating memory for the main program and scheduling it.
When an application is at the runtime stage, the executable file of the program is loaded into RAM, along with any files that the program references. These may include code that the user did not write but that works in the background to make the program run. That code is sent to the computer's processor to be turned into machine code. It then makes the hardware run the program.
Here is a simple example of a runtime system, written in the Beginner's All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code (BASIC) programming language:
] 10 PRINT "HELLO"
] 20 GOTO 10
The above is source code. BASIC is an interpretive programming language, which means its instructions can be run without first compiling the code into a runtime version. To run the program and print the word Hello, the coder would insert another BASIC command:
] RUN
This is the runtime system. It is its own program that puts a layer between the user's OS and the source code. It creates the runtime environment necessary for the source code to interact with the OS. That layer tells the computer how to parse and execute the source code, and it sends requests to the OS.
Runtime errors
Many users first encounter the term runtime in the context of a runtime error. This refers to a problem with the program that keeps it from executing at runtime due to any damaged, missing or incompatible components.
Runtime errors can happen for many reasons. Examples of runtime errors are the following:
- Insufficient system resources. Lack of available system resources can cause a runtime error. For instance, if there is not enough memory for a program to run, the runtime environment cannot do its job. The program will likely abort and return an error message.
- Coding error. A bug in the software can cause a runtime error.
- Broken dependency. If there is a break in a connection to another application that the program requires to execute, an error can result.
A runtime environment usually displays a notification that gives the reason for the crash or where in the program the error occurred. Programmers may have to debug the software, either manually or using debugging tools, to get to the root of a runtime error.
Runtime terminology differences
The term runtime has many meanings in computer science. It can refer to the state of a program, a certain type of program or the time at which a program runs.
The main use of the term runtime is to describe the runtime environment -- the code that allows a program to function. However, the term is used other ways in programming:
- It is used as a noun to denote the final phase of a program lifecycle when the program is executed (as detailed above).
- When written as two words, run time refers to how long the execution of a program takes.
- It can be used as an adjective to describe processes that happen during that phase of the program lifecycle. Examples are the terms runtime error and runtime metrics.
- It is also used as a descriptor of other programs -- including runtime environment, runtime system and runtime library -- that enable the main program to run. Collectively, all of those program components may be referred to as runtimes.
Runtime system
A runtime system is software that comes with programming languages as part of the execution model. It creates the layer described earlier that sits over the OS that contains other programs that help run the main program.
Runtime system is often used synonymously with the term runtime environment. Runtime systems and runtime environments act as small OSes that provide every function required for a program to run.
Runtime environment
Runtime environment is defined more broadly as the environment that the program executes in. In a runtime environment, the OS is included, along with hardware and memory. Runtime environments are used more frequently in IT operations, as opposed to application development.
Runtime library
A runtime library is a set of low-level, platform- and compiler-specific routines that the compiler uses to send instructions to the runtime environment so that the program can run.
Examples of runtime systems and environments
Runtime environments perform low-level tasks, including parallel execution, disk input/output, task scheduling, garbage collection or resource management. They may also implement high-level commands, such as type checking, debugging and code optimization.
Three examples of runtime environments are the following:
- Java Runtime Environment (JRE) is needed to run Java programs, enabling Java to work on multiple OSes. JRE performs the basic tasks that Java needs to execute code, such as loading class libraries, verifying memory access and retrieving system resources.
- Common Language Runtime (CLR) is the runtime environment of Microsoft's .NET Framework. It is a virtual machine that runs and manages code for various high-level services, such as handling object layout and managing references to objects. It also features a garbage collector that manages memory leaks and other programming errors. Like other runtime environments, CLR compiles some intermediate, language-specific code into machine code that the OS can read.
- Adobe Flash Player is another common runtime environment. Adobe Flash Player uses a runtime to run flash code on many different OSes and devices.
Learn more about the differences among runtime environments, engines and systems. Also, find out how developers interpret runtime environment differently than operations personnel.







