Fotolia
CPU vs. microprocessor: What are the differences?
CPUs and microprocessors can execute many of the same tasks, such as arithmetic and I/O processing. However, there are some tasks CPUs can't execute effectively.
CPUs and microprocessors are the bread and butter of a successful operating system. They both execute integral computer tasks, such as arithmetic, data processing, logic and I/O operations, but CPU vs. microprocessor differences aren't all so black and white. Though some IT administrators use CPU and microprocessor interchangeably, the reality is that most CPUs are microprocessors but not every microprocessor is a CPU.
In the early days of IT, CPUs were a system's main workhorse as they handled a variety of computer commands that were often complex and time consuming. However, microprocessors became the answer to many of the complex tasks that CPUs simply couldn't handle on a day-to-day basis, such as image rendering and networking. Both CPUs and microprocessors still execute many of the same tasks in modern IT, but their functions differ slightly.
What is a CPU?
A processor, or CPU, is logic circuitry that responds and processes basic instructions to drive a computer. A CPU is integral to system operations because it's responsible for interpreting a majority of a computer's commands, such as basic arithmetic, logic and I/O processes. A CPU can also allocate commands at will for other chips and components within a system.
Various elements within the CPU enable it to execute these computer commands, such as the arithmetic logic unit, floating point unit, registers, and L1 and L2 cache memory. With the help of these components, a CPU can fulfill functions such as fetch, decode and execute. In this three-part function, the fetch step receives program memory instructions from a system's RAM, the decode step converts the instructions to understand which parts of the CPU are required to continue operations and the execute step performs the operation.
Most CPUs in modern IT are multicore processors, which means the integrated circuitry has two or more processors attached to help improve performance, reduce power consumption and support simultaneous processing of several computer tasks. Generally speaking, a multicore CPU is twice as powerful as a single core CPU.
What is a microprocessor?
On the other hand, a microprocessor -- also known as a logic chip -- is essentially a single-chip implementation of a CPU. A microprocessor contains all of a CPU's functions and can perform arithmetic and logic operations with registers. However, a microprocessor's functions differ in some ways to a CPU. For example, a microprocessor can add, subtract, compare and fetch numbers within a system from one area to another.
When admins turn on a computer, the microprocessor receives the first instruction from the BIOS. From there, the microprocessor either receives further instruction from the BIOS, the OS the BIOS loads into the computer memory or an application that drives the microprocessor. In modern IT, a majority of CPUs tend to be microprocessors by default because of their ability to execute data movement, perform complex calculations and increase speed within a system.
The two main microprocessor vendors that garner significant popularity are Intel and Advanced Micro Devices. Other microprocessors on the market include ARM, Sparc and PowerPC.
The final verdict: CPU vs. microprocessor
Understanding the differences between CPUs and microprocessors can be difficult because of their similarities. Many admins use CPU and microprocessor interchangeably, but the reality is that while a CPU is essentially a microprocessor, not all microprocessors are CPUs.
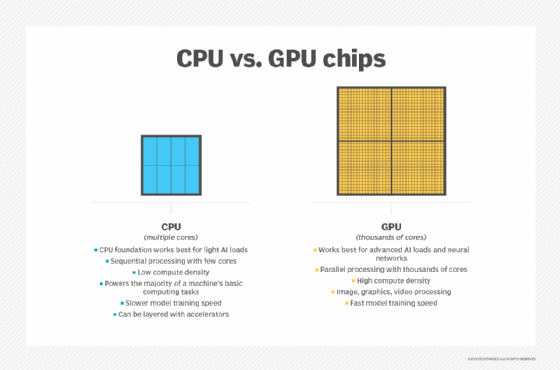
For example, many systems rely on GPUs, which are microprocessors that specialize in rendering and managing images with the help of optimized geometric operations. GPUs can render images much more quickly than a CPU with the help of parallel processing. In addition, there are also neural processing units that specialize in accelerating machine learning algorithms. These types of microprocessors essentially remove certain operations, such as graphics and network processing, from the CPU to enhance CPU speeds and performance.