quad-core processor
What is a quad-core processor?
A quad-core processor is a chip with four independent units called cores that read and execute central processing unit (CPU) instructions, such as add, move data and branch. Inside the chip, each core operates in conjunction with other circuits, such as cache, memory management and input/output ports.
Quad-core processors were the second step in the move into multicore systems that started with dual-core processors in 2005. Quad-core CPUs continue to be popular in all types of systems, including smartphones, computers, PC gaming and data center servers. Some high-end servers feature up to 128 cores. Intel and AMD are among the top manufacturers of these processors.
How does a quad-core processor work?
Each core in a quad-core processor can run its own set of instructions at the same time as the other three cores run theirs. In this way, the processor can support Multithreading, a form of parallelization in which multiple threads are processed simultaneously by different cores.
Multithreading can enhance application performance, but only for threaded applications that are built for parallel processing. Applications that are lightly threaded or that do not support multithreading do not receive the same benefit from a quad-core processor.
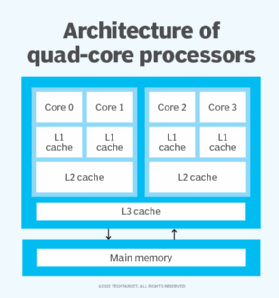
Manufacturers that build quad-core processors typically integrate the cores onto a single semiconductor wafer or onto multiple wafers within a single integrated circuit package. The processors usually include their own cache to speed up performance. However, the way in which the processor cache is implemented can vary from one CPU offering to the next.
In most configurations, each core gets its own Level 1 (L1) cache memory, and all four cores share the same Level 3 (L3) cache if it's included. The Level 2 (L2) cache differ the most among quad-core processors. For example, each core might get its own L2 cache, there might be two L2 chips that two cores share, or all four cores might share the same L2 cache. The choice is up to the manufacturer.
Is a quad-core processor better than a single core?
Many single-core processors use hyper-threading to improve system performance. Hyper-threading enables a single core to run two threads at the same time, making it possible for the processor to support a type of pseudo-parallelism that can help improve processing efficiency. The operating system (OS) sees the physical core as two logical cores.
Hyper-threading can help improve performance when multiple applications are running on a system at the same time. The processor still has only one physical core, and that core can run only one instruction set at a time. As a result, the gains from hyper-threading are often minimal. Both the computer's firmware and OS must support hyper-threading for it to work.
In contrast to hyper-threading, multithreading on a quad-core processor offers a truer form of parallel processing and can deliver better performance.
What affects quad-core processor performance?
The three main factors affecting processor performance are the following:
Number of cores. More cores may mean better performance, though not always.
Clock speed. Just as important as the number of cores is a processor's clock speed. It determines the number of cycles in gigahertz, or GHz, that the processor can execute per second. The higher the clock speed, the better the performance.
Cache. The quantity and quality of the processor's cache can also affect performance. The cache retains the instructions and data that the processor needs to access most frequently. The processor always checks a system's cache first before going to main memory. It checks the cache levels in the following order:
- L1 cache is typically the smallest and fastest cache.
- L2 cache is larger but not as fast.
- L3 cache, if present, is larger still and even slower.
All three cache levels outperform a computer's main memory, which is faster than accessing any of the system's nonvolatile storage.
What to consider when evaluating processors?
When evaluating a processor, customers must consider the CPU's clock speed and cache as well as the number of cores. Although a quad-core processor can help improve performance for many applications, a processor with fewer cores but a faster clock speed and better cache might perform better in some circumstances. This is especially true if the applications are lightly threaded or do not support multithreading.
If different processors have similar clock speeds and cache configurations, it can't be assumed that a quad-core processor would operate twice as fast as a dual-core processor or four times as fast as a single-core processor. Results will vary depending on the habits of the user, the programs run and the compatibility of the processor with other system hardware. Even if an application is highly threaded, that doesn't guarantee that it will use a quad-four processor to its fullest benefit.
Find out what factors to consider when selecting a CPU for a virtual infrastructure.
