thread
What is a thread?
A thread is, fundamentally, a clear, well-defined theme, subject, topic or focus. A thread may exist in human communication, such as a topical group chat or email exchange. A thread also exists as the processing focus of a software program, such as an operating system (OS) or application.
In technology, a thread is typically the smallest set or sequence of instructions that a computer can manage and execute; it is the basic unit of processor (CPU) utilization.
Beyond the computer code of the thread itself, there are four elements used to monitor and control a thread:
- A thread ID is a means of identifying and tracking the thread.
- A program counter tracks the memory location of the instruction being executed in the thread.
- A register set includes temporary memory locations used to store data and processing results from the thread.
- A stack is memory space allocated to the thread and used while the thread is executing.
As shown in Figure 1, a process is normally comprised of multiple (often many) individual threads, which are frequently termed lightweight processes.
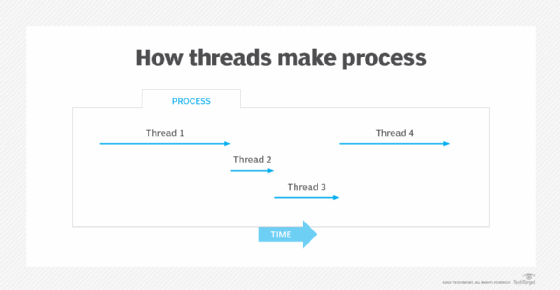
Threads are tightly correlated to CPU design. Traditionally, a CPU core (the execution engine) works on one thread at a time -- an approach called single-threading -- although single-threading CPUs can also work on several instructions at a time, known as superscalar execution.
To optimize execution performance, the CPU can analyze the thread and order the thread's instructions for execution in the most efficient way. CPUs typically include capabilities such as branch prediction, which lets the CPU predict the outcome of thread decision-making and further accelerate performance.
While such techniques sped up single-thread execution, designers had long sought to develop processors capable of handling more than one thread simultaneously. It wasn't until Intel released its Pentium 4 processor in 2002 that this simultaneous multithreading (SMT) technology became mainstream in modern CPUs. Intel refers to SMT as Hyper-Threading Technology. Most CPUs intended for desktop computers can handle two threads per core, where each thread engine acts as a logical core (even though it's a single physical core). Enterprise-class CPUs may support four or eight threads per core.
A computer's OS is primarily responsible for allocating and monitoring the computer's resources. The OS can provide convenient tools for monitoring threads and processes running on the system at any time. For example, Windows 11 users can search for Task Manager and select the Task Manager app from the resulting list. Select the Performance tab and examine the resulting report, which might look like Figure 2.
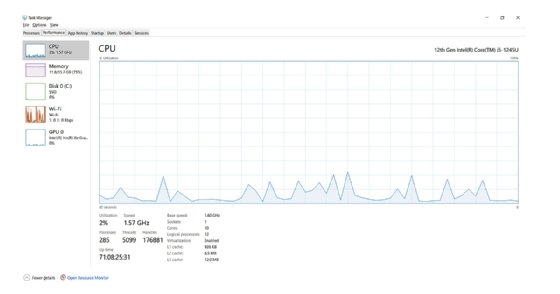
The Windows 11 Task Manager in Figure 2 reports that there are currently 285 unique processes comprised of 5,099 threads running on the computer. Yet all this operational activity consumes only 2 percent of the computer's CPU utilization capacity.
The actual number of threads and processes will vary over time as software starts or stops. For example, opening (launching) new software or installing more drivers will increase the number of threads and processes, while closing (stopping) software will reduce the number. Since threads are components in processes, users typically cannot stop specific threads (this can easily break a process). Instead, users can stop specific processes, such as closing an application or stopping a driver, and all of the threads associated with that process will halt.
Types of threads
The idea of a thread often appears in two major areas: electronic communication and computer science. Although the difference is important for context, the concept of a thread -- working through a specific topic or section of code -- remains consistent.
In communication, we find threads in forums. A thread is often the topic or focus of an electronic exchange between two or more people using mechanisms such as text, email or a wide range of computer forum platforms (including social media). The thread typically starts as a topic or question directed to one or more people, who then respond to the topic or question, often creating a running exchange of communication that will ideally result in consensus, agreement or understanding.
For example, an employee might use email to communicate with their supervisor and HR department regarding a specific employment question. Both the supervisor and HR representative will likely respond to share clarifications and solutions, often driving a series of messages regarding the employee's inquiry until the inquiry is resolved. All the messages involved in the exchange comprise the overall thread.
In computer science, a thread typically refers to a sequence of software code the computer and its CPU must execute. In programming, a thread is the smallest series of related instructions involved in a process, which can involve many threads. For example, a thread may involve a small subroutine intended to ask for and await user input. Another thread might serve to apply a specific mathematical algorithm to data.
A thread serves a similar purpose in an OS. There, a thread represents a single sequential order of activities being executed in a process, also known as the thread of execution or thread of control. The OS typically deals with two common types of threads:
- User-level threads, which are typically related to processes (software) launched and operated by the user using common computer languages such as Java or POSIX.
- Kernel-level threads, which are threads managed and operated in the OS itself. It's the code involved in making the OS, not the user software applications, function. Kernel-level threads can be run to create and manage user-level threads, such as those used to launch and run user applications.
What is multithreading?
Multithreading is a CPU core design that lets two or more threads -- limited sequences of related instructions -- execute simultaneously. Multithreading typically lets each thread share the processor's resources, such as stack space, even though the threads may not communicate or interact at all.
Although the idea of multiprocessing may seem straightforward, it requires sophisticated programming skills to let threads share processor resources without incurring conflicts, such as race conditions or deadlocks, that can disrupt the greater process. For example, programmers versed in multithreaded programming techniques will usually add precautions, such as locking access to certain shared variables or registers, to prevent multiple threads from changing the same content simultaneously.
There are two common approaches to multithreading:
- Parallel multithreading. Also known as true multithreading, this lets the processor core handle two or more threads simultaneously.
- Concurrent multithreading. This is a modification of single-threading where the processor core only handles one thread at a time but timeshares the processor between multiple threads, letting the processor handle more than one thread at a time.
Both approaches can be used in tandem -- for example, letting two parallel thread paths each timeshare multiple threads -- to further optimize software execution performance. This works because of the metadata related to each thread, including thread ID, program counter, etc. Threads are placed into a queue and each granted a small portion of time, which lets the thread perform some execution. When the time slice expires, the thread is halted and its state is saved, loading the next thread in the queue load to operate for its time slice. This process then repeats for each thread in the queue.
Thread switching is so fast, and modern processors are so powerful, that the CPU can seem to run many threads simultaneously.
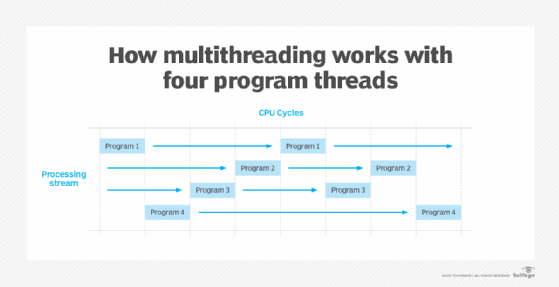
There are also numerous types or models of multithreading, coordinating and processing multiple threads in various ways. For example, some types of multithreading will enforce equal time slices to divide processor time equally, while other approaches can vary time slices according to thread priority or other criteria. Common types of multithreading include the following:
- Pre-emptive.
- Cooperative.
- Coarse grained.
- Interleaved.
- Simultaneous.
- Many to many.
- Many to one.
- One to one.
Finally, there is a difference between multithreading and multiprocessing. Where multithreading allows the same CPU to process or appear to process two or more threads simultaneously, multiprocessing simply adds additional CPUs to handle more processes and threads, effectively using brute force to improve software performance. Most modern processors provide more than one core, so performance-sensitive software is increasingly leveraging the availability of additional cores to support greater parallelism in software execution.
What's the difference between a thread, process and task?
The terms thread, process and task are often used interchangeably, but this is technically incorrect. The three terms are related but represent different scopes:
- A process is the invocation and execution of a computer program.
- A thread is the smallest unit or series of execution for a CPU. It can involve many threads executed at various places in the process.
- A task is like a thread but is somewhat more general, usually representing some small but specific goal. For example, a task is used for simple and short-term compute goals, while a thread offers better management and control for longer-term execution. Threads can run in the background, but tasks cannot.
Learn about the key concepts of state and threading in a .NET microservices architecture. See how to choose the best CPU for virtualization and how CPU, GPU and DPU differ from one another. Explore how improvements in CPU features can help shape server hardware selection.
