closed loop control system
What is a closed loop control system?
A closed loop control system is a mechanical or electronic device that automatically regulates a system to maintain a desired state or set point without human interaction. It uses a feedback system or sensor. Closed loop control is contrasted with open loop control, where there is no self-regulating mechanism and human interaction is typically required.
A simple example of a closed loop control system is a home thermostat. The thermostat can send a signal to the heater to turn it on or off. It uses a temperature sensor to detect the current air temperature. When the temperature is below the set point, it turns the heater on. When the sensor detects the temperature is above the set point, it turns the system off.
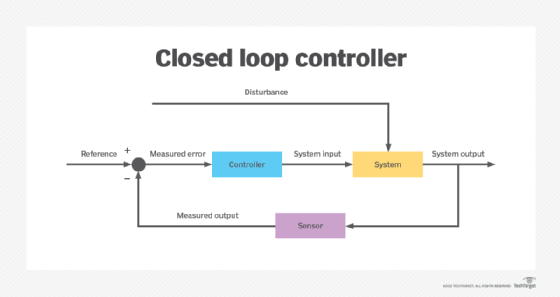
In an open loop system, there is no feedback to the controller about the current state of the system. An example of an open loop control would be to run the heater for 10 minutes every hour, no matter how hot or cold the air temperature is. Closed loop systems are more desirable than open loop systems because they are sensitive to changes.
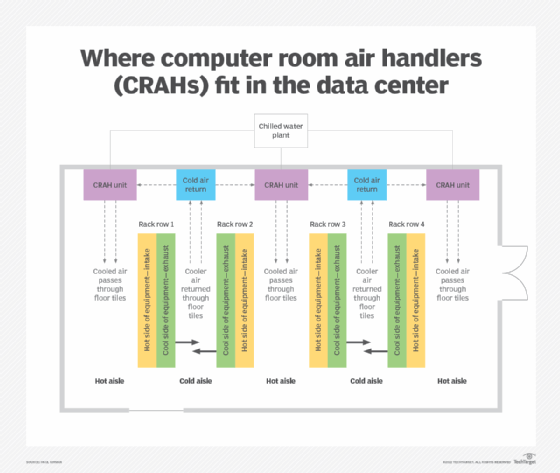
Most modern closed loop systems are electronically controlled. These may use discrete analog electronic comparators for simple systems, such as an oven thermostat. More complicated systems use a microcontroller or programable logic controller to take several inputs and to control multiple outputs. A complex system example would be a building heating, ventilation and air conditioning system in a data center that can use sensors for inside air temperature, outside air temperature and relative humidity to control the operation of a heater and AC. Another complex example is computer room air handlers (CRAHs) in data centers that dissipate heat produced by equipment using fans, cooling coils and a water chiller system.
Old or low-cost systems may use a mechanical closed loop system. Some examples of these are bimetallic temperature switches or self-regulating valves.
Closed loop control system tuning
It is important that a closed loop control system be properly tuned for the best operation of a system. For example, if the air temperature is close to the set point of a thermostat, it may cause the system to rapidly turn the AC on and off; such short cycling could damage the compressor and break the system. Such systems have a dampening value added to control for rapid cycling and unwanted oscillations of the output.
In a closed loop system, the transfer function defines the mathematical relationship between the input and the output. The change on the output by the input or the relationship between the detected sensor value is known as the gain of the system. Defining the transfer function of the system based on the gain and the desired state may require careful calculation for best results.
A more complicated example of a closed loop system would be cruise control in a car. The cruise control wants to maintain a set speed as measured by the speed of the wheels (desired system output). It can control the car's throttle and vary the engine power (system input). The relationship of the throttle to speed is not direct as many factors can influence it, such as cargo weight, hill incline and wind resistance based on speed. Therefore, the control system must be tuned to account for these factors. It may also have other controls, such as shifting the gears in the transmission or applying breaks.
Closed loop control systems advantages and disadvantages
Closed loop control systems have positives and negatives, including the following.
Advantages
- can control for external factors
- more reliable and stable output
- resilient to disturbances and changes
- more resource-efficient
Disadvantages
- more complex
- requires tuning or integration
- susceptible to oscillation or runaway conditions
- sensor failure can cause unwanted system performance
Closed loop control system applications
Closed loop control systems are widely used in industry applications, including agriculture, chemical plants, nuclear power plants, water treatment plants and environmental control. Closed loop control systems enable automation in a number of industrial and environmental settings and regulate processes in industrial control systems, such as supervisory control and data acquisition and distributed control systems.
Software systems may take advantage of a closed loop feedback system. For example, a cloud orchestration system may detect high server load and cause an automated process to generate and deploy new servers to better handle it.
Principles of closed loop control are becoming more prominent in modern system design. Internet of things (IoT) is placing more sensors and generating more data for systems to ingest and make decisions based on. Human operators are more expensive to hire and may need to operate larger systems, requiring more automation. Machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence may be thought of as highly integrated self-learning closed loop control that can take in feedback to new and optimized ways to get a desired output.
See also: feedback loop, closed loop reporting, open loop/closed loop payment cards, and closed loop manufacturing resource planning.
