data abstraction
What is data abstraction?
Data abstraction is the reduction of a particular body of data to a simplified representation of the whole. Abstraction, in general, is the process of removing characteristics from something to reduce it to a set of essential elements. To this end, data abstraction creates a simplified representation of the underlying data, while hiding its complexities and associated operations. In computing, data abstraction is commonly used in object-oriented programming (OOP) and when working with a database management system (DBMS).
What is data abstraction in OOP?
Modern programming languages that incorporate OOP methodologies commonly use data abstraction to hide the low-level details of the programming constructs that define the underlying logic, which in turn simplifies and streamlines the development process. Object-oriented programming organizes software design around data objects, rather than functions or logic. Data abstraction is a key characteristic of OOP that's implemented using classes and objects.
A class is a template definition that bundles related attributes and methods into a named package. It is a special type of object that serves as a blueprint for creating other objects. In addition, a class can include subclasses that inherit some or all the class's attributes and methods, resulting in a type of class hierarchy. Subclasses can also define their own attributes and methods.
An object is a named instance of a class that's created with specifically defined data. The object's attributes are unique from other objects based on the same class. The object serves as a simple representation of the class, abstracting the implementation details of the class itself. In this way, developers can focus primarily on the objects and how to manipulate them, rather than on how to implement the underlying logic.
Suppose, for example, that a development team is building an application for an organization's human resources department. The application contains an Employee class that includes attributes such as first name, last name, contact information, job skills and other relevant information. The Employee class also includes several methods, including one for updating an employee's list of job skills. From this class, the application can instantiate objects that have access to these properties and methods without having to recreate them for each employee record, helping to simplify the overall application development process.
Because the class provides a template for building the objects, developers can generate those objects as often as necessary without being concerned about how the class itself implements the underlying logic and without having to reconstruct the same logic each time an Employee object is needed. For example, the application can invoke the method for updating job skills without being concerned about how the update is carried out. All properties and methods are already defined, whether or not they're needed when instantiating an individual object. In this way, the underlying implementation complexities are abstracted away and hidden during the bulk of the development effort.

What is data abstraction in a DBMS?
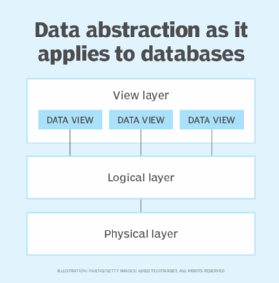
Data abstraction is also used with databases to hide the underlying complexities of how the data is stored and managed. The view of the data that users have is much different from the way in which the data is persisted to storage. Data abstraction, as it applies to databases, is typically divided into three layers:
- View layer. At this level, the user sees the data as it's presented by an application interface. The user might be able to interact with the data or might only be able to view it. In either case, the user typically has access to only certain types of data, has a very limited view of the data in its entirety and has no concept of how or where the data is stored.
- Logical layer. This layer provides a conceptual understanding of the data. It describes the type of data and how that data is related. You can think of this layer in terms of an entity relationship diagram (ERD) that lays out the data objects like a blueprint and shows how they're related.
- Physical layer. This layer focuses on the data's physical storage. It is concerned with where and how the data is stored, how the files are managed, the type of storage and anything else related to physically maintaining the data.
There are no set rules that dictate how the data abstraction layers should be implemented. It will depend on the type of database system, how the vendor has designed the platform, how administrators have implemented that platform, how the data has been modeled and the applications used for accessing the data.
Regardless of the approach, data abstraction remains an important component of any DBMS because it makes it possible for users to easily work the data while allowing changes to occur on the back end without breaking the front-end applications. For example, a database administrator should be able to change where a database file is stored without affecting any applications that retrieve data from that file. A database developer should even be able to change a table's layout as long as an abstraction layer sits on top and can absorb the change. Data abstraction allows for the greatest flexibility in supporting changing business requirements and implementing new applications.
Learn about the difference between DBMS and RDBMS and functional versus object-oriented programming.
