VUCA (volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity)
What is VUCA (volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity)?
VUCA is an acronym that stands for volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity -- qualities that make a situation or condition difficult to analyze, respond to or plan for. Understanding how to mitigate these qualities can greatly improve the strategic abilities of a leader and lead to better outcomes.
Volatility is the quality of being subject to frequent, rapid and significant change. Small triggers may result in large changes. In a volatile market, for example, the prices of commodities can rise or fall considerably in a short period of time, and the direction of a trend may reverse suddenly.
Uncertainty occurs when events and outcomes are unpredictable. The cause and effect are not well understood, and previous experience may not apply to the situation. It is unclear which direction events will go; in an uncertain market, for example, it is not clear if the price will go up or down or by how much.
Complexity involves a multiplicity of issues and factors, some of which may be intricately interconnected. The relationships between items and people are difficult to understand. A change in one place may cause unintended changes to other things down the line. Cause and effect are obscured by many layers, and it is not clear which factors are important in the decision-making process. In a complex market, for example, the changes in gas prices affect the prices of many other items that are not directly related.
Ambiguity is shaped by a lack of clarity and difficulty understanding exactly what the situation is. Information may be misread or misinterpreted. During ambiguous situations, all the facts are not clear. The goal or intended outcome may not be evident to all parties involved. In an ambiguous market, for example, not all information is public and unseen factors may be affecting prices.
VUCA use and history
The acronym VUCA was first used in the U.S. Army War College in 1987 and was publicly published in 1991 by Herbert Barber. The method was developed after the concepts presented by Warren Bennis and Burt Nanus in their book Leaders: The Strategies for Taking Charge. VUCA was applied to the conditions following the end of the Cold War and the conflict in Afghanistan at that time.
The term VUCA can be applied to a situation in general. Sometimes it is used dismissively to discount the value of planning. Someone might unhelpfully say, "Because of the current VUCA, any plans we make will be quickly out of date and useless, so why bother planning?" In this sense, its use is similar to FUD (fear, uncertainty and doubt).
The proper use of VUCA is to apply it to a situation to help quantify risks and create mitigation strategies. Use the VUCA method to go through what is known and not known about a situation or plan. This helps create better understanding of the situation and what the vulnerabilities and risks are. Using VUCA can help leaders manage the ever-changing modern business landscape.
The following questions can be used in a thought exercise to identify the VUCA in a situation:
- Volatility. What are the highest and lowest possible values that we can expect? How fast can these values change? What amount of change can we absorb before it negatively impacts us?
- Uncertainty. What can change? What are potential signs of change? Will we know when things change? How fast can we respond to a change?
- Complexity. How well do we understand the structures involved? How are these items interconnected? What is our ability to stop a chain reaction or cascading failure?
- Ambiguity. What is our visibility into the internal and external factors? What is the possibility for misunderstanding and confusion? How can directions be issued more clearly? What signifies that more information is needed before making a decision?
VUCA mitigation strategies
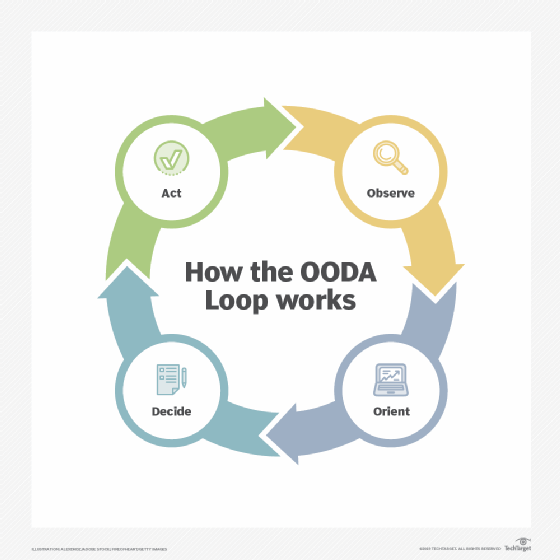
By using VUCA, people can identify potential surprises and outcomes. From there, they can make mitigation and response strategies to prepare for the potential for rapid change in VUCA situations. They can go from "unknown unknowns" to "known unknowns" and be sufficiently prepared. Leaders may also apply the OODA loop of observe, orient, decide and act for good decision-making.
Volatility. Accept change. Build in slack and wiggle room for unaccounted issues.
Uncertainty. Seek new viewpoints and take time to understand triggers and indicators. Monitor key metrics and add indicators of success and failure at every step. Have regular reviews and port-mortems. Perform what-if exercises to help train staff and get ready for unforeseen occurrences.
Complexity. Communicate clearly and frequently with all parties. Encourage collaboration between teams and groups. Identify areas where more insight is needed and add talent to address them. Build in fail-safe and backup systems.
Ambiguity. Perform tests to bring clear understanding to ambiguous information. Be prepared to change as more information is discovered.
VUCA in technology fields
Technology is a rapidly changing and advancing field where experts may not agree or have differing opinions. Global supply chains and interconnected systems are complex and difficult to untangle. Disruptive technologies are introduced daily. Therefore, applying the principles of VUCA to technology structure can offer invaluable insights.
Before starting a new project, perform a VUCA analysis. This will identify potential weaknesses and risks. Institute Agile, CI/CD and DevOps methodologies to be able to rapidly respond to changing needs and opportunities. Keep up to date with industry news to be able to take advantage of trends and emerging technology. Have in place crisis management, a disaster recovery plan and a business continuity plan.
VUCA was originally developed for confusing battlefield conditions, so it is especially applicable to cybersecurity scenarios. Use the VUCA method to identify knowns and unknowns. See where systems are missing insight. Build in metrics and establish baselines to be able to quickly detect deviations, and perform war gaming and red team tests to find vulnerable spots.