Types of AI algorithms and how they work
AI algorithms can help businesses gain a competitive advantage. Learn the main types of AI algorithms, how they work, and why companies must thoroughly evaluate benefits and risks.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning play an increasingly crucial role in helping companies across industries achieve their business goals. Research firm Frost & Sullivan's "Global State of AI, 2024" report found that 89% of IT and business decision-makers believe AI and machine learning will help them grow revenue, increase operational efficiency, improve customer experiences and innovate.
AI algorithms can help sharpen decision-making, make predictions in real time and save companies hours of time by automating key business workflows. They can bubble up new ideas and bring other business benefits -- but only if organizations understand how they work, know which type is best suited to the problem at hand and take steps to minimize AI risks.
Let's begin the work of understanding AI algorithms.
What is an AI algorithm?
AI algorithms are a set of instructions or rules that enable machines to learn, analyze data and make decisions based on that knowledge. These algorithms can perform tasks that would typically require human intelligence, such as recognizing patterns, understanding natural language, problem-solving and decision-making.
In any discussion of AI algorithms, it's important to also underscore the value of using the right data in the training of algorithms.
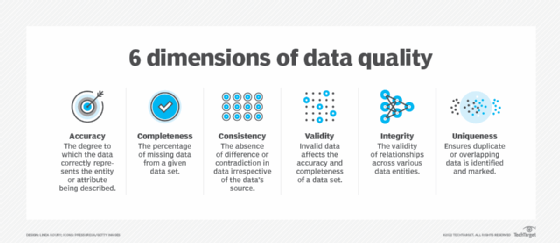
There are numerous characteristics that define what the right data for an AI algorithm should be. At the most basic level, the data needs to be relevant to the issue the algorithm is attempting to solve. The right data should be accurate and free from bias as much as possible. The axiom "garbage in, garbage out" sums up why quality data is critical for an AI algorithm to function effectively.
This article is part of
What is enterprise AI? A complete guide for businesses
Types of AI algorithms
There are three main types of AI algorithms.
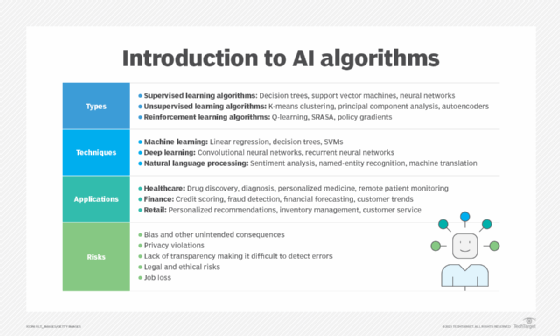
1. Supervised learning algorithms. In supervised learning, the algorithm learns from a labeled data set, where the input data is associated with the correct output. This approach is used for tasks such as classification and regression problems such as linear regression, time series regression and logistic regression. Supervised learning is used in various applications, such as image classification, speech recognition and sentiment analysis.
Examples of supervised learning algorithms include decision trees, support vector machines, gradient descent and neural networks.
2. Unsupervised learning algorithms. In unsupervised learning, an area that is evolving quickly due in part to new generative AI techniques, the algorithm learns from an unlabeled data set by identifying patterns, correlations or clusters within the data. This approach is commonly used for tasks like clustering, dimensionality reduction and anomaly detection. Unsupervised learning is used in various applications, such as customer segmentation, image compression and feature extraction.
Examples of unsupervised learning algorithms include k-means clustering, principal component analysis and autoencoders.
3. Reinforcement learning algorithms. In reinforcement learning, the algorithm learns by interacting with an environment, receiving feedback in the form of rewards or penalties, and adjusting its actions to maximize the cumulative rewards. This approach is commonly used for tasks like game playing, robotics and autonomous vehicles.
Examples of reinforcement learning algorithms include Q-learning; SARSA, or state-action-reward-state-action; and policy gradients.
Hybrid approaches in AI algorithms
Hybrid approaches in AI algorithms combine elements of supervised learning, unsupervised learning, reinforcement learning and other methods to take advantage of their respective strengths. The following are some key hybrid approaches:
Semisupervised learning. This approach combines supervised and unsupervised learning. It uses a small amount of labeled data alongside a large amount of unlabeled data to train models.
Self-supervised learning. This is a type of unsupervised learning where the model generates its own labels from the input data. It then uses the self-generated labels for supervised training.
Model-based reinforcement learning. In this approach, supervised learning is used to build a model of the environment, while reinforcement learning makes the decisions.
Generative adversarial networks. A GAN approach pits an unsupervised learning algorithm against a supervised learning algorithm in a competitive framework. The overall idea is to improve accuracy.
Algorithms have been around for thousands of years
Derived from the name of the ninth-century Persian mathematician Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi, the term algorithm has been in use for thousands of years to denote a detailed set of step-by-step instructions for solving a problem or completing a task. The ancient Greeks, for example, developed mathematical algorithms for calculating square roots and finding prime numbers.
In the computer age, the availability of massive amounts of digital data is changing how we think about algorithms, and the types and complexity of the problems computer algorithms can be trained to solve.
Techniques used in AI algorithms
There are several techniques that are widely used in AI algorithms, including the following:
- Machine learning. Machine learning is a subset of AI and is the most prevalent approach for training AI algorithms. ML uses statistical methods to enable machines to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. ML algorithms, as explained above, can be broadly classified into three types: supervised learning, unsupervised learning and reinforcement learning. Common machine learning techniques include linear regression, decision trees, support vector machines and neural networks.
- Deep learning. Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that involves the use of artificial neural networks with multiple layers -- think ResNet50 -- to learn complex patterns in large amounts of data. Deep learning has been successful in a wide range of applications, such as computer vision, speech recognition and natural language processing. Popular deep learning techniques include convolutional neural networks and recurrent neural networks.
- Natural language processing. NLP is a field of AI that deals with the interaction between computers and human language. NLP techniques enable machines to understand, interpret and generate human language in textual and spoken forms. Common NLP techniques include sentiment analysis, named entity recognition and machine translation.
Other emerging AI algorithm training techniques
Improvements in hardware, new techniques and the growth of data are accelerating the evolution in algorithms. The following are some examples of emerging AI algorithm training techniques:
- Transfer learning. Transfer learning is a technique in which knowledge from a previously trained model is applied to a new but related task. This approach enables developers to benefit from existing models and data to improve learning in new domains, reducing the need for large amounts of new training data and computational resources.
- Bayesian networks. A Bayesian network is a graphical model that represents a set of variables and their conditional dependencies using a directed graph. It is a type of probabilistic model based on Bayes' theorem of conditional probability.
- Genetic algorithms. These are optimization techniques inspired by the process of natural selection that are used to find solutions to complex problems.
- Federated deep learning. Federated deep learning is an approach where the compute power of individual devices is used to distribute the learning process, rather than aggregating all data in a central location.
- Reinforcement learning with human feedback. RLHF is a technique that incorporates human preferences into the reinforcement learning process.
General applications and use cases for AI algorithms
AI algorithms have numerous applications across all industries, making it safe to say that the state of AI is near ubiquitous in business. The following are some examples of AI's reach:
Healthcare. AI algorithms can assist in diagnosis, drug discovery, personalized medicine and remote patient monitoring. In healthcare, AI algorithms can help doctors and other healthcare professionals make better decisions by providing insights from large amounts of data. For example, AI algorithms can analyze medical images to identify anomalies or predict disease progression.
Finance. AI is used for fraud detection, credit scoring, algorithmic trading and financial forecasting. In finance, AI algorithms can analyze large amounts of financial data to identify patterns or anomalies that might indicate fraudulent activity. AI algorithms can also help banks and financial institutions make better decisions by providing insight into customer behavior or market trends.
Retail and e-commerce. AI enables personalized recommendations, inventory management and customer service automation. In retail and e-commerce, AI algorithms can analyze customer behavior to provide personalized recommendations or optimize pricing. AI algorithms can also help automate customer service by providing chat functions.
Manufacturing. AI serves multiple purposes in manufacturing, including predictive maintenance, quality control and production optimization. AI algorithms can be used to analyze sensor data to predict equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Supply chain. AI models can be used in supply chain management for demand forecasting to optimize inventory. AI algorithms are also used for route optimization for deliveries.
Energy. AI algorithms are used in smart grid optimizations for energy distribution. AI models are also used for renewable energy forecasting, helping to predict potential wind and solar power generation based on weather data.
Transformer algorithms and the rise of LLMs
Based primarily on the transformer deep learning algorithm, large language models have been built on massive amounts of data to generate amazingly human-sounding language, as users of ChatGPT and interfaces of other LLMs know. They have become one of the most widely used forms of generative AI.
ChatGPT, developed by OpenAI, uses the company's family of LLMs; as of October 2024 that includes GPT-4. Google has developed its own portfolio of LLMs, which include the Gemini family, while Meta has been advancing its open source Llama LLMs.
A common deployment pattern for LLMs today is to fine-tune an existing model for specific purposes. Enterprise users will also commonly deploy an LLM with a retrieval-augmented generation approach that pulls updated information from an organization's database or knowledge base systems.
The need for responsible AI
It's important to understand the full scope and potential of AI algorithms. These algorithms enable machines to learn, analyze data and make decisions based on that knowledge. As we've seen, they are widely used across all industries and have the potential to revolutionize various aspects of our lives.
However, as we integrate AI into more aspects of our lives, it is crucial to consider the ethical implications and challenges to ensure responsible AI adoption.
One of the biggest ethical concerns with AI algorithms is bias. If the data used to train the algorithm is biased, the algorithm will likely produce biased results. This can lead to discrimination and unfair treatment of certain groups of people. It is crucial to ensure AI algorithms are unbiased and do not perpetuate existing biases or discrimination.
Common bias mitigation techniques include the following:
- Diverse and representative training data.
- Regular audits of AI systems for bias.
- Implementing fairness constraints in algorithms.
- Utilizing adversarial debiasing techniques.
Another ethical concern with AI algorithms is privacy. As AI algorithms collect and analyze large amounts of data, it is important to ensure individuals' privacy is protected. This includes ensuring sensitive information is not being used inappropriately and that individuals' data is not being used without their consent.
Here are some common AI privacy protection measures:
- Data anonymization and encryption.
- Differential privacy techniques.
- Federated learning for decentralized data processing.
- Implementing strict data access controls.
Responsible AI is also about ensuring AI decision-making processes are transparent and explainable, two elements that are crucial for building trustworthy AI.
Common approaches to enhance transparency include the following:
- Developing interpretable AI models.
- Implementing LIME, or local interpretable model-agnostic explanations.
- Utilizing SHAP values, or Shapley additive explanations values.
To address these ethical concerns and challenges, various doctrines of ethical-based AI have been developed, including those set by the White House. The following doctrines outline principles for responsible AI adoption, such as transparency, fairness, accountability and privacy:
- The White House's Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights outlines principles for responsible AI adoption, including safe and effective systems, algorithmic discrimination protections, and data privacy.
- IEEE's Ethically Aligned Design provides guidelines for the ethical development of autonomous and intelligent systems.
- The EU's Ethics Guidelines for Trustworthy AI emphasizes human agency, technical robustness, privacy, transparency and accountability.
In addition to ethical considerations, it is crucial for business leaders to thoroughly evaluate the potential benefits and risks of AI algorithms before implementing them.
And for data scientists, it is important to stay up to date with the latest developments in AI algorithms, as well as to understand their potential applications and limitations. By understanding the capabilities and limitations of AI algorithms, data scientists can make informed decisions about how best to use these powerful tools.
Editor's note: This article was originally written by Fred Tabsharani. It was updated and significantly expanded by Sean Michael Kerner in 2024 to reflect new developments in AI algorithms.
Sean Michael Kerner is an IT consultant, technology enthusiast and tinkerer. He has pulled Token Ring, configured NetWare and been known to compile his own Linux kernel. He consults with industry and media organizations on technology issues.






