write-back
What is write-back in storage?
Write-back is a technique used to cache data between the local processor or central processing unit and the final storage location, which is typically either main memory -- RAM -- or disk.
With write-back caching, the processor writes data to its local cache first before writing that cached data to memory or disk. The cached data is then only written to memory or disk later in intervals as a background task or as applications attempt to access the data.
How does write-back work?
In general terms, caching is a traditional and well-established means of accelerating processor and overall computer performance. Generally, a processor reads and writes data to a small amount of extremely fast local memory called a cache. Cache is directly accessible to the processor and often contains small pieces of data and code that the processor recently used.
When a processor reads data, it checks the cache first. When a processor writes data, that data is first written to the cache. The cache contents are only then written to memory or disk using several different policies or algorithms, including the following:
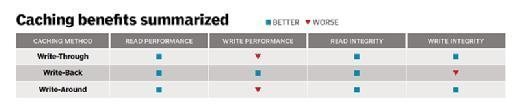
- Write-back cache. With a write-back caching policy, the processor writes to the cache first and then considers the data written to memory or disk -- even though that data will only be written later. This allows the processor to continue working even though the data in cache might be different from the data in memory or disk. This poses a potential risk of data loss.
- Write-through cache. With a write-through caching policy, the processor writes to the cache first and then waits until the data is updated in memory or disk. This ensures data is always consistent between cache and other storage assets. However, it takes longer to write to memory and much longer to write to disk than it does to write to cache, so the processor must wait and often suffer reduced performance as a result.
- Write-around cache. A write-around caching policy foregoes the local processor cache and writes processor data directly to main memory or disk. This technique is often used when the processor has little expectation or need to access data from local cache. However, cache access always results in cache misses because data is never available in the cache and must be read from storage. This can either improve or impair application performance, depending on the application's data access needs.
When the processor writes to cache in write-back mode, the data in cache is fresh and the corresponding data in main memory, which no longer matches the data in cache, is stale. If a request for stale data in main memory arrives from another application program, the cache controller updates the data in main memory before the application accesses it. Even without requests from applications, the cache is copied to memory or storage at other opportunities such as idle processor cycles. Since a write-through cache always waits for cache data to be written to memory or disk, the data is never stale.
To better understand the role of caching and the differences in caching techniques, consider the analogy of physical sticky notes and paper files. When a processor writes to a cache, that's analogous to a person writing on a sticky note and putting it on their monitor -- it's current or fresh info to which a person needs frequent and immediate access. It's much faster than going over to a file cabinet and searching for the info every time it's needed.
However, the information on that sticky note might be newer and different from the stale information in a file in the file cabinet. Eventually, the information on that sticky note needs to find its way into the file cabinet. With write-back caching, the information on the sticky note is copied to the file in the file cabinet later as time allows, or when some other person or application needs to access that file and finds that the newer information is missing or outdated. With write-through caching, the information on the sticky note is immediately copied to the file in the file cabinet, ensuring anyone who needs the file will have the latest information.
What is write-back cache used for?
Write-back cache is a policy or technique used to manage the way that a processor's local cache memory interacts with other storage assets within the computer, including main memory, disk and some storage-critical applications.
Write-back cache simply writes to the processor's local cache and then lets the processor continue its normal operation. Data in the cache is written to its final destination later.
Consequently, the principal purpose of write-back cache is to effectively boost computer performance. Each cache write shaves off a small bit of time, making the computer appear to operate slightly faster. Write-back cache is often the preferred caching technique for noncritical computing tasks where there's only a small risk of data loss if the cache contents aren't successfully written to storage.
Write-back vs. write-through
Write-back and write-through are primary approaches to processor caching. Both techniques categorize the way that a cache moves data to a final storage location.
Write-back cache allows the processor to put new data into the cache and continue working normally. Data in the cache is moved to main memory or disk later as a background task. This means data in the cache could differ from data in storage for short periods of time.
Write-through cache halts application processing until data in the cache is also updated in main memory or disk. This ensures cache and storage data are always consistent before an application is allowed to continue.
What are the benefits and challenges of write-back cache?
All types of processor cache can provide a boost to processor performance because a processor can access data from its local cache faster than it could access that same data from other storage assets. Cache offers its greatest benefits for applications that require the processor to read the same fragments of data often.
As a specific cache technique, write-back cache allows the processor to continue working on an application before cached data is copied to storage such as main memory or disk. This provides an additional performance boost to the computer, and cache contents are updated to storage later as a background task.
However, write-back cache isn't suited to all application types, as there can be differences between the fresh or newer data in the cache and the stale or older data in storage. These differences will exist until the cache contents are finally committed or written to storage. Often, these differences last no longer than a few milliseconds, but there's a risk of data loss if the associated application closes or crashes before the cache is finally committed. Critical applications that can't tolerate any risk of data loss can benefit from write-through or write-around cache.
Learn which caching tools and techniques can be used to increase application performance and response times.
